Background:Echinococcus granulosus represents a significant threat to animal husbandry and human health, but its consequences are often underestimated. Vaccination can prevent E. granulosus infection. We investigated the immune protective effect induced by the recombinant protein P29 of E. granulosus (rEg.P29) peptide vaccine. Methods: The CD4+ T-, CD8+ T-, Treg-, and CD8+CD107a+ T-cell proportions in the spleen and peripheral blood of infected mice were analyzed using flow cytometry. Additionally, we measured the proportions of IFN-γ and IL-2 secreted by memory T cells, CD19+CD138-B cells, CD19+CD138+ plasmablasts, CD19-CD138+ plasma cells, and CD19+IgD-IgG+ and CD19+IgD-IgA+ memory B cells. Results: No significant differences were noted in CD4+ T-, CD8+ T-, and CD8+CD107a+ Treg-cell percentages among the experimental groups. However, IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α levels and vaccine-specific antibody concentrations in the plasma were significantly elevated in the rEg.P29T+B + CpG + infection and rEg.P29 + CpG + infection groups compared to those in the PBS + infection and CpG + infection groups. Similarly, CD19-CD138+ plasma cell and CD19+IgD-IgG+ and CD19+IgD-IgA+ memory B-cell populations, along with specific antibodies, were significantly higher in these groups. Especially, the average cyst burden in the rEg.P29T+B + CpG + infection and rEg.P29 + CpG + infection groups was significantly reduced compared to that in the PBS + infection and CpG + infection groups. Conclusions: Synthetic peptide vaccines targeting rEg.P29 can effectively inhibit cysts, offering a novel strategy for the development of vaccines against E. granulosus. These findings provide a foundation for further research on the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of rEg.P29-based vaccines.
Product Citations: 216
In Vaccines on 3 March 2025 by Lv, Y., Tang, J., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal of Nanobiotechnology on 13 January 2025 by Figueroa-Valdés, A. I., Luz-Crawford, P., et al.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease characterized by articular cartilage degradation. Persistent low-grade inflammation defines OA pathogenesis, with crucial involvement of pro-inflammatory M1-like macrophages. While mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) and their small extracellular vesicles (sEV) hold promise for OA treatment, achieving consistent clinical-grade sEV products remains a significant challenge. This study aims to develop fully characterized, reproducible, clinical-grade batches of sEV derived from umbilical cord (UC)-MSC for the treatment of OA while assessing its efficacy and safety. Initially, a standardized, research-grade manufacturing protocol was established to ensure consistent sEV production. UC-MSC-sEV characterization under non-cGMP conditions showed consistent miRNA and protein profiles, suggesting their potential for standardized manufacturing. In vitro studies evaluated the efficacy, safety, and potency of sEV; animal studies confirmed their effectiveness and safety. In vitro, UC-MSC-sEV polarized macrophages to an anti-inflammatory M2b-like phenotype, through STAT1 modulation, indicating their potential to create an anti-inflammatory environment in the affected joints. In silico studies confirmed sEV's immunosuppressive signature through miRNA and proteome analysis. In an OA mouse model, sEV injected intra-articularly (IA) induced hyaline cartilage regeneration, validated by histological and μCT analyses. The unique detection of sEV signals within the knee joint over time highlights its safety profile by confirming the retention of sEV in the joint. The product development of UC-MSC-sEV involved refining, standardizing, and validating processes in compliance with GMP standards. The initial assessment of the safety of the clinical-grade product via IA administration in a first-in-human study showed no adverse effects after a 12 month follow-up period. These results support the progress of this sEV-based therapy in an early-phase clinical trial, the details of which are presented and discussed in this work. This study provides data on using UC-MSC-sEV as local therapy for OA, highlighting their regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties and safety in preclinical and a proof-of-principle clinical application.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Cancer Science on 1 November 2024 by Pacifico, T., Stolfi, C., et al.
In the colorectal cancer (CRC) niche, the transcription factors signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) are hyperactivated in both malignant cells and tumor-infiltrating leukocytes (TILs) and cooperate to maintain cancer cell proliferation/survival and drive protumor inflammation. Through drug repositioning studies, the anthelmintic drug rafoxanide has recently emerged as a potent and selective antitumor molecule for different types of cancer, including CRC. Here, we investigate whether rafoxanide could negatively modulate STAT3/NF-κB and inflammation-associated CRC. The antineoplastic effect of rafoxanide was explored in a murine model of CRC resembling colitis-associated disease. Cell proliferation and/or STAT3/NF-κB activation were evaluated in colon tissues taken from mice with colitis-associated CRC, human CRC cells, and CRC patient-derived explants and organoids after treatment with rafoxanide. The STAT3/NF-κB activation and cytokine production/secretion were assessed in TILs isolated from CRC specimens and treated with rafoxanide. Finally, we investigated the effects of TIL-derived supernatants cultured with or without rafoxanide on CRC cell proliferation and STAT3/NF-κB activation. The results showed that rafoxanide restrains STAT3/NF-κB activation and inflammation-associated colon tumorigenesis in vivo without apparent effects on normal intestinal cells. Rafoxanide markedly reduces STAT3/NF-κB activation in cultured CRC cells, CRC-derived explants/organoids, and TILs. Finally, rafoxanide treatment impairs the ability of TILs to produce protumor cytokines and promote CRC cell proliferation. We report the novel observation that rafoxanide negatively affects STAT3/NF-κB oncogenic activity at multiple levels in the CRC microenvironment. Our data suggest that rafoxanide could potentially be deployed as an anticancer drug in inflammation-associated CRC.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 7 October 2024 by Jin, C., Jiang, P., et al.
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic autoimmune liver disease characterized by multilineage immune dysregulation, which subsequently causes inflammation, fibrosis, and even cirrhosis of liver. Due to the limitation of traditional assays, the local hepatic immunopathogenesis of PBC has not been fully characterized. Here, we utilize single-cell RNA sequencing technology to depict the immune cell landscape and decipher the molecular mechanisms of PBC patients. We reveal that cholangiocytes and hepatic stellate cells are involved in liver inflammation and fibrosis. Moreover, Kupffer cells show increased levels of inflammatory factors and decreased scavenger function related genes, while T cells exhibit enhanced levels of inflammatory factors and reduced cytotoxicity related genes. Interestingly, we identify a liver-resident Th1-like population with JAK-STAT activation in the livers of both PBC patients and murine PBC model. Finally, blocking the JAK-STAT pathway alleviates the liver inflammation and eliminates the liver-resident Th1-like cells in the murine PBC model. In conclusion, our comprehensive single-cell transcriptome profiling expands the understanding of pathological mechanisms of PBC and provides potential targets for the treatment of PBC in patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Res Commun on 1 October 2024 by Cen, B., Wei, J., et al.
The molecular mechanisms regulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) are not fully understood. Here, we show that the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ (PPARδ) suppresses CTL cytotoxicity by inhibiting RelA DNA binding. Treatment of ApcMin/+ mice with the PPARδ agonist GW501516 reduced the activation of normal and tumor-associated intestinal CD8+ T cells and increased intestinal adenoma burden. PPARδ knockout or knockdown in CTLs increased their cytotoxicity against colorectal cancer cells, whereas overexpression of PPARδ or agonist treatment decreased it. Correspondingly, perforin, granzyme B, and IFNγ protein and mRNA levels were higher in PPARδ knockout or knockdown CTLs and lower in PPARδ overexpressing or agonist-treated CTLs. Mechanistically, we found that PPARδ binds to RelA, interfering with RelA-p50 heterodimer formation in the nucleus, thereby inhibiting its DNA binding in CTLs. Thus, PPARδ is a critical regulator of CTL effector function. Significance: Here, we provide the first direct evidence that PPARδ plays a critical role in suppressing the immune response against tumors by downregulating RelA DNA-binding activity. This results in decreased expression of perforin, granzyme B, and IFNγ. Thus, PPARδ may serve as a valuable target for developing future cancer immunotherapies.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cell Biology
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
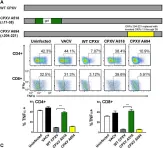
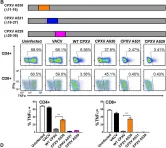
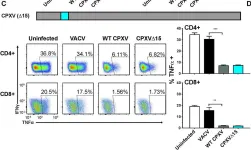
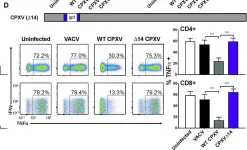
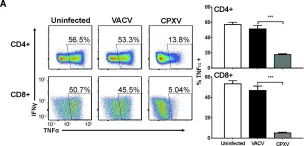
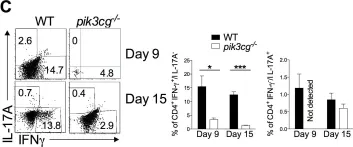
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.9.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
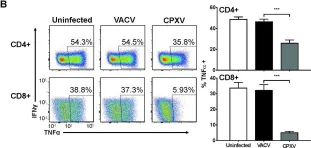
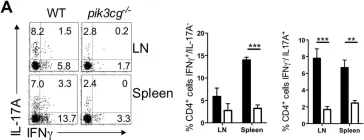
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
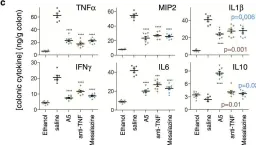
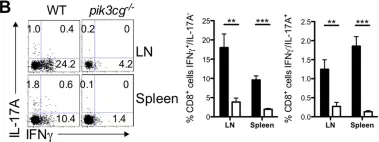
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
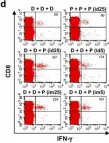
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In Nat Commun on 25 March 2021 by Rol, Á., Todorovski, T., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In Cell Biosci on 27 February 2016 by Peng, S., Qiu, J., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Biosci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In PLoS One on 3 October 2012 by Comerford, I., Litchfield, W., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In PLoS One on 3 October 2012 by Comerford, I., Litchfield, W., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In PLoS One on 3 October 2012 by Comerford, I., Litchfield, W., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
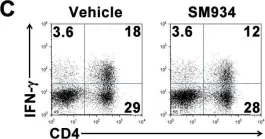
In PLoS One on 6 March 2012 by Hou, L. F., He, S. J., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13