Isolating high-quality different cell types is a powerful approach for understanding cellular compositions and features in the heart, but it is challenging. The available protocols typically focus on isolating one or two cell types. Here, we present a protocol to simultaneously isolate high-quality and high-quantity cardiomyocytes and non-myocyte cells, including immune cells, from adult rat hearts. We describe steps for purifying cells using bovine serum albumin. We also detail procedures for viability analysis and cell type identification using fluorescence-activated cell sorting. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Zhang et al.,1 Valkov et al.,2 Vang et al.,3 and Li et al.4.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Product Citations: 46
In STAR Protocols on 20 September 2024 by Zimmer, A., Wang, E. R., et al.
In Organogenesis on 31 December 2023 by Hisanaga, M., Tsuchiya, T., et al.
Decellularized scaffolds are promising biomaterials for tissue and organ reconstruction; however, strategies to effectively suppress the host immune responses toward these implants, particularly those without chemical crosslinking, remain warranted. Administration of mesenchymal stem cells is effective against immune-mediated inflammatory disorders. Herein, we investigated the effect of isogeneic abdominal adipose-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (ADMSCs) on xenogeneic biomaterial-induced immunoreactions. Peripheral bronchi from pigs, decellularized using a detergent enzymatic method, were engrafted onto tracheal defects of Brown Norway (BN) rats. BN rats were implanted with native pig bronchi (Xenograft group), decellularized pig bronchi (Decellularized Xenograft), or Decellularized Xenograft and ADMSCs (Decellularized Xenograft+ADMSC group). In the latter group, ADMSCs were injected intravenously immediately post implantation. Harvested graft implants were assessed histologically and immunohistochemically. We found that acute rejections were milder in the Decellularized Xenograft and Decellularized Xenograft+ADMSC groups than in the Xenograft group. Mild inflammatory cell infiltration and reduced collagen deposition were observed in the Decellularized Xenograft+ADMSC group. Additionally, ADMSC administration decreased CD8+ lymphocyte counts but increased CD163+ cell counts. In the Decellularized Xenograft+ADMSC group, serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and IL-10 were elevated and tissue deposition of IgM and IgG was low. The significant immunosuppressive effects of ADMSCs illustrate their potential use as immunosuppressive agents for xenogeneic biomaterial-based implants.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
-
Veterinary Research
In Cell Transplantation on 11 November 2023 by Tanoue, Y., Tsuchiya, T., et al.
Cell therapy using mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) is being studied for its immunosuppressive effects. In organ transplantation, the amount of MSCs that accumulate in transplanted organs and other organs may differ depending on administration timing, which may impact their immunosuppressive effects. In vitro, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) suppress lymphocyte activation under cell-to-cell contact conditions. However, in vivo, it is controversial whether ADMSCs are more effective in accumulating in transplanted organs or in secondary lymphoid organs. Herein, we aimed to investigate whether the timing of ADMSC administration affects its immunosuppression ability in a rat lung transplantation model. In the transplantation study, rats were intramuscularly administered half the usual dose of tacrolimus (0.5 mg/kg) every 24 h after lung transplantation. ADMSCs (1 × 106) were administered via the jugular vein before (PreTx) or after (PostTx) transplantation. Cell tracking using quantum dots was performed. ADMSCs accumulated predominantly in the lung and liver; fewer ADMSCs were distributed in the grafted lung in the PreTx group than in the PostTx group. The rejection rate was remarkably low in the ADMSC-administered groups, particularly in the PostTx group. Serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interferon-γ, and interleukin (IL)-6 levels showed a greater tendency to decrease in the PreTx group than in the PostTx group. The proportion of regulatory T cells in the grafted lung 10 days after transplantation was higher in the PostTx group than in the PreTx group. PostTx administration suppresses rejection better than PreTx administration, possibly due to regulatory T cell induction by ADMSCs accumulated in the transplanted lungs, suggesting a mechanism different from that in heart or kidney transplantation that PreTx administration is more effective than PostTx administration. These results could help establish cell therapy using MSCs in lung transplantation.
In Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part B, Applied Biomaterials on 1 March 2023 by Sun, P., Wu, H., et al.
We previously showed decellularized fish swim bladder can be used as vascular patch and tube graft in rats, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have showed the capability to inhibit neointimal hyperplasia in different animal models. We hypothesized that decellularized fish swim bladder patch loaded with MSCs (bioinspired patch) can inhibit neointimal hyperplasia in a rat aortic patch angioplasty model. Rat MSCs were grown in vitro and flow cytometry was used to confirm their quality. 3.6 × 105 MSCs were mixed into 100 μl of sodium alginate (SA)/hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogel, two layers of fish swim bladders (5 mm × 5 mm) were sutured together, bioinspired patch was created by injection of hydrogel with MSCs into the space between two layers of fish swim bladder patches. Decellularized rat thoracic aorta patch was used as control. Patches were harvested at days 1 and 14 after implantation. Samples were examined by histology, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. The decellularized rat thoracic aorta patch and the fish swim bladder patch had a similar healing process after implantation. The bioinspired patch had a similar structure like native aorta. Bioinspired patch showed a decreased neointimal thickness (p = .0053), fewer macrophages infiltration (p = .0090), and lower proliferation rate (p = .0291) compared to the double layers fish swim bladder patch group. Decellularized fish swim bladder patch loaded with MSCs can inhibit neointimal hyperplasia effectively. Although this is a preliminary animal study, it may have a potential application in large animals or clinical research.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
-
FC/FACS
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Isolation and characterization of farm pig adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.
In Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research = Revista Brasileira De Pesquisas Médicas E Biológicas / Sociedade Brasileira De Biofísica ... [et Al.] on 9 December 2022 by Garcia, G. A., Oliveira, R. G., et al.
Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (ASCs) are considered important tools in regenerative medicine and are being tested in several clinical studies. Porcine models are frequently used to obtain adipose tissue, due to the abundance of material and because they have immunological and physiological similarities with humans. However, it is essential to understand the effects and safe application of ASCs from pigs (pASCs) as an alternative therapy for diseases. Although minipigs are easy-to-handle animals that require less food and space, acquiring and maintaining them in a bioterium can be costly. Thus, we present a protocol for the isolation and proliferation of ASCs isolated from adipose tissue of farm pigs. Adipose tissue samples were extracted from the abdominal region of the animals. Because the pigs were not raised in a controlled environment, such as a bioterium, it was necessary to carry out rigorous procedures for disinfection. After this procedure, cells were isolated by mechanical dissociation and enzymatic digestion. A proliferation curve was performed and used to calculate the doubling time of the population. The characterization of pASCs was performed by immunophenotyping and cell differentiation in osteogenic and adipogenic lineages. The described method was efficient for the isolation and cultivation of pASCs, maintaining cellular attributes, such as surface antigens and multipotential differentiation during in vitro proliferation. This protocol presents the isolation and cultivation of ASCs from farm pig as an alternative for the isolation and cultivation of ASCs from minipigs, which require strictly controlled maintenance conditions and a more expensive process.
-
FC/FACS
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
-
Veterinary Research
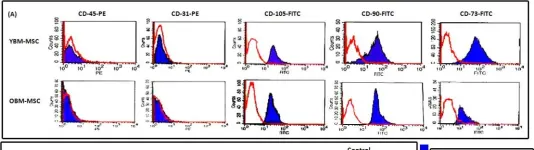
In BMC Cell Biol on 12 October 2011 by Asumda, F. Z. & Chase, P. B.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from BMC Cell Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1