Adoptive cell therapy including chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells targeting CD19 has been approved by FDA to treat B cell-derived malignancies with remarkable success. The success has not yet been expanded to treating Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). We previously showed that a nanobody and single-chain fragment variable (scFv) CD13 (Nanobody)/TIM-3 (scFv) directed bispecific split CAR (bissCAR) T cells, while effective in eliminating AML in preclinical models, also caused substantial toxicity to human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and other lineages. To maintain the bissCART specificity and efficacy, yet reduce toxicity to normal cells including HSCs, we generated new anti-TIM-3 nanobodies and constructed new cognate nanobodies-directed CD13/41BB and TIM3/CD3zeta nbiCARTs. The resultant nbiCARTs showed strong antitumor activity to CD13/TIM3 positive leukemic cells in vitro and in preclinical models. Importantly, the 3rd generation of nbiCARTs had little toxicity to human bone marrow-derived colony forming progenitors ex vivo and the human HSCs in mice with a humanized immune system. Together, the current studies generated novel and 3rd G CD13/TIM-3 nbiCARTs that displayed stronger antitumor activity yet minimal toxicity to normal tissues like HSCs that express a moderate level of CD13, paving the way to further evaluate the novel CD13/TIM-3CARTs in treating aggressive and refractory AML in clinical studies.
Product Citations: 114
In Oncoimmunology on 1 December 2025 by Zhang, X., Feng, Z., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 28 March 2025 by Jin, C., Chen, R., et al.
B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell immunotherapy has shown promising results in the treatment of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (R/RMM). This study presents the updated long-term outcomes from our center.
Between July 30, 2018, and September 27, 2023, 141 patients with R/RMM who received BCMA CAR-T therapy were enrolled. Patients underwent conditioning chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and fludarabine, followed by BCMA CAR-T cell infusion at a median dose of 2.36×106 cells/kg. The study evaluated overall response rates, long-term efficacy, safety profiles, and their associations with clinical and disease characteristics.
At a median follow-up of 20.2 months, the safety profile of the therapy was manageable. Grade 3/4 cytokine release syndrome occurred in 36.2% of patients, with no cases of severe neurotoxicity reported. 1-month post-infusion, grade ≥3 anemia persisted in 39.6% of patients, while neutropenia (43.3%) and thrombocytopenia (52.2%) were observed. The objective response rate (ORR) among evaluable patients was 94.8%, with 50.7% achieving a complete response (CR). The 4-year progression-free survival and overall survival rates were 37.4% (95% CI, 29.1% to 48.1%) and 63.2% (95% CI, 54.8% to 72.8%), respectively, with survival curves showing gradual flattening over time. Patients with a history of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and those with extramedullary disease demonstrated significantly inferior efficacy and survival outcomes. Peak CAR-T cell expansion was positively correlated with ORR (p<0.001) and CR (p<0.001). Notably, patients with prior ASCT exhibited significantly lower CAR-T cell expansion compared with those without prior ASCT (p<0.001). Immunophenotypic analysis of infused CAR-T cells demonstrated impaired fitness in patients who received ASCT in the past year.
BCMA CAR-T therapy in patients with R/RMM results in significant and sustained responses, with a manageable safety profile on a large scale. Prior ASCT and extramedullary disease represent adverse prognostic factors. Patients with a history of ASCT demonstrate limited peak CAR-T cell expansion.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports Medicine on 19 November 2024 by Della Volpe, L., Midena, F., et al.
Ex vivo activation is a prerequisite to reaching adequate levels of gene editing by homology-directed repair (HDR) for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC)-based clinical applications. Here, we show that shortening culture time mitigates the p53-mediated DNA damage response to CRISPR-Cas9-induced DNA double-strand breaks, enhancing the reconstitution capacity of edited HSPCs. However, this results in lower HDR efficiency, rendering ex vivo culture necessary yet detrimental. Mechanistically, ex vivo activation triggers a multi-step process initiated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation, which generates mitogenic reactive oxygen species (ROS), promoting fast cell-cycle progression and subsequent proliferation-induced DNA damage. Thus, p38 inhibition before gene editing delays G1/S transition and expands transcriptionally defined HSCs, ultimately endowing edited cells with superior multi-lineage differentiation, persistence throughout serial transplantation, enhanced polyclonal repertoire, and better-preserved genome integrity. Our data identify proliferative stress as a driver of HSPC dysfunction with fundamental implications for designing more effective and safer gene correction strategies for clinical applications.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Genetics
In Scandinavian Journal of Immunology on 1 November 2024 by Sinha, S., Singh, K., et al.
For an effective control of tuberculosis (TB), there is a persistent need for biomarkers that can report true estimates of TB infection (TBI) and predict its progression towards active TB disease. We investigated whether the cell-mediated immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) antigens could provide such biomarkers. The study subjects (n = 174) comprised a cohort of smear-positive, drug-sensitive, HIV-negative pulmonary TB patients (n = 54) and their household contacts (HC, n = 120). Whole blood cultures, in the presence or absence of Mtb antigens- membrane (MtM), purified protein derivative (PPD) and alpha-crystallin (Acr), or the mitogen PHA were subjected to determinations, by flow cytometry, for T cell proliferative and, by ELISA, for IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-6 cytokine responses. Additionally, serum levels of the three cytokines were also estimated. The strongest cell-proliferative and cytokine responses were induced by MtM and IL-6 was the most abundantly produced cytokine. While none of the responses induced by Mtb antigens or the serum cytokines levels could discriminate between TB and HC, the ex vivo cytokine responses induced by PHA or 'spontaneously' could apparently do so. The concentrations of IFN-γ induced by PHA in TB blood cultures were significantly lower than in HC cultures (AUC = 0.72). Conversely, the spontaneous IFN-γ or TNF-α secretions in TB cultures were significantly higher than in HC cultures (AUC = 0.66). Our results suggest that IL-6 responses to MtM could be a sensitive indicator of TBI, and low levels of PHA-induced or high levels of spontaneous IFN-γ secretions in HC blood cultures may indicate a progressive infection.
© 2024 The Scandinavian Foundation for Immunology.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Identification of cells of leukemic stem cell origin with non-canonical regenerative properties.
In Cell Reports Medicine on 16 April 2024 by Hollands, C. G., Boyd, A. L., et al.
Despite most acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients entering remission following chemotherapy, outcomes remain poor due to surviving leukemic cells that contribute to relapse. The nature of these enduring cells is poorly understood. Here, through temporal single-cell transcriptomic characterization of AML hierarchical regeneration in response to chemotherapy, we reveal a cell population: AML regeneration enriched cells (RECs). RECs are defined by CD74/CD68 expression, and although derived from leukemic stem cells (LSCs), are devoid of stem/progenitor capacity. Based on REC in situ proximity to CD34-expressing cells identified using spatial transcriptomics on AML patient bone marrow samples, RECs demonstrate the ability to augment or reduce leukemic regeneration in vivo based on transfusion or depletion, respectively. Furthermore, RECs are prognostic for patient survival as well as predictive of treatment failure in AML cohorts. Our study reveals RECs as a previously unknown functional catalyst of LSC-driven regeneration contributing to the non-canonical framework of AML regeneration.
Crown Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
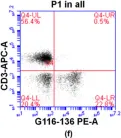
In Int J Mol Sci on 11 May 2019 by Shen, N., Song, G., et al.
Fig.3.F

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
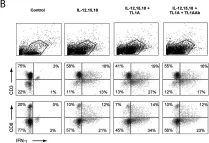
In PLoS One on 15 January 2014 by Reichwald, K., Jørgensen, T. Z., et al.
Fig.8.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In PLoS One on 15 January 2014 by Reichwald, K., Jørgensen, T. Z., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
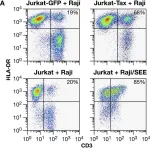
In PLoS Pathog on 26 February 2010 by Mazurov, D., Ilinskaya, A., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4