Pfizer/BioNTec BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine robustly elicits neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in clinical trials and real-world settings. However, booster vaccinations are frequently associated with self-limited adverse events. Here, by applying a high-dimensional immune profiling approach to peripheral blood, we linked early vaccine-induced immune dynamics with adverse events and neutralizing antibody responses. The dynamics of two dendritic cell subsets (DC3s and AS-DCs) were identified as the specific correlates for adverse events; the combination of these cell dynamics stratified the vaccinees with severe reactogenicity, while the stratification did not affect the neutralizing antibody titers. Furthermore, the NKT-like cell dynamics that correlated with adverse events and antibody titers were accounted for distinct magnitudes of both events by sex and age. The identified immune correlates for adverse events and antibody responses may pave the way for a rational vaccine strategy for reducing the reactogenicity of mRNA vaccines without compromising the immunogenicity.
Product Citations: 52
Distinct immune cell dynamics mark adverse events and antibody responses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine
Preprint on Research Square on 17 September 2021 by Takano, T., Morikawa, M., et al.
-
COVID-19
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The CD28-Transmembrane Domain Mediates Chimeric Antigen Receptor Heterodimerization With CD28.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 10 April 2021 by Muller, Y. D., Nguyen, D. P., et al.
Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CD19-CAR)-engineered T cells are approved therapeutics for malignancies. The impact of the hinge domain (HD) and the transmembrane domain (TMD) between the extracellular antigen-targeting CARs and the intracellular signaling modalities of CARs has not been systemically studied. In this study, a series of 19-CARs differing only by their HD (CD8, CD28, or IgG4) and TMD (CD8 or CD28) was generated. CARs containing a CD28-TMD, but not a CD8-TMD, formed heterodimers with the endogenous CD28 in human T cells, as shown by co-immunoprecipitation and CAR-dependent proliferation of anti-CD28 stimulation. This dimerization was dependent on polar amino acids in the CD28-TMD and was more efficient with CARs containing CD28 or CD8 HD than IgG4-HD. The CD28-CAR heterodimers did not respond to CD80 and CD86 stimulation but had a significantly reduced CD28 cell-surface expression. These data unveiled a fundamental difference between CD28-TMD and CD8-TMD and indicated that CD28-TMD can modulate CAR T-cell activities by engaging endogenous partners.
Copyright © 2021 Muller, Nguyen, Ferreira, Ho, Raffin, Valencia, Congrave-Wilson, Roth, Eyquem, Van Gool, Marson, Perez, Wells, Bluestone and Tang.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Biomedicines on 18 February 2021 by Joo, H., Oh, M. K., et al.
Therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have attracted considerable attention because of their immunomodulatory properties against immune-mediated, inflammatory diseases. Here, we demonstrated enhanced immunomodulatory properties of EVs secreted from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inducer thapsigargin (TSG)-primed human Wharton's jelly-derived MSCs (WJ-MSCs). EVs from TSG-primed WJ-MSCs (TSG-EV) showed increased yield and expression of immunomodulatory factors, such as transforming growth factor-β1 (TGFβ), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), and especially indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), compared to control EVs. TSG-EV showed a significantly enhanced immunosuppressive effect on human peripheral blood-derived T cell proliferation and Th1 and Th17 differentiation, whereas Treg and M2-type macrophage were enriched compared to a control EV-treated group. Furthermore, TSG-EV substantially mitigated mouse experimental colitis by reducing the inflammatory response and maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. A significant increase of Tregs and M2-type macrophages in colitic colons of a TSG-EV-treated mouse suggests an anti-inflammatory effect of TSG-EV in colitis model, possibly mediated by Treg and macrophage polarization. These data indicate that TSG treatment promoted immunomodulatory properties of EVs from WJ-MSCs, and TSG-EV may provide a new therapeutic approach for treatment of colitis.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
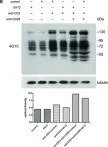
Molecular bases for HOIPINs-mediated inhibition of LUBAC and innate immune responses.
In Communications Biology on 3 April 2020 by Oikawa, D., Sato, Y., et al.
The NF-κB and interferon antiviral signaling pathways play pivotal roles in inflammatory and innate immune responses. The LUBAC ubiquitin ligase complex, composed of the HOIP, HOIL-1L, and SHARPIN subunits, activates the canonical NF-κB pathway through Met1-linked linear ubiquitination. We identified small-molecule chemical inhibitors of LUBAC, HOIPIN-1 and HOIPIN-8. Here we show that HOIPINs down-regulate not only the proinflammatory cytokine-induced canonical NF-κB pathway, but also various pathogen-associated molecular pattern-induced antiviral pathways. Structural analyses indicated that HOIPINs inhibit the RING-HECT-hybrid reaction in HOIP by modifying the active Cys885, and residues in the C-terminal LDD domain, such as Arg935 and Asp936, facilitate the binding of HOIPINs to LUBAC. HOIPINs effectively induce cell death in activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells, and alleviate imiquimod-induced psoriasis in model mice. These results reveal the molecular and cellular bases of LUBAC inhibition by HOIPINs, and demonstrate their potential therapeutic uses.
-
WB
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Exosomal PD-L1 promotes tumor growth through immune escape in non-small cell lung cancer.
In Experimental & Molecular Medicine on 9 August 2019 by Kim, D. H., Kim, H., et al.
Programmed cell death protein-1/programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1) pathway blockade is a promising new cancer therapy. Although PD-1/PD-L1 treatment has yielded clinical benefits in several types of cancer, further studies are required to clarify predictive biomarkers for drug efficacy and to understand the fundamental mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 interaction between host and tumor cells. Here, we show that exosomes derived from lung cancer cells express PD-L1 and play a role in immune escape by reducing T-cell activity and promoting tumor growth. The abundance of PD-L1 on exosomes represented the quantity of PD-L1 expression on cell surfaces. Exosomes containing PD-L1 inhibited interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) secretion by Jurkat T cells. IFN-γ secretion was restored by PD-L1 knockout or masking on the exosomes. Both forced expression of PD-L1 on cells without PD-L1 and treatment with exosomes containing PD-L1 enhanced tumor growth in vivo. PD-L1 was present on exosomes isolated from the plasma of patients with non-small cell lung cancer, and its abundance in exosomes was correlated with PD-L1 positivity in tumor tissues. Exosomes can impair immune functions by reducing cytokine production and inducing apoptosis in CD8+ T cells. Our findings indicate that tumor-derived exosomes expressing PD-L1 may be an important mediator of tumor immune escape.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
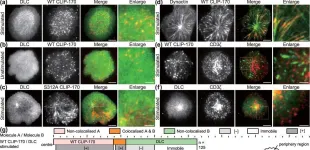
In Sci Rep on 28 November 2018 by Lim, W. M., Ito, Y., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
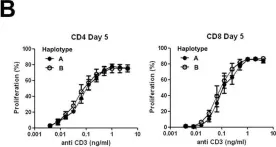
In PLoS One on 12 November 2016 by Carreras-Sureda, A., Rubio-Moscardo, F., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
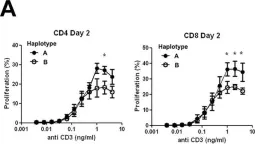
In PLoS One on 12 November 2016 by Carreras-Sureda, A., Rubio-Moscardo, F., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
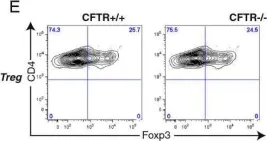
In Respir Res on 17 December 2013 by Kushwah, R., Gagnon, S., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Respir Res by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In J Cell Mol Med on 1 August 2010 by Hu, J., Dang, N., et al.
Fig.7.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Mol Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5