The molecular mechanisms responsible for the heightened reactivity of quiescent T cells in human early life remain largely elusive. Our previous research identified that quiescent adult naïve CD4+ T cells express LINE1 (long interspersed nuclear elements 1) spliced in previously unknown isoforms, and their down-regulation marks the transition to activation. Here, we unveil that neonatal naïve T cell quiescence is characterized by enhanced energy production and protein synthesis. This phenotype is associated with the absence of LINE1 expression attributed to tonic T cell receptor/mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling and (polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 (PTBP1)-mediated LINE1 splicing suppression. The absence of LINE1 expression primes these cells for rapid execution of the activation program by directly regulating protein synthesis. LINE1 expression progressively increases in childhood and adults, peaking in elderly individuals, and, by decreasing protein synthesis, contributes to immune senescence in aging. Our study proposes LINE1 as a critical player of human T cell function across the human life span.
Product Citations: 17
LINE1 modulate human T cell function by regulating protein synthesis during the life span.
In Science Advances on 11 October 2024 by Burattin, F. V., Vadalà, R., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Increased peritoneal B1-like cells during acute phase of human septic peritonitis.
In IScience on 19 July 2024 by von Loeffelholz, C., Winkler, R., et al.
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by dysregulated host responses to infection. Myeloid cell accumulation and lymphocyte decline are widely recognized phenomena in septic patients. However, the fate of specific immune cells remains unclear. Here, we report the results of a human explorative study of patients with septic peritonitis and patients undergoing abdominal surgery without sepsis. We analyzed pairwise peritoneal fluid and peripheral blood taken 24 h after surgery to characterize immediate immune cell changes. Our results show that myeloid cell expansion and lymphocyte loss occur in all patients undergoing open abdominal surgery, indicating that these changes are not specific to sepsis. However, B1-like lymphocytes were specifically increased in the peritoneal fluid of septic patients, correlating positively with sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE-II) clinical severity scores. In support of this notion, we identified an accumulation of peritoneal B1b lymphocytes in septic mice.
© 2024 The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Immune cell phenotype and function patterns across the life course in individuals from rural Uganda.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 2 April 2024 by Nalwoga, A., Nakibuule, M., et al.
To determine the pattern of immune cell subsets across the life span in rural sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), and to set a reference standard for cell subsets amongst Africans, we characterised the major immune cell subsets in peripheral blood including T cells, B cells, monocytes, NK cells, neutrophils and eosinophils, in individuals aged 3 to 89 years from Uganda.
Immune phenotypes were measured using both conventional flow cytometry in 72 individuals, and full spectrum flow cytometry in 80 individuals. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) IFN-γ T cell responses were quantified in 332 individuals using an ELISpot assay. Full blood counts of all study participants were also obtained.
The percentages of central memory (TCM) and senescent CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets, effector memory (TEM) CD8+ T cells and neutrophils increased with increasing age. On the other hand, the percentages of naïve T (TN) and B (BN) cells, atypical B cells (BA), total lymphocytes, eosinophils and basophils decreased with increasing age. There was no change in CD4+ or CD8+ T effector memory RA (TEMRA) cells, exhausted T cells, NK cells and monocytes with age. Higher eosinophil and basophil percentages were observed in males compared to females. T cell function as measured by IFN-γ responses to EBV increased with increasing age, peaking at 31-55 years.
The percentages of cell subsets differ between individuals from SSA compared to those elsewhere, perhaps reflecting a different antigenic milieu. These results serve as a reference for normal values in this population.
Copyright © 2024 Nalwoga, Nakibuule, Roshan, Kwizera Mbonye, Miley, Whitby, Newton, Rochford and Cose.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 12 October 2022 by Bencze, D., Fekete, T., et al.
Generally, a reciprocal antagonistic interaction exists between the antiviral type I interferon (IFN) and the antibacterial nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3)-dependent IL-1β pathways that can significantly shape immune responses. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), as professional type I IFN-producing cells, are the major coordinators of antiviral immunity; however, their NLRP3-dependent IL-1β secretory pathway is poorly studied. Our aim was to determine the functional activity of the IL-1β pathway and its possible interaction with the type I IFN pathway in pDCs. We found that potent nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) inducers promote higher levels of pro-IL-1β during priming compared to those activation signals, which mainly trigger interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-mediated type I IFN production. The generation of cleaved IL-1β requires certain secondary signals in pDCs and IFN-α or type I IFN-inducing viruses inhibit IL-1β production of pDCs, presumably by promoting the expression of various NLRP3 pathway inhibitors. In line with that, we detected significantly lower IL-1β production in pDCs of psoriasis patients with elevated IFN-α levels. Collectively, our results show that the NLRP3-dependent IL-1β secretory pathway is inducible in pDCs; however, it may only prevail under inflammatory conditions, in which the type I IFN pathway is not dominant.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma on 27 July 2022 by Hammad, R., Eldosoky, M. A., et al.
Natural killer (NK) and B1a cells are implicated in innate immune surveillance against chronic hepatitis C virus (CHCV). NK group 2D (NKG2D) receptor is important for B cell differentiation. This study was designed to assess whether B1a cells and NK Cells expressing NKG2D are implicated in post-hepatitis C infection hepatocellular carcinoma (post-HCV HCC) and cirrhosis using flow cytometry and investigate the association between NK-expressing NKG2D and B1a in complications of CHCV infection.
In this cross-sectional study, 111 participants were included and divided into the post-HCV HCC (n = 50), post-HCV liver cirrhosis (n = 31), and CHCV (n = 30) groups.
The percentage of B1a cells (B1a%) and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of NKG2D (NKG2D MFI) showed a significant increase in the CHCV group compared with those in the post-HCV liver cirrhosis and post-HCV HCC groups (P < 0.05). A positive correlation was observed between NKG2D MFI and B1a% (r = 0.6, P < 0.001). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve revealed that NKG2D MFI and B1a% differentiated between patients with CHCV infection and those with HCC with a sensitivity of 92% and 98%, respectively, and differentiated between patients with CHCV infection and those with liver cirrhosis with a sensitivity of 94% and 90%, respectively.
Downregulation of B1a frequency and NKG2D intensity is implicated in the progression of CHCV infection to cirrhosis and HCC. NKG2D receptor is associated with the frequency of circulating B1a cells. NKG2D intensity and B1a% can be used as indicators of CHCV progression.
© 2022 Hammad et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Signal Transduct Target Ther on 25 March 2022 by Dai, Z., Mu, W., et al.
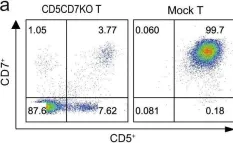
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Signal Transduct Target Ther by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In Signal Transduct Target Ther on 25 March 2022 by Dai, Z., Mu, W., et al.
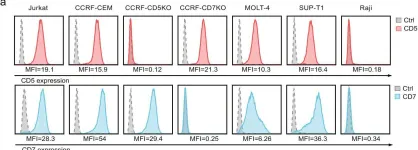
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Signal Transduct Target Ther by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2