Neutrophils are essential innate immune cells with unusual anti-microbial properties while dysfunctions of neutrophils lead to severe health problems such as lethal infections. Generation of neutrophils from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) is highly promising to produce off-the-shelf neutrophils for transfusion therapies. However, the anti-microbial potencies of hiPSCs derived neutrophils (iNEUs) remain less documented. Here, we develop a scalable approach to generate iNEUs in a chemical defined condition. iNEUs display typical neutrophil characters in terms of phagocytosis, migration, formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), etc. Importantly, iNEUs display a strong killing potency against various bacteria such as K.pneumoniae, P.aeruginosa, E.coli and S.aureus. Moreover, transfusions of iNEUs in mice with neutrophil dysfunction largely enhance their survival in lethal infection of different bacteria. Together, our data show that hiPSCs derived neutrophils hold strong anti-microbial potencies to protect severe infections under neutrophil dysfunction conditions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 92
Human induced pluripotent stem cells derived neutrophils display strong anti-microbial potencies.
In Cell Regeneration (London, England) on 21 March 2025 by Hu, X., Kang, B., et al.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Heliyon on 15 October 2024 by Zhu, A., Zhou, L., et al.
The vastly spreading COVID-19 pneumonia is caused by SARS-CoV-2. Lymphopenia and cytokine levels are tightly associated with disease severity. However, virus-induced immune dysregulation at cellular and molecular levels remains largely undefined. Here, the leukocytes in the pleural effusion, sputum, and peripheral blood biopsies from severe and mild patients were analyzed at single-cell resolution. Drastic T cell hyperactivation accompanying elevated T cell exhaustion was observed, predominantly in pleural effusion. The mechanistic investigation identified a group of CD14+ monocytes and macrophages highly expressing CD163 and MRC1 in the biopsies from severe patients, suggesting M2 macrophage polarization. These M2-like cells exhibited up-regulated IL10, CCL18, APOE, CSF1 (M-CSF), and CCL2 signaling pathways. Further, cell type specific dysregulation of transposable elements was observed in Severe COVID-19 patients. Together, our results suggest that severe SARS-CoV-2 infection causes immune dysregulation by inducing M2 polarization and subsequent T cell exhaustion. This study improves our understanding of COVID-19 pathogenesis.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Neutrophil glucose flux as a therapeutic target in antiphospholipid syndrome.
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 13 June 2024 by Tambralli, A., Harbaugh, A., et al.
Neutrophil hyperactivity and neutrophil extracellular trap release (NETosis) appear to play important roles in the pathogenesis of the thromboinflammatory autoimmune disease known as antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). The understanding of neutrophil metabolism has advanced tremendously in the past decade, and accumulating evidence suggests that a variety of metabolic pathways guide neutrophil activities in health and disease. Our previous work characterizing the transcriptome of APS neutrophils revealed that genes related to glycolysis, glycogenolysis, and the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) were significantly upregulated. Here, we found that neutrophils from patients with APS used glycolysis more avidly than neutrophils from people in the healthy control group, especially when the neutrophils were from patients with APS with a history of microvascular disease. In vitro, inhibiting either glycolysis or the PPP tempered phorbol myristate acetate- and APS IgG-induced NETosis, but not NETosis triggered by a calcium ionophore. In mice, inhibiting either glycolysis or the PPP reduced neutrophil reactive oxygen species production and suppressed APS IgG-induced NETosis ex vivo. When APS-associated thrombosis was evaluated in mice, inhibiting either glycolysis or the PPP markedly suppressed thrombosis and circulating NET remnants. In summary, these data identify a potential role for restraining neutrophil glucose flux in the treatment of APS.
Regulation of CD47 expression on CD14+ monocytes by interferon-α in PBC patients.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 19 December 2023 by Su, X., Jin, W., et al.
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic intrahepatic cholestatic autoimmune liver disease characterized by inflammatory injury of small and medium-sized bile ducts in the liver. The pathogenesis of PBC has yet to be entirely understood. CD47/signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) is closely related to developing autoimmune diseases by promoting inflammatory response. However, the effect of CD47/SIRPα on inflammatory response in PBC patients is still unclear.
We investigated the expression of CD47/SIRPα and the effect of inflammatory cytokines on the CD47 expression, analyzed potential autoantibodies against CD47 and the effect of anti-CD47 antibody on the inflammatory response in PBC, provided laboratory basis for the study of the pathogenesis and targets for non-invasive diagnosis and treatment on PBC.
The expression levels of CD47 and SIRPα on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were measured in 14 patients with PBC (the PBC group) and 13 healthy subjects (the Control group) by flow cytometry (FCM). The PBMC derived from healthy subjects were stimulated with healthy subjects' serum, PBC patients' serum, IFN-α or TNF-α, and the CD47 expression level on CD14+ monocytes was detected by FCM. The level of serum anti-CD47 antibody or IFN-α in PBC patients and healthy subjects was analyzed by ELISA. FCM was used to examine the TNF-α expression level in CD14+ monocytes of healthy subjects stimulated with isotype control antibody, anti-CD47 antibody, LPS or LPS combined with CD47 antibody.
The CD47 expression level on the CD14+ monocytes in PBC patients was statistically higher than that in the Control group (P<0.01). Compared with the Control group (PBMC+healthy serum), the CD47 expression on CD14+ monocyte stimulated with the PBC patients' serum (PBMC+PBC patients' serum) was increased (P<0.001); the CD47 expression on CD14+ monocyte stimulated with IFN-α (PBMC + IFN-α) increased gradually with the increased concentration of IFN-α (P<0.05). However, there was no similar trend on CD14+ monocyte stimulated with the TNF-α (PBMC+TNF-α) (P>0.05). The levels of serum anti-CD47 antibody and IFN-α in the PBC patients were higher than those in healthy subjects (P<0.05). The TNF-α expression level in CD14+ monocyte stimulated with the LPS (PBMC+LPS) or anti-CD47 antibody+LPS group (PBMC+LPS+anti-CD47 antibody) was significantly increased than that in the Control group (PBMC+isotype control antibody) (P<0.01 and P<0.001, respectively). The TNF-α expression level in CD14+ monocyte stimulated with the anti-CD47 antibody + LPS was higher than that with the LPS (P< 0.05).
The CD47 may be related to the pathogenesis of PBC by inflammatory response. The CD47/SIRPα signal were imbalanced in PBC patients. The presence of serum anti-CD47 antibodies in PBC patients provides a laboratory basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Su, Jin, Liu, Zhu and Li.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports Medicine on 19 September 2023 by Ahmadi, A. R., Atiee, G., et al.
Preclinical studies demonstrate that pharmacological mobilization and recruitment of endogenous bone marrow stem cells and immunoregulatory cells by a fixed-dose drug combination (MRG-001) improves wound healing, promotes tissue regeneration, and prevents allograft rejection. In this phase I, first-in-human study, three cohorts receive subcutaneous MRG-001 or placebo, every other day for 5 days. The primary outcome is safety and tolerability of MRG-001. Fourteen subjects received MRG-001 and seven received a placebo. MRG-001 is safe over the selected dose range. There are no clinically significant laboratory changes. The intermediate dose group demonstrates the most significant white blood cell, stem cell, and immunoregulatory cell mobilization. PBMC RNA sequencing and gene set enrichment analysis reveal 31 down-regulated pathways in the intermediate MRG-001 dose group compared with no changes in the placebo group. MRG-001 is safe across all dose ranges. MRG-001 may be a clinically useful therapy for immunoregulation and tissue regeneration (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04646603).
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
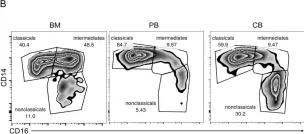
In Sci Rep on 7 March 2023 by Vuoti, E., Lehenkari, P., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
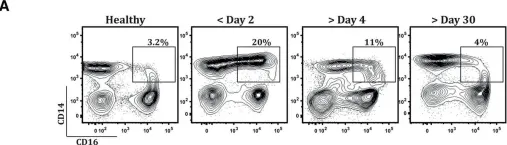
In PLoS Negl Trop Dis on 1 March 2016 by Singla, M., Kar, M., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS Negl Trop Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2