Background: Globally, colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer among males and the second-most diagnosed cancer among females. In cancer, stem cells are a subset of neoplastic cells capable of tumorigenesis and exhibit properties like normal stem cells. Moreover, they are resistant to conventional cancer treatments and can repopulate the tumor following treatment. Cancer cells are stimulated to undergo apoptosis by photodynamic therapy (PDT), which involves a light source, a photosensitizer, and reactive oxygen species. Methods: In this study, colon cancer stem cells were isolated from colon cancer cells and characterized using flow cytometry and immunofluorescence techniques. To treat colon cancer stem cells (CCSCs), single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) were coupled with hyaluronic acid (HA) and loaded with chlorin-e6 (Ce6). Nanobiocomposite toxicity was assessed using CCSCs with two fluences of 5 J/cm2 and 10 J/cm2. The cellular changes were observed at 24 and 48 h using microscopy, Results: LDH cytotoxicity assay, and cell death induction by annexin propidium iodide assay. An intracellular analysis of reactive oxygen species (ROS) detected oxidative stress within CCSCs. Conclusions: Overall, the results showed that the newly synthesized nanobiocomposite enhanced the ability of PDT to act as a photosensitizer carrier and induced cell death in CCSCs.
Product Citations: 42
In Pharmaceutics on 3 April 2025 by Sundaram, P., Kumar, S. S. D., et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Journal of Proteome Research on 1 December 2023 by Louati, K., Maalej, A., et al.
Pesticides are increasingly used in combinations in crop protection, resulting in enhanced toxicities for various organisms. Although protein adductomics is challenging, it remains a powerful bioanalytical tool to check environmental exposure and characterize xenobiotic adducts as putative toxicity biomarkers with high accuracy, facilitated by recent advances in proteomic methodologies and a mass spectrometry high-throughput technique. The present study aims to predict the potential neurotoxicity effect of imidacloprid and λ-cyhalothrin insecticides on human neural cells. Our protocol consisted first of 3D in vitro developing neurospheroids derived from human brain tumors and then treatment by pesticide mixture. Furthermore, we adopted a bottom-up proteomic-based approach using nanoflow ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with a high-resolution mass spectrometer for protein-adduct analysis with prediction of altered sites. Two proteins were selected, namely, calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-II (CaMK2) and annexin-A1 (ANXA1), as key targets endowed with primordial roles. De novo sequencing revealed several adduct formations in the active site of 82-ANXA1 and 228-CaMK2 as a result of neurotoxicity, predicted by the added mass shifts for the structure of electrophilic precursors. To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to adopt a proteomic-based approach to investigate in depth pesticide molecular interactions and their potential to adduct proteins which play a crucial role in the neurotoxicity mechanism.
-
IHC
-
Cancer Research
CD24-Siglec axis is an innate immune checkpoint against metaflammation and metabolic disorder.
In Cell Metabolism on 2 August 2022 by Wang, X., Liu, M., et al.
The molecular interactions that regulate chronic inflammation underlying metabolic disease remain largely unknown. Since the CD24-Siglec interaction regulates inflammatory response to danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), we have generated multiple mouse strains with single or combined mutations of Cd24 or Siglec genes to explore the role of the CD24-Siglec interaction in metaflammation and metabolic disorder. Here, we report that the CD24-Siglec-E axis, but not other Siglecs, is a key suppressor of obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. Inactivation of the CD24-Siglec-E pathway exacerbates, while CD24Fc treatment alleviates, diet-induced metabolic disorders, including obesity, dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Mechanistically, sialylation-dependent recognition of CD24 by Siglec-E induces SHP-1 recruitment and represses metaflammation to protect against metabolic syndrome. A first-in-human study of CD24Fc (NCT02650895) supports the significance of this pathway in human lipid metabolism and inflammation. These findings identify the CD24-Siglec-E axis as an innate immune checkpoint against metaflammation and metabolic disorder and suggest a promising therapeutic target for metabolic disease.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Single-cell proteomics defines the cellular heterogeneity of localized prostate cancer.
In Cell Reports Medicine on 19 April 2022 by de Vargas Roditi, L., Jacobs, A., et al.
Localized prostate cancer exhibits multiple genomic alterations and heterogeneity at the proteomic level. Single-cell technologies capture important cell-to-cell variability responsible for heterogeneity in biomarker expression that may be overlooked when molecular alterations are based on bulk tissue samples. This study aims to identify prognostic biomarkers and describe the heterogeneity of prostate cancer and the associated microenvironment by simultaneously quantifying 36 proteins using single-cell mass cytometry analysis of over 1.6 million cells from 58 men with localized prostate cancer. We perform this task, using a high-dimensional clustering pipeline named Franken to describe subpopulations of immune, stromal, and prostate cells, including changes occurring in tumor tissues and high-grade disease that provide insights into the coordinated progression of prostate cancer. Our results further indicate that men with localized disease already harbor rare subpopulations that typically occur in castration-resistant and metastatic disease.
© 2022 The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 24 March 2021 by Lee, A. C. K., Lau, P. M., et al.
Chemo-resistance hinders treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Although there are many models that can be found in the literature, the root mechanism to explain chemo-resistance is still not fully understood. To gain a better understanding of this phenomenon, a chemo-resistant line, R-HepG2, was developed from a chemo-sensitive HepG2 line through an exposure of doxorubicin (DOX). The R-HepG2 exhibited a cancer stem cell (CSC) phenotype with an over-expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), conferring it a significant enhancement in drug efflux and survival. With these observations, we hypothesize that metabolic alteration in this drug-resistant CSC is the root cause of chemo-resistance. Our results show that, unlike other metabolic-reprogrammed CSCs that exhibit glycolytic phenotype described by the "Warburg effect", the R-HepG2 was metabolically quiescent with glucose independence, high metabolic plasticity, and relied on glutamine metabolism via the mitochondria for its chemo-resistance Intriguingly, drug efflux by P-gp in R-HepG2 depended on the mitochondrial ATP fueled by glutamine instead of glycolytic ATP. Armed with these observations, we blocked the glutamine metabolism in the R-HepG2 and a significant reduction of DOX efflux was obtained. We exploited this metabolic vulnerability using a combination of DOX and metformin in a glutamine-free condition to target the R-HepG2, resulting in a significant DOX sensitization. In conclusion, our findings highlight the metabolic modulation of chemo-resistance in CSCs. We delineate the altered metabolism that drives chemo-resistance and offer a new approach to target this CSC through metabolic interventions.
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
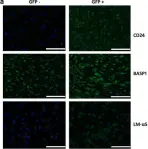
In Stem Cell Res Ther on 9 March 2018 by Tang, R., Jing, L., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Stem Cell Res Ther by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1