ABSTRACT Primary human cells cultured in organoid format have great promise as potential regenerative cellular therapies. However, their immunogenicity and mutational profile remain unresolved, impeding effective long-term translation to the clinic. In this study we report, for the first time, the generation of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-I and HLA-II knock-out expandable human primary cholangiocyte organoids (PCOs) using CRISPR-Cas9 as a potential ‘universal’ low-immunogenic therapy for bile duct disorders. HLA-edited PCOs (ePCOs) displayed the same phenotypical and functional characteristics as parental un-edited PCOs. Despite minimal off-target edits, single-molecule DNA-sequencing demonstrated that ePCOs and PCOs acquire substantial mutations in culture at similar rates but without evident selection for cancer-driver mutations. ePCOs induced reduced T cell-mediated immunity and a donor-dependent NK cell cytotoxicity in vitro and evaded cytotoxic responses with increased graft survival in humanized mice in vivo . Our findings have important implications for assessment of safety and immunogenicity of organoid cellular therapies.
Product Citations: 130
Immune and Mutational Profile of Gene-Edited Low-Immunogenic Human Primary Cholangiocyte Organoids
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 22 January 2025 by Petrus-Reurer, S., Baez-Ortega, A., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Science Advances on 18 October 2024 by Thielman, N. R. J., Funes, V., et al.
Axon guidance molecules are frequently altered in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) and influence PDA progression. However, the molecular mechanism remained unclear. Using genetically engineered mouse models to examine semaphorin 3D (SEMA3D), we identified a dual role for tumor- and nerve-derived SEMA3D in the malignant transformation of pancreatic epithelial cells and invasive PDA development. Pancreatic-specific knockout of the SEMA3D gene from the KRASG12D and TP53R172H mutation knock-in, PDX1-Cre(KPC) mouse model demonstrated delayed tumor initiation, prolonged survival, absence of metastasis, and reduced M2 macrophage expression. Mechanistically, tumor- and nerve-derived SEMA3D indirectly reprograms macrophages through KRASMUT-dependent ARF6 signaling in PDA cells, resulting in increased lactate production, which is sensed by GPCR132 on macrophages to stimulate protumorigenic M2 polarization. Multiplex immunohistochemistry demonstrated increased M2-polarized macrophages proximal to nerves in SEMA3D-expressing human PDA tissue. This study suggests that altered SEMA3D expression leads to an acquisition of cancer-promoting functions, and nerve-derived SEMA3D is "hijacked" by PDA cells to support growth and metastasis in a KRASMUT-dependent manner.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Cytosolic DNA sensor AIM2 promotes KRAS-driven lung cancer independent of inflammasomes.
In Cancer Science on 1 June 2024 by Alanazi, M., Weng, T., et al.
Constitutively active KRAS mutations are among the major drivers of lung cancer, yet the identity of molecular co-operators of oncogenic KRAS in the lung remains ill-defined. The innate immune cytosolic DNA sensor and pattern recognition receptor (PRR) Absent-in-melanoma 2 (AIM2) is best known for its assembly of multiprotein inflammasome complexes and promoting an inflammatory response. Here, we define a role for AIM2, independent of inflammasomes, in KRAS-addicted lung adenocarcinoma (LAC). In genetically defined and experimentally induced (nicotine-derived nitrosamine ketone; NNK) LAC mouse models harboring the KrasG12D driver mutation, AIM2 was highly upregulated compared with other cytosolic DNA sensors and inflammasome-associated PRRs. Genetic ablation of AIM2 in KrasG12D and NNK-induced LAC mouse models significantly reduced tumor growth, coincident with reduced cellular proliferation in the lung. Bone marrow chimeras suggest a requirement for AIM2 in KrasG12D-driven LAC in both hematopoietic (immune) and non-hematopoietic (epithelial) cellular compartments, which is supported by upregulated AIM2 expression in immune and epithelial cells of mutant KRAS lung tissues. Notably, protection against LAC in AIM2-deficient mice is associated with unaltered protein levels of mature Caspase-1 and IL-1β inflammasome effectors. Moreover, genetic ablation of the key inflammasome adapter, ASC, did not suppress KrasG12D-driven LAC. In support of these in vivo findings, AIM2, but not mature Caspase-1, was upregulated in human LAC patient tumor biopsies. Collectively, our findings reveal that endogenous AIM2 plays a tumor-promoting role, independent of inflammasomes, in mutant KRAS-addicted LAC, and suggest innate immune DNA sensing may provide an avenue to explore new therapeutic strategies in lung cancer.
© 2024 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
In GLIA on 1 October 2023 by Usui-Ouchi, A., Giles, S., et al.
In the retina, microglia are resident immune cells that are essential for development and function. Retinal microglia play a central role in mediating pathological degeneration in diseases such as glaucoma, retinitis pigmentosa, age-related neurodegeneration, ischemic retinopathy, and diabetic retinopathy. Current models of mature human retinal organoids (ROs) derived from iPS cell (hiPSC) do not contain resident microglia integrated into retinal layers. Increasing cellular diversity in ROs by including resident microglia would more accurately represent the native retina and better model diseases in which microglia play a key role. In this study, we develop a new 3D in vitro tissue model of microglia-containing retinal organoids by co-culturing ROs and hiPSC-derived macrophage precursor cells (MPCs). We optimized the parameters for successful integration of MPCs into retinal organoids. We show that while in the ROs, MPCs migrate to the equivalent of the outer plexiform layer where retinal microglia cells reside in healthy retinal tissue. While there, they develop a mature morphology characterized by small cell bodies and long branching processes which is only observed in vivo. During this maturation process these MPCs cycle through an activated phase followed by a stable mature microglial phase as seen by the down regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Finally, we characterized mature ROs with integrated MPCs using RNAseq showing an enrichment of cell-type specific microglia markers. We propose that this co-culture system may be useful for understanding the pathogenesis of retinal diseases involving retinal microglia and for drug discovery directly in human tissue.
© 2023 The Authors. GLIA published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In JCO Precision Oncology on 1 September 2023 by Sud, S., Poellmann, M. J., et al.
There are currently no predictive molecular biomarkers to identify patients with oligometastatic disease (OMD) who will benefit from definitive-intent radiation therapy (RT). We prospectively characterized circulating tumor cell (CTC) kinetics in patients with OMD undergoing definitive-intent RT.
This prospective correlative biomarker study included patients with any solid malignancy ≤5 metastatic sites in ≤3 anatomic organ systems undergoing definitive-intent RT to all disease sites. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) were captured and enumerated using a biomimetic cell rolling and nanotechnology-based assay functionalized with antibodies against epithelial cell adhesion molecule, against human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, and against epidermal growth factor receptor before and during RT and at follow-up visits up to 2 years post-RT.
We enrolled 43 patients with a median follow-up of 14.3 months. The pretreatment CTC level (cells captured/mL) was not associated with the number of disease sites (median one metastatic site/patient, range 1-5) or metastasis location (bone, brain, visceral) on Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P > .05. Post-RT, 56% of patients received systemic therapy, and 72% of patients experienced subsequent local or systemic progression. For 90% of patients, a CTC level <15 within 130 days post-RT corresponded to a durable control of irradiated lesions. Patients with a favorable versus an unfavorable clearance profile experienced significantly longer progression-free survival after RT (median 13 v 4 months, log-rank test, P = .0011). On logistic regression, CTC level >15 at a given time point was associated with clinical disease progression within the subsequent 6 months (odds ratio 3.31, P = .007). In 26% of patients with disease progression, a CTC level >15 preceded radiographic or clinical progression.
CTCs may serve as a biomarker for disease control in OMD and may predict disease progression before standard assessments for patients receiving diverse cancer-directed therapies.
-
Cancer Research
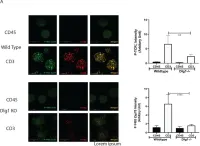
In Vaccines (Basel) on 7 December 2021 by Guha, J. & Chari, R.
Fig.4.A

-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Vaccines (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
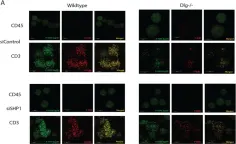
In Vaccines (Basel) on 7 December 2021 by Guha, J. & Chari, R.
Fig.1.A

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Vaccines (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
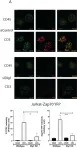
In Vaccines (Basel) on 7 December 2021 by Guha, J. & Chari, R.
Fig.1.B

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Vaccines (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
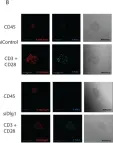
In Vaccines (Basel) on 7 December 2021 by Guha, J. & Chari, R.
Fig.2.A

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Vaccines (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4