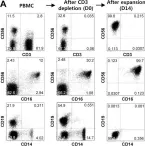
Anti-CD20 therapy is a highly effective treatment for multiple sclerosis (MS). In this study, we investigated MS-related changes in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) subsets compared to healthy controls and longitudinal changes related to the treatment.
Multicolor spectral flow cytometry analysis was performed on 78 samples to characterize disease- and treatment-related PBMC clusters. Blood samples from MS patients were collected at baseline and up to 8 months post-treatment, with three collection points after treatment initiation. Unsupervised clustering tools and manual gating were applied to identify subclusters of interest and quantify changes.
B cells were depleted from the periphery after anti-CD20 treatment as expected, and we observed an isolated acute, transitory drop in the proportion of natural killer (NK) and NKT cells among the main populations of PBMC (P = 0.03, P = 0.004). Major affected PBMC subpopulations were cytotoxic immune cells (NK, NKT, and CD8+ T cells), and we observed a higher proportion of cytotoxic cells with reduced brain-homing ability and a higher regulatory function as a long-term anti-CD20-related effect. Additionally, anti-CD20 therapy altered distributions of memory CD8+ T cells and reduced exhaustion markers in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
The findings of this study elucidate phenotypic clusters of NK and CD8+ T cells, which have previously been underexplored in the context of anti-CD20 therapy. Phenotypic modifications towards a more regulatory and controlled phenotype suggest that these subpopulations may play a critical and previously unrecognized role in mediating the therapeutic efficacy of anti-CD20 treatments.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Product Citations: 44
In Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology on 1 October 2024 by Waede, M., Voss, L. F., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports Medicine on 18 June 2024 by Guo, H. Z., Feng, R. X., et al.
Environmental lipids are essential for fueling tumor energetics, but whether these exogenous lipids transported into cancer cells facilitate immune escape remains unclear. Here, we find that CD36, a transporter for exogenous lipids, promotes acute myeloid leukemia (AML) immune evasion. We show that, separately from its established role in lipid oxidation, CD36 on AML cells senses oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) to prime the TLR4-LYN-MYD88-nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway, and exogenous palmitate transfer via CD36 further potentiates this innate immune pathway by supporting ZDHHC6-mediated MYD88 palmitoylation. Subsequently, NF-κB drives the expression of immunosuppressive genes that inhibit anti-tumor T cell responses. Notably, high-fat-diet or hypomethylating agent decitabine treatment boosts the immunosuppressive potential of AML cells by hijacking CD36-dependent innate immune signaling, leading to a dampened therapeutic effect. This work is of translational interest because lipid restriction by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved lipid-lowering statin drugs improves the efficacy of decitabine therapy by weakening leukemic CD36-mediated immunosuppression.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Developmental Cell on 6 May 2024 by Fowler, J. L., Zheng, S. L., et al.
The developmental origin of blood-forming hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) is a longstanding question. Here, our non-invasive genetic lineage tracing in mouse embryos pinpoints that artery endothelial cells generate HSCs. Arteries are transiently competent to generate HSCs for 2.5 days (∼E8.5-E11) but subsequently cease, delimiting a narrow time frame for HSC formation in vivo. Guided by the arterial origins of blood, we efficiently and rapidly differentiate human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) into posterior primitive streak, lateral mesoderm, artery endothelium, hemogenic endothelium, and >90% pure hematopoietic progenitors within 10 days. hPSC-derived hematopoietic progenitors generate T, B, NK, erythroid, and myeloid cells in vitro and, critically, express hallmark HSC transcription factors HLF and HOXA5-HOXA10, which were previously challenging to upregulate. We differentiated hPSCs into highly enriched HLF+ HOXA+ hematopoietic progenitors with near-stoichiometric efficiency by blocking formation of unwanted lineages at each differentiation step. hPSC-derived HLF+ HOXA+ hematopoietic progenitors could avail both basic research and cellular therapies.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Depleting myeloid-biased haematopoietic stem cells rejuvenates aged immunity.
In Nature on 1 April 2024 by Ross, J. B., Myers, L. M., et al.
Ageing of the immune system is characterized by decreased lymphopoiesis and adaptive immunity, and increased inflammation and myeloid pathologies1,2. Age-related changes in populations of self-renewing haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are thought to underlie these phenomena3. During youth, HSCs with balanced output of lymphoid and myeloid cells (bal-HSCs) predominate over HSCs with myeloid-biased output (my-HSCs), thereby promoting the lymphopoiesis required for initiating adaptive immune responses, while limiting the production of myeloid cells, which can be pro-inflammatory4. Ageing is associated with increased proportions of my-HSCs, resulting in decreased lymphopoiesis and increased myelopoiesis3,5,6. Transfer of bal-HSCs results in abundant lymphoid and myeloid cells, a stable phenotype that is retained after secondary transfer; my-HSCs also retain their patterns of production after secondary transfer5. The origin and potential interconversion of these two subsets is still unclear. If they are separate subsets postnatally, it might be possible to reverse the ageing phenotype by eliminating my-HSCs in aged mice. Here we demonstrate that antibody-mediated depletion of my-HSCs in aged mice restores characteristic features of a more youthful immune system, including increasing common lymphocyte progenitors, naive T cells and B cells, while decreasing age-related markers of immune decline. Depletion of my-HSCs in aged mice improves primary and secondary adaptive immune responses to viral infection. These findings may have relevance to the understanding and intervention of diseases exacerbated or caused by dominance of the haematopoietic system by my-HSCs.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland) on 25 May 2023 by Dons'koi, B. V., Baksheev, S. M., et al.
NKp46 is an NK cell receptor uniquely expressed by NK cells and a small subset of innate lymphoid cells. In our previous studies, we suggested a tight connection between the activity of NK cells and the expression of NKp46 and supported the clinical significance of NKp46 expression in NK cells in women with reproductive failures. In this study, we investigated the expression of NKp46 in NK cells in the peripheral blood of women in early pregnancy and analyzed its association with pregnancy loss.
In a blinded study, we examined blood samples and analyzed the subsequent pregnancy outcomes from 98 early pregnant women (5th-7th week of gestation-w.g.) and 66 women in the 11th-13th week of pregnancy who served as controls. We studied the expression of NKp46 and the levels of anti-cardiolipin antibodies (aCL). The results of aCL were shared with the clinic, while the expression of NKp46 was blinded and not analyzed until the end of the study.
A misbalance in the NKp46+NK cells subpopulations was associated with an unfavorable ongoing pregnancy. A decreased level of NKp46high cells (<14%) was strongly associated with miscarriage. A decreased level of the double-bright subpopulation (NKp46hightCD56++) also was a negative prognostic factor for the pregnancy course, but its increased level (>4%) was strongly associated with a successful pregnancy course.
Our results showed that accentuated levels of NKp46+NK cells lead to a negative prognosis for early pregnancy courses in women.
-
FC/FACS
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
In PLoS One on 18 January 2013 by Lim, O., Lee, Y., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1