Invasive fungal infections (IFIs) are responsible for elevated rates of morbidity and mortality, causing around of 1.5 million deaths annually worldwide. One of the main causative agents of IFIs is Candida albicans, and non-albicans Candida species have emerged as a spreading global public health concernment. Furthermore, COVID-19 has contributed to a boost in the incidence of IFIs, such as mucormycosis, in which Rhizopus oryzae is the most prevalent causative agent. The effector host immune response against IFIs depends on the activity of T cells, which are susceptible to the regulatory effects triggered by fungal virulence factors. The fungal cell wall plays a crucial role as a virulence factor, and its remodeling compromises the development of a specific T-cell response. The redirection of Jurkat T cells to target Candida spp. by recognizing targets expressed on the fungal cell wall can be facilitated using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) technology. This study generated an M-CAR that contains an scFv with specificity to α-1,6 mannose backbone of fungal mannan, and the expression of M-CAR on the surface of modified Jurkat cells triggered a strong activation against Candida albicans (hyphae form), Candida tropicalis (hyphae form), Candida parapsilosis (pseudohyphal form), and Candida glabrata (yeast form). Moreover, M-CAR Jurkat cells recognized Rhizopus oryzae spores, which induced high expression of cell activation markers. Thus, a novel Mannan-specific CAR enabled strong signal transduction in modified Jurkat cells in the presence of Candida spp. or R. oryzae.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Product Citations: 109
In Bioengineered on 1 December 2025 by Guimarães, J. G., de Campos, G. Y., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 25 March 2025 by Wang, Y. T., Branche, E., et al.
Understanding flavivirus immunity is critical for the development of pan-flavivirus vaccines. Dendritic cells (DC) coordinate antiviral innate and adaptive immune responses, and they can be targeted by flaviviruses as a mechanism of immune evasion. Using an unbiased genome-wide approach designed to specifically identify flavivirus-modulated pathways, we found that, while dengue virus (DENV) robustly activates DCs, Zika virus (ZIKV) causes minimal activation of genes involved in DC activation, maturation, and antigen presentation, reducing cytokine secretion and the stimulation of allogeneic and peptide-specific T cell responses. Mechanistically, ZIKV inhibits DC maturation by suppressing NF-κB p65 recruitment and the subsequent transcription of proinflammatory and DC maturation-related genes. Thus, we identify a divergence in the effects of ZIKV and DENV on the host T cell response, highlighting the need to factor such differences into the design of anti-flavivirus vaccines.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.) on 26 December 2024 by Armbruster, A., Hörner, M., et al.
Methods for the precise temporal control of cell surface receptor activation are indispensable for the investigation of signaling processes in mammalian cells. Optogenetics enables such precise control, but its application in primary cells is limited by the imperative for genetic manipulation of target cells. We here describe a method that overcomes this obstacle and enables the precise activation of the T cell receptor in nongenetically engineered human T cells by light. Our optogenetic receptor activation system OptoREACT employs a TCR-specific scFv fused to PIF6 that interacts with tetramerized PhyB in a light-dependent manner and thereby clusters and activates the T cell receptor in response to red light. OptoREACT not only omits genetic manipulation of the target cell but, because of its modular nature, is likely applicable to a broad range of oligomerization-activated cell surface receptors.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 13 December 2024 by Guimarães, J. G., de Campos, G. Y., et al.
ABSTRACT Invasive fungal infections (IFIs) are responsible for elevated rates of morbidity and mortality, causing around of 1.5 million deaths annually worldwide. One of the main causative agents of IFIs is Candida albicans , and non-albicans Candida species have emerged as a spreading global public health concernment. Furthermore, COVID-19 has contributed to a boost in the incidence of IFIs, such as mucormycosis, in which Rhizopus oryzae is the most prevalent causative agent. The effector host immune response against IFIs depends on the activity of T cells, which are susceptible to the regulatory effects triggered by fungal virulence factors. The fungal cell wall plays a crucial role as a virulence factor, and its remodeling compromises the development of a specific T-cell response. The redirection of Jurkat T cells to target Candida spp. by recognizing targets expressed on the fungal cell wall can be facilitated using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) technology. This study generated an M-CAR that contains an scFv with specificity to α-1,6 mannose backbone of fungal mannan, and the expression of M-CAR on the surface of modified Jurkat cells triggered a strong activation against Candida albicans (hyphae form), Candida tropicalis (hyphae form), Candida parapsilosis (pseudohyphal form), and Candida glabrata (yeast form). Moreover, M-CAR Jurkat cells recognized Rhizopus oryzae spores, which induced high expression of cell activation markers. Thus, a novel Mannan-specific CAR enabled strong signal transduction in modified Jurkat cells in the presence of Candida spp. or R. oryzae .
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
MR1 presents vitamin B6-related compounds for recognition by MR1-reactive T cells.
In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on 3 December 2024 by McInerney, M. P., Awad, W., et al.
The major histocompatibility complex class I related protein (MR1) presents microbially derived vitamin B2 precursors to mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells. MR1 can also present other metabolites to activate MR1-restricted T cells expressing more diverse T cell receptors (TCRs), some with anti-tumor reactivity. However, knowledge of the range of the antigen(s) that can activate diverse MR1-reactive T cells remains incomplete. Here, we identify pyridoxal (vitamin B6) as a naturally presented MR1 ligand using unbiased mass spectrometry analyses of MR1-bound metabolites. Pyridoxal, and the related compound, pyridoxal 5-phosphate bound to MR1 and enabled cell surface upregulation of wild type MR1*01 and MR1 expressing the Arg9His polymorphism associated with the MR1*04 allotype in a manner dependent on Lys43-mediated Schiff-base formation. Crystal structures of MR1*01 in complex with pyridoxal and pyridoxal 5-phosphate showed how these ligands were accommodated within the A-pocket of MR1. T cell lines transduced with the 7.G5 TCR, which has reported "pan-cancer" specificity, were specifically activated by pyridoxal presented by antigen-presenting cells expressing MR1*01 and MR1 allotypes bearing the less common Arg9His polymorphism. 7.G5 T cells also recognized, to a lesser extent, pyridoxal 5-phosphate and, importantly, recognition of both vitamers was blocked by an anti-MR1 antibody. 7.G5 TCR reactivity toward pyridoxal was enhanced when presented by the Arg9His polymorphism-bearing MR1 allotypes. Vitamin B6, and vitamers thereof, have been associated with various cancers, and here we describe a link between this ligand, MR1, and its allomorphs, and the pan-cancer 7.G5 TCR. This work identifies an MR1 ligand that can activate a diverse MR1-restricted TCR.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Viruses on 17 October 2024 by Eisa, M., Flores, N., et al.
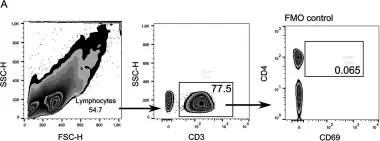
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Viruses by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Viruses on 17 October 2024 by Eisa, M., Flores, N., et al.
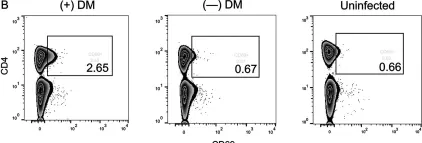
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Viruses by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Microbiol Spectr on 31 August 2022 by Castro Eiro, M. D., Natale, M. A., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Microbiol Spectr by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Microbiol Spectr on 31 August 2022 by Castro Eiro, M. D., Natale, M. A., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Microbiol Spectr by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4