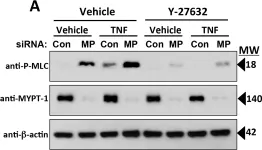
Capillary leak in severe sepsis involves disruption of endothelial cell tight junctions. We modeled this process by TNF treatment of cultured human dermal microvascular endothelial cell (HDMEC) monolayers, which unlike human umbilical vein endothelial cells form claudin-5-dependent tight junctions and a high-resistance permeability barrier. Continuous monitoring with electrical cell-substrate impedance sensing revealed that TNF disrupts tight junction-dependent HDMEC barriers in discrete steps: an ~5% increase in transendothelial electrical resistance over 40 minutes; a decrease to ~10% below basal levels over 2 hours (phase 1 leak); an interphase plateau of 1 hour; and a major fall in transendothelial electrical resistance to < 70% of basal levels by 8-10 hours (phase 2 leak), with EC50 values of TNF for phase 1 and 2 leak of ~30 and ~150 pg/ml, respectively. TNF leak is reversible and independent of cell death. Leak correlates with disruption of continuous claudin-5 immunofluorescence staining, myosin light chain phosphorylation and loss of claudin-5 co-localization with cortical actin. All these responses require NF-κB signaling, shown by inhibition with Bay 11 or overexpression of IκB super-repressor, and are blocked by H-1152 or Y-27632, selective inhibitors of Rho-associated kinase that do not block other NF-κB-dependent responses. siRNA combined knockdown of Rho-associated kinase-1 and -2 also prevents myosin light chain phosphorylation, loss of claudin-5/actin co-localization, claudin-5 reorganization and reduces phase 1 leak. However, unlike H-1152 and Y-27632, combined Rho-associated kinase-1/2 siRNA knockdown does not reduce the magnitude of phase 2 leak, suggesting that H-1152 and Y-27632 have targets beyond Rho-associated kinases that regulate endothelial barrier function. We conclude that TNF disrupts TJs in HDMECs in two distinct NF-κB-dependent steps, the first involving Rho-associated kinase and the second likely to involve an as yet unidentified but structurally related protein kinase(s).
Product Citations: 4
In PLoS ONE on 31 March 2015 by Clark, P. R., Kim, R. K., et al.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Leukemia on 1 September 2012 by van Dongen, J. J., Lhermitte, L., et al.
Most consensus leukemia & lymphoma antibody panels consist of lists of markers based on expert opinions, but they have not been validated. Here we present the validated EuroFlow 8-color antibody panels for immunophenotyping of hematological malignancies. The single-tube screening panels and multi-tube classification panels fit into the EuroFlow diagnostic algorithm with entries defined by clinical and laboratory parameters. The panels were constructed in 2-7 sequential design-evaluation-redesign rounds, using novel Infinicyt software tools for multivariate data analysis. Two groups of markers are combined in each 8-color tube: (i) backbone markers to identify distinct cell populations in a sample, and (ii) markers for characterization of specific cell populations. In multi-tube panels, the backbone markers were optimally placed at the same fluorochrome position in every tube, to provide identical multidimensional localization of the target cell population(s). The characterization markers were positioned according to the diagnostic utility of the combined markers. Each proposed antibody combination was tested against reference databases of normal and malignant cells from healthy subjects and WHO-based disease entities, respectively. The EuroFlow studies resulted in validated and flexible 8-color antibody panels for multidimensional identification and characterization of normal and aberrant cells, optimally suited for immunophenotypic screening and classification of hematological malignancies.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Molecular & Cellular Proteomics : MCP on 1 September 2012 by Sharivkin, R., Walker, M. D., et al.
Heterogeneity, shortage of material, and lack of progenitor-specific cell surface markers are major obstacles to elucidating the mechanisms underlying developmental processes. Here we report a proteomics platform that alleviates these difficulties and demonstrate its effectiveness in fractionating heterogeneous cultures of early endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells. The approach, designated differential cell-capture antibody array, is based on highly parallel, comparative screening of live cell populations using hundreds of antibodies directed against cell-surface antigens. We used this platform to fractionate the hitherto unresolved early endoderm compartment of CXCR4+ cells and identify several endoderm (CD61+ and CD63+) and non-endoderm (CD271+, CD49F+, CD44+ and B2M+) sub-populations. We provide evidence that one of these sub-populations, CD61+, is directly derived from CXCR4+ cells, displays characteristic kinetics of emergence, and exhibits a distinct gene expression profile. The results demonstrate the potential of the cell-capture antibody array as a powerful proteomics tool for detailed dissection of heterogeneous cellular systems.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Major histocompatibility complex class I expression in human tonsillar and laryngeal epithelium.
In Clinical and Experimental Immunology on 1 August 2006 by Hobbs, C. G., Rees, L. E., et al.
Understanding the immunological structure of the upper aerodigestive tract is important for analysing the interaction between incident challenges, such as human papillomavirus infection, and disease, particularly head and neck cancer. We have shown previously that tonsillar and laryngeal epithelium express major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II locus products, but that expression of human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DQ is reduced compared to HLA-DR. This may confer a decreased repertoire of presented T cell epitopes generated by the processing of exogenous peptides in upper airway mucosa. To determine whether the peptide repertoire presented by MHC class I loci varies in stratified squamous epithelium, laryngeal and tonsillar biopsies were taken from 19 otherwise healthy patients (M : F 6 : 13, 16-64 years). Quantitative immunofluorescence microscopy, using antibodies to MHC class I alpha-chain (pan-locus specific, HLA-A, HLA-B + C) and beta(2)-microglobulin, showed lower expression of the alpha-chain in laryngeal and tonsillar epithelium than in either lamina propria (tonsil 73% versus 89%, P < 0.0001; larynx 68% versus 85%, P < 0.005). Within the epithelium itself, the intensity of alpha-chain expression decreased from the basal to apical layers. In paired squamous epithelia from the two sites, alpha-chain expression was significantly higher in the tonsil compared to the larynx (79% versus 62%, P < 0.05). We suggest that these findings reflect functional stratification of these epithelia with the superficial layer, most exposed to incident challenges, less equipped to present antigens to conventional T cells. This may affect immunosurveillance directed at viral and tumour-related epitopes in the upper airway.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS One on 31 March 2015 by Clark, P. R., Kim, R. K., et al.
Fig.9.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1