Early initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) following HIV-1 infection restricts the size of the latent reservoir, following both horizontal and vertical infections. Here, we comprehensively profile the reservoirs and immunological milieus of nine young adults who acquired HIV-1 perinatally and remained on suppressive long-term ART (median: 20 years) since infancy (LeukoHIV cohort). Genome-intact reservoirs are markedly smaller compared to a cohort of adults on suppressive ART started in adulthood, with some LeukoHIV individuals characterized by an absence or near absence of intact proviruses in up to a billion peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Higher frequencies of functional CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells with increased cytotoxic activity are detectable in the LeukoHIV cohort compared to an adult reference cohort, while one LeukoHIV participant displayed a potent HIV-1-specific CD8+ T cell response. Collectively, our data suggest that long-term ART initiated in early life following perinatal transmission may facilitate an immune environment better equipped to restrict the HIV-1 reservoir.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 150
In Cell Reports Medicine on 17 June 2025 by Bone, B., Cotugno, N., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Immunology on 1 April 2025 by Rea, A., Santana-Hernández, S., et al.
Transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) and activin A suppress natural killer (NK) cell function and proliferation, limiting the efficacy of adoptive NK cell therapies. Inspired by the partial resistance to TGFβ of NK cells with SMAD4 haploinsufficiency, we used CRISPR-Cas9 for knockout of SMAD4 in human NK cells. Here we show that SMAD4KO NK cells were resistant to TGFβ and activin A inhibition, retaining their cytotoxicity, cytokine secretion and interleukin-2/interleukin-15-driven proliferation. They showed enhanced tumor penetration and tumor growth control, both as monotherapy and in combination with tumor-targeted therapeutic antibodies. Notably, SMAD4KO NK cells outperformed control NK cells treated with a TGFβ inhibitor, underscoring the benefit of maintaining SMAD4-independent TGFβ signaling. SMAD4KO conferred TGFβ resistance across diverse NK cell platforms, including CD19-CAR NK cells, stem cell-derived NK cells and ADAPT-NK cells. These findings position SMAD4 knockout as a versatile and compelling strategy to enhance NK cell antitumor activity, providing a new avenue for improving NK cell-based cancer immunotherapies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Communications (London, England) on 1 February 2025 by Fincham, R. E. A., Periasamy, P., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
CREB Is Critically Implicated in Skin Mast Cell Degranulation Elicited via FcεRI and MRGPRX2.
In Cells on 11 October 2024 by Li, Z., Schneikert, J., et al.
Skin mast cells (MCs) mediate acute allergic reactions in the cutaneous environment and contribute to chronic dermatoses, including urticaria, and atopic or contact dermatitis. The cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), an evolutionarily well conserved transcription factor (TF) with over 4,000 binding sites in the genome, was recently found to form a feedforward loop with KIT, maintaining MC survival. The most selective MC function is degranulation with its acute release of prestored mediators. Herein, we asked whether CREB contributes to the expression and function of the degranulation-competent receptors FcεRI and MRGPRX2. Interference with CREB by pharmacological inhibition (CREBi, 666-15) or RNA interference only slightly affected the expression of these receptors, while KIT was strongly attenuated. Interestingly, MRGPRX2 surface expression moderately increased following CREB-knockdown, whereas MRGPRX2-dependent exocytosis simultaneously decreased. FcεRI expression and function were regulated consistently, although the effect was stronger at the functional level. Preformed MC mediators (tryptase, histamine, β-hexosaminidase) remained comparable following CREB attenuation, suggesting that granule synthesis did not rely on CREB function. Collectively, in contrast to KIT, FcεRI and MRGPRX2 moderately depend on unperturbed CREB function. Nevertheless, CREB is required to maintain MC releasability irrespective of stimulus, insinuating that CREB may operate by safeguarding the degranulation machinery. To our knowledge, CREB is the first factor identified to regulate MRGPRX2 expression and function in opposite direction. Overall, the ancient TF is an indispensable component of skin MCs, orchestrating not only survival and proliferation but also their secretory competence.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cell Biology
In Molecular Therapy. Oncology on 19 September 2024 by Wang, J., Tian, L., et al.
Limited therapeutic options are available for patients with breast cancer brain metastases (BCBM), and thus there is an urgent need for novel treatment approaches. We previously engineered an effective oncolytic herpes simplex virus 1 (oHSV) expressing a full-length anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody (mAb) with a human IgG1 scaffold (OV-αCD47-G1) that was used to treat both ovarian cancer and glioblastoma. Here, we demonstrate that the combination of OV-αCD47-G1 and temozolomide (TMZ) improve outcomes in preclinical models of BCBM. The combination of TMZ with OV-αCD47-G1 synergistically increased macrophage phagocytosis against breast tumor cells and led to greater activation of NK cell cytotoxicity. In addition, the combination of OV-αCD47-G1 with TMZ significantly prolonged the survival of tumor-bearing mice when compared with TMZ or OV-αCD47-G1 alone. Combination treatment with the mouse counterpart of OV-αCD47-G1, termed OV-A4-IgG2b, also enhanced mouse macrophage phagocytosis, NK cell cytotoxicity, and survival in an immunocompetent model of mice bearing BCBM compared with TMZ or OV-A4-IgG2b alone. Collectively, these results suggest that OV-αCD47-G1 combined with TMZ should be explored in patients with BCBM.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
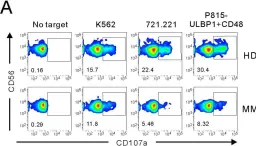
In Int J Mol Sci on 30 October 2020 by Kim, J. M., Yi, E., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
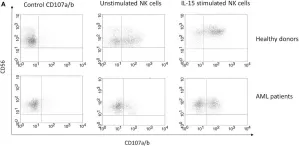
In Front Immunol on 22 August 2017 by Sánchez-Correa, B., Bergua, J. M., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2