h4>SUMMARY/h4> Pro-inflammatory signaling is a hallmark feature of human cancer, including in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), most notably myelofibrosis (MF). Dysregulated inflammatory signaling contributes to fibrotic progression in MF; however, the individual cytokine mediators elicited by malignant MPN cells to promote collagen-producing fibrosis and disease evolution remain yet to be fully elucidated. Previously we identified a critical role for combined constitutive JAK/STAT and aberrant NF-κB pro-inflammatory signaling in myelofibrosis development. Using single-cell transcriptional and cytokine-secretion studies of primary MF patient cells and two separate murine models of myelofibrosis, we extend this previous work and delineate the role of CXCL8/CXCR2 signaling in MF pathogenesis and bone marrow fibrosis progression. MF patient hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells are enriched in a CXCL8/CXCR2 gene signature and display dose-dependent proliferation and fitness in response to exogenous CXCL8 ligand in vitro . Genetic deletion of Cxcr2 in the hMPL W515L adoptive transfer model abrogates fibrosis and extends overall survival, and pharmacologic inhibition of the CXCR1/2 pathway improves hematologic parameters, attenuates bone marrow fibrosis, and synergizes with JAK inhibitor therapy. Our mechanistic insights provide a rationale for therapeutic targeting of the CXCL8/CXCR2 pathway in MF patients at risk for continued fibrotic progression.
Product Citations: 10
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 10 December 2021 by Dunbar, A., Kim, D., et al.
In eLife on 22 February 2018 by Lee, C. H., Zhang, H. H., et al.
Many mediators and regulators of extravasation by bona fide human memory-phenotype T cells remain undefined. Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are innate-like, antibacterial cells that we found excelled at crossing inflamed endothelium. They displayed abundant selectin ligands, with high expression of FUT7 and ST3GAL4, and expressed CCR6, CCR5, and CCR2, which played non-redundant roles in trafficking on activated endothelial cells. MAIT cells selectively expressed CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta (C/EBPδ). Knockdown of C/EBPδ diminished expression of FUT7, ST3GAL4 and CCR6, decreasing MAIT cell rolling and arrest, and consequently the cells' ability to cross an endothelial monolayer in vitro and extravasate in mice. Nonetheless, knockdown of C/EBPδ did not affect CCR2, which was important for the step of transendothelial migration. Thus, MAIT cells demonstrate a program for extravasastion that includes, in part, C/EBPδ and C/EBPδ-regulated genes, and that could be used to enhance, or targeted to inhibit T cell recruitment into inflamed tissue.
In Cell Metabolism on 9 January 2018 by Wang, T., Fahrmann, J. F., et al.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are critical for cancer progression and chemoresistance. How lipid metabolism regulates CSCs and chemoresistance remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate that JAK/STAT3 regulates lipid metabolism, which promotes breast CSCs (BCSCs) and cancer chemoresistance. Inhibiting JAK/STAT3 blocks BCSC self-renewal and expression of diverse lipid metabolic genes, including carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1B (CPT1B), which encodes the critical enzyme for fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO). Moreover, mammary-adipocyte-derived leptin upregulates STAT3-induced CPT1B expression and FAO activity in BCSCs. Human breast-cancer-derived data suggest that the STAT3-CPT1B-FAO pathway promotes cancer cell stemness and chemoresistance. Blocking FAO and/or leptin re-sensitizes them to chemotherapy and inhibits BCSCs in mouse breast tumors in vivo. We identify a critical pathway for BCSC maintenance and breast cancer chemoresistance.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Squamous Cell Tumors Recruit γδ T Cells Producing either IL17 or IFNγ Depending on the Tumor Stage.
In Cancer Immunology Research on 1 May 2017 by Lo Presti, E., Toia, F., et al.
The identification of reciprocal interactions between tumor-infiltrating immune cells and the microenviroment may help us understand mechanisms of tumor growth inhibition or progression. We have assessed the frequencies of tumor-infiltrating and circulating γδ T cells and regulatory T cells (Treg) from 47 patients with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), to determine if they correlated with progression or survival. Vδ1 T cells infiltrated SSC tissue to a greater extent than normal skin, but SCC patients and healthy subjects had similar amounts circulating. However, Vδ2 T cells were present at higher frequencies in circulation than in the tissue of either cancer patients or healthy donors. Tregs were decreased in the peripheral blood of SCC patients, but were significantly increased in the tumor compartment of these patients. Tumor-infiltrating γδ T cells preferentially showed an effector memory phenotype and made either IL17 or IFNγ depending on the tumor stage, whereas circulating γδ T cells of SCC patients preferentially made IFNγ. Different cell types in the tumor microenvironment produced chemokines that could recruit circulating γδ T cells to the tumor site and other cytokines that could reprogram γδ T cells to produce IL17. These findings suggest the possibility that γδ T cells in SCC are recruited from the periphery and their features are then affected by the tumor microenvironment. Elevated frequencies of infiltrating Vδ2 T cells and Tregs differently correlated with early and advanced tumor stages, respectively. Our results provide insights into the functions of tumor-infiltrating γδ T cells and define potential tools for tumor immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Res; 5(5); 397-407. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In FEBS Open Bio on 4 April 2015 by Han, X., Feng, Y., et al.
CXCR1, a receptor for interleukin-8 (IL-8), plays an important role in defending against pathogen invasion during neutrophil-mediated innate immune response. Human CXCR1 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) with its characteristic seven transmembrane domains (TMs). Functional and structural analyses of several GPCRs have revealed that conserved residues on TM3 (including the highly conserved Asp-Arg-Tyr (DRY) motif) and TM6 near intracellular loops contain domains critical for G protein coupling as well as GPCR activation. The objective of this study was to elucidate the role of critical amino acid residues on TM3 near intracellular loop 2 (i2) and TM6 near intracellular loop 3 (i3), including S132(3.47) (Baldwin location), D134(3.49), M241(6.34), and F251(6.44), in G protein coupling and CXCR1 activation. The results demonstrate that mutations of D134(3.49) at DRY motif of CXCR1 (D134N and D134V) completely abolished the ligand binding and functional response of the receptor. Additionally, point mutations at positions 241 and 251 between TM6 and i3 loop generated mutant receptors with modest constitutive activity via Gα15 signaling activation. Our results show that D134(3.49) on the highly conserved DRY motif has a distinct role for CXCR1 compared to its homologues (CXCR2 and KSHV-GPCR) in G protein coupling and receptor activation. In addition, M241(6.34) and F251(6.44) along with our previously identified V247(6.40) on TM6 are spatially located in a "hot spot" likely essential for CXCR1 activation. Identification of these amino acid residues may be useful for elucidating mechanism of CXCR1 activation and designing specific antagonists for the treatment of CXCR1-mediated diseases.
-
FC/FACS
In Immun Ageing on 28 March 2009 by Gasparoto, T. H., Vieira, N. A., et al.
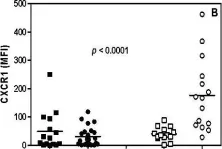
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Immun Ageing by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1