Fibrosis is defined as an excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) components. Many organs are subjected to fibrosis including the lung, liver, heart, skin, kidney, and muscle. Muscle fibrosis occurs in response to trauma, aging, or dystrophies and impairs muscle function. Fibrosis represents a hurdle for the treatment of human muscular dystrophies. While data on the mechanisms of fibrosis have mostly been investigated in mice, dystrophic mouse models often do not recapitulate fibrosis as observed in human patients. Consequently, the cellular and molecular mechanisms that lead to fibrosis in human muscle still need to be identified.
Combining mass cytometry, transcriptome profiling, in vitro co-culture experiments, and in vivo transplantation in immunodeficient mice, we investigated the role and nature of nonmyogenic cells (fibroadipogenic progenitors, FAPs) from human fibrotic muscles of healthy individuals (FibMCT ) and individuals with oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD; FibMOP ), as compared with nonmyogenic cells from human nonfibrotic muscle (MCT ).
We found that the proliferation rate of FAPs from fibrotic muscle is 3-4 times higher than those of FAPs from nonfibrotic muscle (population doubling per day: MCT 0.2 ± 0.1, FibMCT 0.7 ± 0.1, and FibMOP 0.8 ± 0.3). When cocultured with muscle cells, FAPs from fibrotic muscle impair the fusion index unlike MCT FAPs (myoblasts alone 57.3 ± 11.1%, coculture with MCT 43.1 ± 8.9%, with FibMCT 31.7 ± 8.2%, and with FibMOP 36.06 ± 10.29%). We also observed an increased proliferation of FAPs from fibrotic muscles in these co-cultures in differentiation conditions (FibMCT +17.4%, P < 0.01 and FibMOP +15.1%, P < 0.01). This effect is likely linked to the increased activation of the canonical TGFβ-SMAD pathway in FAPs from fibrotic muscles evidenced by pSMAD3 immunostaining (P < 0.05). In addition to the profibrogenic TGFβ pathway, we identified endothelin as a new actor implicated in the altered cross-talk between muscle cells and fibrotic FAPs, confirmed by an improvement of the fusion index in the presence of bosentan, an endothelin receptor antagonist (from 33.8 ± 10.9% to 52.9 ± 10.1%, P < 0.05).
Our data demonstrate the key role of FAPs and their cross-talk with muscle cells through a paracrine signalling pathway in fibrosis of human skeletal muscle and identify endothelin as a new druggable target to counteract human muscle fibrosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Product Citations: 25
In Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle on 1 June 2022 by Bensalah, M., Muraine, L., et al.
CD147 Promotes Tumor Lymphangiogenesis in Melanoma via PROX-1.
In Cancers on 28 September 2021 by Reger de Moura, C., Landras, A., et al.
Malignant melanoma is one of the most aggressive skin cancers and is characterized by early lymph node metastasis and the capacity to develop resistance to therapies. Hence, understanding the regulation of lymphangiogenesis through mechanisms contributing to lymphatic vessel formation represents a treatment strategy for metastatic cancer. We have previously shown that CD147, a transmembrane glycoprotein overexpressed in melanoma, regulates the angiogenic process in endothelial cells. In this study, we show a correlation between high CD147 expression levels and the number of lymphatic vessels expressing LYVE-1, Podoplanin, and VEGFR-3 in human melanoma lymph nodes. CD147 upregulates in vitro lymphangiogenesis and its related mediators through the PROX-1 transcription factor. In vivo studies in a melanoma model confirmed that CD147 is involved in metastasis through a similar mechanism as in vitro. This study, demonstrating the paracrine role of CD147 in the lymphangiogenesis process, suggests that CD147 could be a promising target for the inhibition of melanoma-associated lymphangiogenesis.
-
IHC
-
Cancer Research
Plasmodium vivax binds host CD98hc (SLC3A2) to enter immature red blood cells.
In Nature Microbiology on 1 August 2021 by Malleret, B., El Sahili, A., et al.
More than one-third of the world's population is exposed to Plasmodium vivax malaria, mainly in Asia1. P. vivax preferentially invades reticulocytes (immature red blood cells)2-4. Previous work has identified 11 parasite proteins involved in reticulocyte invasion, including erythrocyte binding protein 2 (ref. 5) and the reticulocyte-binding proteins (PvRBPs)6-10. PvRBP2b binds to the transferrin receptor CD71 (ref. 11), which is selectively expressed on immature reticulocytes12. Here, we identified CD98 heavy chain (CD98), a heteromeric amino acid transporter from the SLC3 family (also known as SLCA2), as a reticulocyte-specific receptor for the PvRBP2a parasite ligand using mass spectrometry, flow cytometry, biochemical and parasite invasion assays. We characterized the expression level of CD98 at the surface of immature reticulocytes (CD71+) and identified an interaction between CD98 and PvRBP2a expressed at the merozoite surface. Our results identify CD98 as an additional host membrane protein, besides CD71, that is directly associated with P. vivax reticulocyte tropism. These findings highlight the potential of using PvRBP2a as a vaccine target against P. vivax malaria.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
-
Cardiovascular biology
In Cancers on 2 February 2021 by Benyahia, Z., Blackman, M. C. N. M., et al.
To survive and proliferate in solid tumors, cancer cells adapt and evolve rapidly in microenvironments where oxygen and substrate bioavailability fluctuates over time and space. This creates metabolic heterogeneity. Cancer cells can further cooperate metabolically, for example by swapping glycolytic end-product lactate for blood-borne glucose. This type of cooperation can be targeted therapeutically, since transmembrane lactate exchanges are facilitated by lactate-proton symporters of the monocarboxylate (MCT) family. Among new drugs, AZD3965 is a first-in-class selective MCT1 inhibitor currently tested in Phase I/II clinical trials for patients with different types of cancers. Because MCT1 can function bidirectionally, we tested here whether and how malignant and nonmalignant cells adapt their metabolism and MCT repertoire when AZD3965 inhibits either lactate import or export. Using breast-associated malignant and nonmalignant cell lines as models, we report that AZD3965 is not directly cytotoxic. In the presence of glucose and glutamine, oxidative cells can survive when lactate uptake is blocked, and proliferating cells compensate MCT1 inhibition by overexpressing MCT4, a specialized facilitator of lactate export. Phenotypic characterization of mice focusing on metabolism, muscle and brain physiology found partial and transient memory retention defect as sole consequence of MCT1 inhibition by AZD3965. We therefore conclude that AZD3965 is compatible with anticancer therapy.
-
Cancer Research
In Oncogene on 1 August 2018 by Dai, L., Del Valle, L., et al.
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the causative agent of several human cancers such as Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), which represents the most common AIDS-associated malignancy that lacks effective treatment options. Despite its clear role in AIDS malignancies, the fact that only a small set of KSHV-infected patients will eventually develop these tumors implies that additional co-factors are required for the development of KSHV-related cancers. In the current study, we demonstrate for the first time that KSHV de novo infection or viral latent proteins are able to transactivate human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K) through a variety of cellular signaling pathways and transcriptional factors. Moreover, we found that HERV-K transactivation, particularly activation of its encoded oncogenic NP9 protein, plays an important role in KSHV pathogenesis and tumorigenesis in vitro and in vivo. Our data provide innovative insights into the mechanisms of HERV-K transactivation contributing to viral oncogenesis, which may represent a promising target for KS treatment.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Oncotarget on 11 April 2017 by Van Hée, V. F., Labar, D., et al.
Fig.4.B
![Fig.4.B showing Western Blotting from the publication: Radiosynthesis and validation of (±)-[18F]-3-fluoro-2-hydroxypropionate ([18F]-FLac) as a PET tracer of lactate to monitor MCT1-dependent lactate uptake in tumors.](https://images.citeab.com/s--fBuWI0C2--/t_full_trimmed/v1744828122/xrv4ygba12pyhxkvx6gy.webp)
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
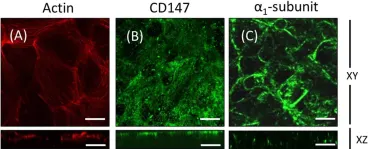
In Front Physiol on 25 October 2016 by Lobato-Álvarez, J. A., Roldán, M. L., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
IHC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Physiol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
![Fig.4.B showing Western Blotting from the publication: Radiosynthesis and validation of (±)-[18F]-3-fluoro-2-hydroxypropionate ([18F]-FLac) as a PET tracer of lactate to monitor MCT1-dependent lactate uptake in tumors.](https://images.citeab.com/s--k2DkoYOJ--/t_medium_trimmed/v1744828122/xrv4ygba12pyhxkvx6gy.webp)