mRNA vaccines have shown great efficacy against SARS-CoV-2, yet challenges remain in optimizing vaccine components to achieve enhanced immune response and vaccine stability. In this study, we developed CPVax-CoV, a new lyophilized mRNA vaccine that features novel thiolactone-based ionizable lipids and newly designed untranslated regions (UTRs) for enhanced expression. Incorporation of these optimized components into our vaccine candidate CPVax-CoV significantly improved immune responses in mice compared to commercially available mRNA vaccines. Moreover, lyophilized CPVax-CoV has proven to be thermostable, maintaining its biological activity for up to one year at 4 °C and 25 °C after lyophilization, overcoming the cold-chain limitations of current mRNA vaccines. This vaccine demonstrates protective efficacy against ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and the Omicron XBB variant, offering a scalable solution for global distribution and pandemic preparedness. These findings underscore the potential of this platform for future next-generation mRNA vaccine development.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 40
In NPJ Vaccines on 1 July 2025 by Mata, E., Broset, E., et al.
-
COVID-19
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Oncology Letters on 1 May 2025 by Wang, Y., Wang, W., et al.
Exosomes can be used to mediate the delivery of nucleic acids such as microRNA-125b-5p (miR-125b-5p), a tumor-suppressor in certain types of cancer, into tumor cells. The present study investigated the use of bone mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome (BMSCs-Exo) delivery of miR-125b-5p in ovarian cancer (OC). BMSCs were transfected with miR-125b-5p mimic, from which exosomes termed Exo-miR-125b-5p mimic were extracted. The expression levels of miR-125b-5p in OC tissue samples, BMSCs, exosomes and SKOV3 cells were quantified using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. The influence of Exo-miR-125b-5p mimic on the biological functions of OC was evaluated through cell proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis assays. The targeting relationship between miR-125b-5p and DEAD-box helicase 5 (DDX5) was verified, and the expression levels of DDX5 in OC samples and SKOV3 cells were quantified using western blotting. miR-125b-5p was downregulated in tumor tissue samples from patients with OC. BMSCs-Exo reduced the malignant properties of SKOV3 cells in vitro, and these effects were be advanced by miR-125b-5p upregulation. miR-125b-5p targeted and inhibited DDX5 expression. DDX5 overexpression inhibited Exo-miR-125b-5p-induced suppression of OC development. Overall, this study highlights that BMSCs-Exo-encapsulated miR-125b-5p inhibited OC progression via DDX5 downregulation, providing insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying OC.
Copyright: © 2025 Wang et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Preprint on Research Square on 10 January 2025 by Mata, E., Broset, E., et al.
Abstract mRNA vaccines have shown great efficacy against SARS-CoV-2, yet challenges remain in optimizing vaccine components to achieve enhanced immune response and vaccine stability. In this study, we developed CPVax-CoV, a new lyophilized mRNA vaccine that features novel thiolactone-based ionizable lipids and newly designed untranslated regions (UTRs) for enhanced expression. Incorporation of these optimized components into our vaccine candidate CPVax-CoV significantly improved immune responses in mice compared to commercially available mRNA vaccines. Moreover, lyophilized CPVax-CoV has proven to be thermostable, maintaining its biological activity for up to one year at 4°C and 25°C after lyophilization, overcoming the cold-chain limitations of current mRNA vaccines. This vaccine demonstrates protective efficacy against ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and Omicron XBB variant, offering a scalable solution for global distribution and pandemic preparedness. These findings underscore the potential of this platform for future next-generation mRNA vaccine development.
-
COVID-19
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Macrophage CD5L is a target for cancer immunotherapy.
In EBioMedicine on 1 May 2023 by Sanchez-Moral, L., Paul, T., et al.
Reprogramming of immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) presents an attractive therapeutic strategy in cancer. The aim of this study was to explore the role of macrophage CD5L protein in TAM activity and assess its potential as a therapeutic target.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against recombinant CD5L were raised by subcutaneous immunization of BALB/c mice. Peripheral blood monocytes were isolated from healthy donors and stimulated with IFN/LPS, IL4, IL10, and conditioned medium (CM) from different cancer cell lines in the presence of anti-CD5L mAb or controls. Subsequently, phenotypic markers, including CD5L, were quantified by flow cytometry, IF and RT-qPCR. Macrophage CD5L protein expression was studied in 55 human papillary lung adenocarcinoma (PAC) samples by IHC and IF. Anti-CD5L mAb and isotype control were administered intraperitoneally into a syngeneic Lewis Lung Carcinoma mouse model and tumor growth was measured. Tumor microenvironment (TME) changes were determined by flow cytometry, IHC, IF, Luminex, RNAseq and RT-qPCR.
Cancer cell lines CM induced an immunosuppressive phenotype (increase in CD163, CD206, MERTK, VEGF and CD5L) in cultured macrophages. Accordingly, high TAM expression of CD5L in PAC was associated with poor patient outcome (Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test p = 0.02). We raised a new anti-CD5L mAb that blocked the immunosuppressive phenotype of macrophages in vitro. Its administration in vivo inhibited tumor progression of lung cancer by altering the intratumoral myeloid cell population profile and CD4+ T-cell exhaustion phenotype, thereby significantly modifying the TME and increasing the inflammatory milieu.
CD5L protein plays a key function in modulating the activity of macrophages and their interactions within the TME, which supports its role as a therapeutic target in cancer immunotherapy.
For a full list of funding bodies, please see the Acknowledgements.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
ICC-IF
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Elevated Interleukin-37 Associated with Dengue Viral Load in Patients with Dengue Fever.
In Current Microbiology on 6 April 2023 by Zhang, J. A., Wang, J. J., et al.
Dengue remains a public health issue worldwide. Similar to chronic infectious diseases, stimulation of cytokine production is not enough to drive immune effector cells for effective virus clearance. One possible mechanism is the virus induces a large number of negative stimulatory cytokines inhibiting immune response. Interleukin 37 (IL-37) plays a crucial regulatory role in infection and immunity, inhibits innate and adaptive immunity as an anti-inflammatory cytokine by inhibiting proinflammatory mediators and pathways. To date, there are few studies reporting correlations between dengue fever (DF) and IL-37. In this study we found that the serum IL-37b and IL-37b-producing monocytes in patients were significantly increased in DF patients. A majority of the IL-37b produced by DF patients was produced by monocytes, not lymphocytes. Increased levels of IL-6, IL-10, and IFN-α were also found in DF patients. However, we failed to detect IL-1β, IL-17A and TNF-α in plasma, because of off-target. In our study, there was no relation between IL-6, IL-10, and IFN-α expressions and IL-37b in serum (P > 0.05). The IL-37b-producing monocytes were negatively correlated with the level of IFN-α in serum and platelet count, and positively correlated with lymphocytes percentage (P < 0.05, respectively). Additionally, serum DENV nonstructural protein 1 levels were positively correlated with monocytes percentages (P < 0.05). Our data represents findings for IL-37b expression and its potential mechanisms in DF patients' immune response.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 22 October 2022 by Gerwinn, T., Salemi, S., et al.
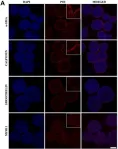
Fig.2.A

-
IHC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Cell Dev Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 22 October 2022 by Gerwinn, T., Salemi, S., et al.
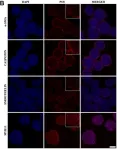
Fig.2.B

-
IHC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Cell Dev Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 22 October 2022 by Gerwinn, T., Salemi, S., et al.
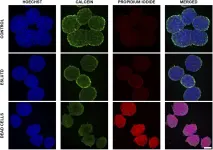
Fig.1.A

-
IHC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Cell Dev Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3