HIV-1 Nef enhances virus propagation by down-regulating CD4 and SERINC5. However, recent evidence points to the existence of an additional Nef-sensitive restriction mechanism. We now show that Nef suppresses the aberrant cleavage of HIV-1 gp41 by ADAM10, a virion-associated cellular ectodomain sheddase, and thus increases the amount of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env) on virions. Additionally, Nef inhibits the shedding of at least some cellular ADAM10 substrates, resulting in their accumulation on HIV-1 virions. Whereas Nef+ HIV-1 replicated only marginally better in the absence of ADAM10, the propagation of Nef- HIV-1 was notably rescued in ADAM10- T cell lines. Crucially, Nef- HIV-1 also benefited from the absence of ADAM10 in primary CD4+ T cells. Collectively, our results indicate that ADAM10 negatively affects both laboratory-adapted and primary HIV-1 strains by shedding the ectodomains of viral and cellular transmembrane proteins from virions and that Nef rescues virus replication by counteracting ADAM10.
Product Citations: 64
The ectodomain sheddase ADAM10 restricts HIV-1 propagation and is counteracted by Nef.
In Science Advances on 18 April 2025 by Olety, B., Usami, Y., et al.
Efficient Genome Editing Using 'NanoMEDIC' AsCas12a-VLPs Produced with Pol II-Transcribed crRNA.
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 27 November 2024 by Borovikova, S. E., Shepelev, M., et al.
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are an attractive vehicle for the delivery of Cas nuclease and guide RNA ribonucleoprotein complexes (RNPs). Most VLPs are produced by packaging SpCas9 and its sgRNA, which is expressed from the RNA polymerase III (Pol III)-transcribed U6 promoter. VLPs assemble in the cytoplasm, but U6-driven sgRNA is localized in the nucleus, which hinders the efficient formation and packaging of RNPs into VLPs. In this study, using the nuclease packaging mechanism of 'NanoMEDIC' VLPs, we produced VLPs with AsCas12a and exploited its ability to process pre-crRNA. This allowed us to direct crRNA in the cytoplasm as part of a Pol II-driven transcript where AsCas12a excised mature crRNA, thus boosting RNP incorporation into VLPs. CMV-driven crRNA increased Venus and CCR5 transgene knockout levels in 293 cells from 30% to 50-90% and raised the level of endogenous CXCR4 knockout in Jurkat T cells from 1% to 20%. Changing a single crRNA to an array of three or six identical crRNAs improved CXCR4 knockout rates by up to 60-70%. Compared to SpCas9-VLPs, the editing efficiencies of AsCas12a-VLPs were higher, regardless of promoter usage. Thus, we showed that AsCas12a and CMV-driven crRNA could be efficiently packaged into VLPs and mediate high levels of gene editing. AsCas12a-VLPs are a new and promising tool for the delivery of RNPs into mammalian cells that will allow efficient target genome editing and may be useful for gene therapy applications.
Single-molecule and super-resolved imaging deciphers membrane behavior of onco-immunogenic CCR5.
In IScience on 22 December 2022 by Hunter, P., Payne-Dwyer, A. L., et al.
The ability of tumors to establish a pro-tumorigenic microenvironment is an important point of investigation in the search for new therapeutics. Tumors form microenvironments in part by the "education" of immune cells attracted via chemotactic axes such as that of CCR5-CCL5. Further, CCR5 upregulation by cancer cells, coupled with its association with pro-tumorigenic features such as drug resistance and metastasis, has suggested CCR5 as a therapeutic target. However, with several conformational "pools" being reported, phenotypic investigations must be capable of unveiling conformational heterogeneity. Addressing this challenge, we performed super-resolution structured illumination microscopy (SIM) and single molecule partially TIRF-coupled HILO (PaTCH) microscopy of CCR5 in fixed cells. SIM data revealed a non-random spatial distribution of CCR5 assemblies, while Intensity-tracking of CCR5 assemblies from PaTCH images indicated dimeric sub-units independent of CCL5 perturbation. These biophysical methods can provide important insights into the structure and function of onco-immunogenic receptors and many other biomolecules.© 2022 The Author(s).
In Journal of Translational Medicine on 24 January 2022 by Weichseldorfer, M., Tagaya, Y., et al.
The chemokine receptor CCR5 is the major coreceptor for HIV-1 cell entry. We previously observed that not all CCR5 mAbs reduce HIV-1 infection, suggesting that only some CCR5 populations are permissive for HIV-1 entry. This study aims to better understand the relevant conformational states of the cellular coreceptor, CCR5, involved in HIV entry. We hypothesized that CCR5 assumes multiple configurations during normal cycling on the plasma membrane, but only particular forms facilitate HIV-1 infection.
To this end, we quantified different CCR5 populations using six CCR5 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) with different epitope specificities and visualized them with super-resolution microscopy. We quantified each surface CCR5 population before and after HIV-1 infection.
Based on CCR5 conformational changes, down-modulation, and trafficking rates (internalization and recycling kinetics), we were able to distinguish among heterogeneous CCR5 populations and thus which populations might best be targeted to inhibit HIV-1 entry. We assume that a decreased surface presence of a particular CCR5 subpopulation following infection means that it has been internalized due to HIV-1 entry, and that it therefore represents a highly relevant target for future antiviral therapy strategies. Strikingly, this was most true for antibody CTC8, which targets the N-terminal region of CCR5 and blocks viral entry more efficiently than it blocks chemokine binding.
Defining the virus-host interactions responsible for HIV-1 transmission, including specific coreceptor populations capable of establishing de novo infections, is essential for the development of an HIV-1 vaccine. This study hopefully will facilitate further development of inhibitors to block CCR5 usage by HIV-1, as well as inform future HIV-1 vaccine design.
© 2022. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
A cell-based multiplex immunoassay platform using fluorescent protein-barcoded reporter cell lines.
In Communications Biology on 25 November 2021 by Song, S., Manook, M., et al.
Multiplex immunoassays with acellular antigens are well-established based on solid-phase platforms such as the Luminex® technology. Cell barcoding by amine-reactive fluorescent dyes enables analogous cell-based multiplex assays, but requires multiple labeling reactions and quality checks prior to every assay. Here we describe generation of stable, fluorescent protein-barcoded reporter cell lines suitable for multiplex screening of antibody to membrane proteins. The utility of this cell-based system, with the potential of a 256-plex cell panel, is demonstrated by flow cytometry deconvolution of barcoded cell panels expressing influenza A hemagglutinin trimers, or native human CCR2 or CCR5 multi-span proteins and their epitope-defining mutants. This platform will prove useful for characterizing immunity and discovering antibodies to membrane-associated proteins.
© 2021. The Author(s).
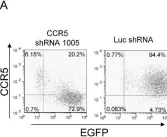
In Genet Vaccines Ther on 10 June 2009 by Shimizu, S., Kamata, M., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Genet Vaccines Ther by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1