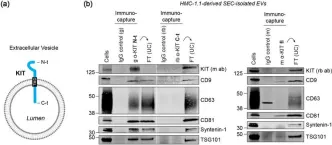
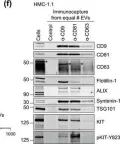
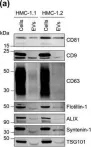
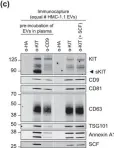
Tumour-derived extracellular vesicles (TEVs) play a crucial role in cancer progression, metastasis and therapy resistance but their distinct profiles across different cancer stages and molecular subtypes remain underexplored. This study initially analysed TEVs from all CMS subtypes in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells and continued focusing on the epithelial (CMS2) and mesenchymal (CMS4) subtypes using six cell lines and clinical samples. Investigation of the cargo of vesicles secreted by the two subtypes revealed significant differences in mRNA, miRNA, and protein profiles between the two subtypes. Notably, CMS2 predominantly secreted smaller, Tetraspanin-8 (TSPAN8) enriched EVs, while CMS4 produced both larger and smaller EVs, enriched in TSPAN4. This underscores the complexity of vesicle heterogeneity between these subtypes. Additionally, we assessed miRNA profiles from plasma-derived bulk TEVs in CRC patients. Our integrative analysis identified a subtype-specific miRNA signature, indicating that TEVs from CMS2 and CMS4 cells can be detected in circulation and may serve as potential diagnostic tool for CRC.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Product Citations: 354
In Journal of Extracellular Vesicles on 1 November 2025 by Asif, P. J., Borghuis, L., et al.
In Haematologica on 1 November 2025 by Ammeti, D., Barozzi, S., et al.
Endosome transcriptomics reveal trafficking of Cajal bodies into multivesicular bodies.
In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on 14 October 2025 by Singh, J., Williams, J. K., et al.
All eukaryotic cells secrete exosomes, a type of extracellular vesicles derived from the endocytic compartments known as multivesicular bodies (MVBs), or late endosomes (LEs). Exosomes contain a diverse range of cargo such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and small molecules but whether these contents have a biological function remains an area of intense investigation. Over the last decade, numerous studies have described the transcriptome of exosomes but very little is known about the RNA content of the MVBs, the source compartment for exosome biogenesis. Here, we determine the small-RNA transcriptome of highly purified MVBs and report that various classes of nuclear small regulatory RNAs such as small-Cajal body associated RNAs, small-nucleolar RNAs, and small-nuclear RNAs traffic to MVBs. We show that this RNA-trafficking requires the function of endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) machinery but is independent of canonical LC3 lipidation mediated selective autophagy. Furthermore, blocking the activity of a PI3K Class 3 enzyme, VPS34, required for recruitment of the ESCRT machinery to the endosome, prevents the turnover of these nuclear RNAs in MVBs. Our results provide a mechanism for targeting nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes, such as Cajal bodies, for degradation and turnover by the cytoplasmic endo-lysosomal pathway.
-
WB
-
Cell Biology
In eLife on 30 September 2025 by Kapustin, A. N., Tsakali, S. S., et al.
The extracellular matrix (ECM) supports blood vessel architecture and functionality and undergoes active remodelling during vascular repair and atherogenesis. Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are essential for vessel repair and, via their secretome, can invade from the vessel media into the intima to mediate ECM remodelling. Accumulation of fibronectin (FN) is a hallmark of early vascular repair and atherosclerosis. Here, we show that FN stimulates human VSMCs to secrete small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) by activating the β1 integrin/FAK/Src pathway as well as Arp2/3-dependent branching of the actin cytoskeleton. We found that sEVs are trapped by the ECM in vitro and colocalise with FN in symptomatic atherosclerotic plaques in vivo. Functionally, ECM-trapped sEVs induced the formation of focal adhesions (FA) with enhanced pulling forces at the cellular periphery preventing cellular spreading and adhesion. Proteomic and GO pathway analysis revealed that VSMC-derived sEVs display a cell adhesion signature and are specifically enriched with collagen VI on the sEV surface. In vitro assays identified collagen VI as playing a key role in cell adhesion and invasion directionality. Taken together, our data suggests that the accumulation of FN is a key early event in vessel repair acting to promote secretion of collagen VI enriched sEVs by VSMCs. These sEVs stimulate directional invasion, most likely by triggering peripheral focal adhesion formation and actomyosin contraction to exert sufficient traction force to enable VSMC movement within the complex vascular ECM network.
© 2023, Kapustin et al.
In Nature Communications on 30 September 2025 by LeBleu, V. S., Smaglo, B., et al.
Oncogenic KRAS is amongst the key genetic drivers for initiation and maintenance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Here, we show that engineered exosomes with KrasG12D specific siRNA (iExoKrasG12D) reveal a biodistribution in pancreas with negligible toxicity in preclinical studies in mice and Rhesus macaques. Clinical testing of iExoKrasG12D in the iEXPLORE (iExoKrasG12D in Pancreatic Cancer) Phase I study employed a non-randomized single-arm classical 3 + 3 dose escalation design (Phase Ia), followed by an accelerated titration design (Phase Ib) (NCT03608631). The primary outcomes included safety, tolerability and target engagement, and the secondary outcomes aimed to assess disease control. Patients with advanced metastatic disease were enrolled after failure of multiple lines of therapy. iExoKrasG12D therapy was well-tolerated: the primary outcomes were met with iExoKrasG12D showing no dose-limiting toxicity. The maximum tolerated dose was not reached even at the highest dose. In some cases, iExoKrasG12D therapy was associated with stable disease response (secondary outcome). Downregulation of KRASG12D DNA and suppression of phospho-Erk was documented together with an increase in intratumoral CD8+ T cells following treatment. The CD8+ T cell recruitment priming by iExoKrasG12D informed on potential efficacy of immune checkpoint therapy and lead to validation testing in preclinical PDAC models. Combination therapy of iExoKrasG12D and anti-CTLA-4 antibodies, but not anti-PD1, revealed robust pre-clinical anti-tumor efficacy via FAS mediated CD8+ T cell anti-tumor activity. This first-in-human, precision medicine clinical trial and supporting preclinical functional studies offer new insights into priming of immunotherapy by oncogenic Kras inhibitor for future opportunistic combination therapy for PDAC patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
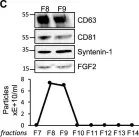
In Front Mol Biosci on 16 October 2024 by Evalt, E. D., Govindaraj, S., et al.
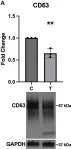
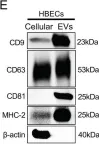
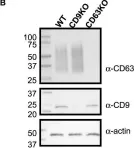
Fig.4.A
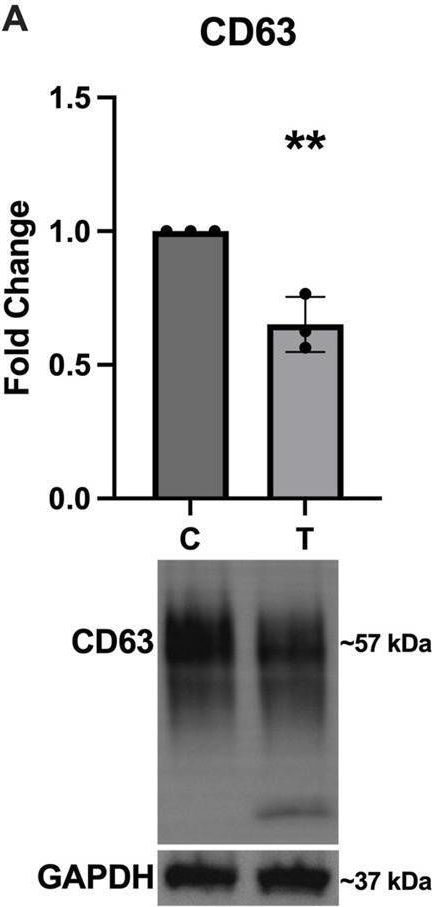
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
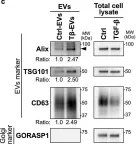
In Front Mol Biosci on 16 October 2024 by Evalt, E. D., Govindaraj, S., et al.
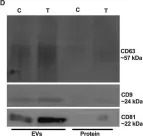
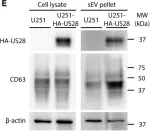
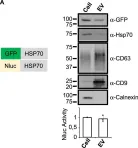
Fig.3.D
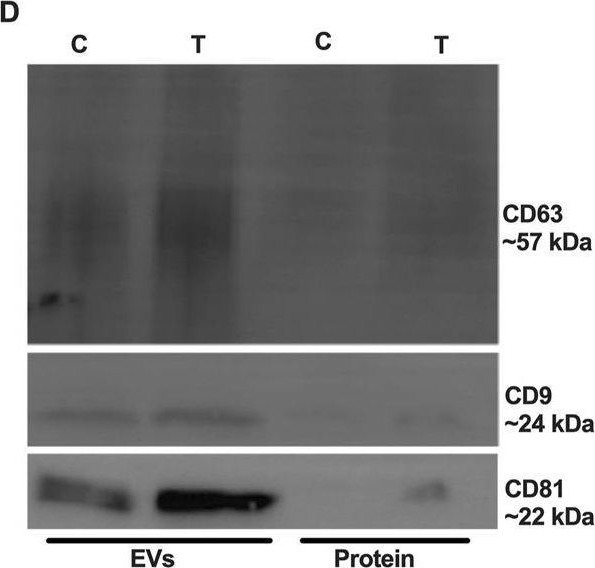
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
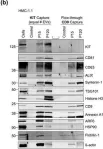
In Int J Mol Sci on 25 July 2024 by Saari, H., Marttila, H., et al.
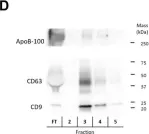
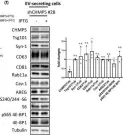
Fig.2.D
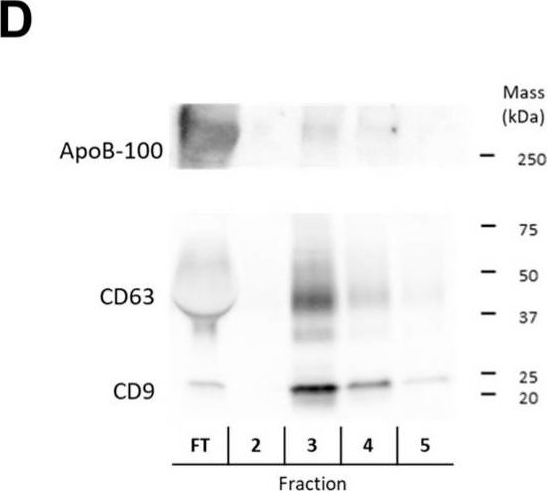
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from International Journal of Molecular Sciences by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
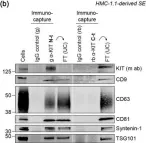
In Int J Mol Sci on 25 July 2024 by Saari, H., Marttila, H., et al.
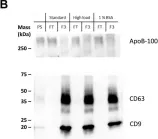
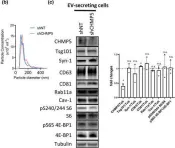
Fig.3.B
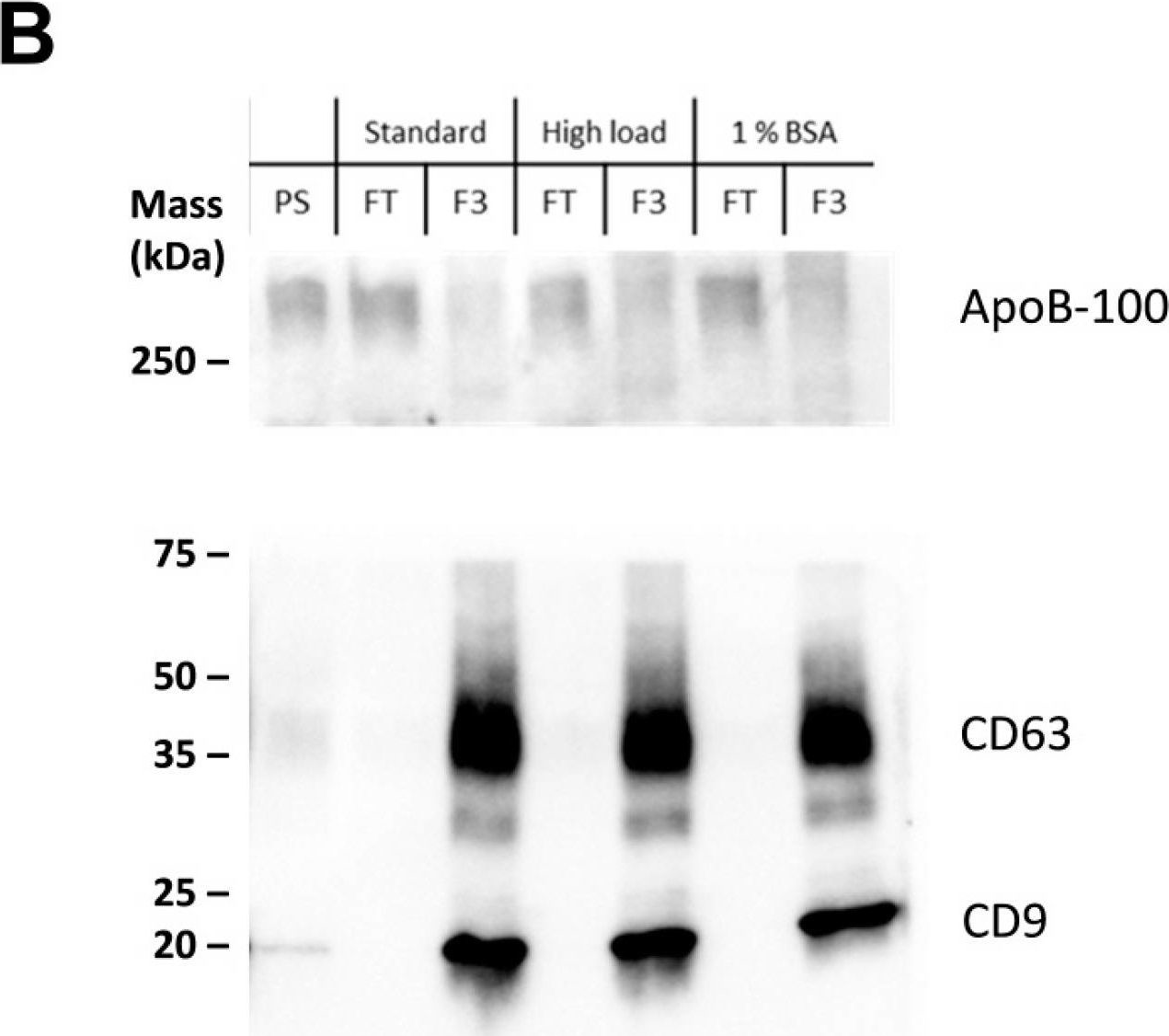
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from International Journal of Molecular Sciences by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In Commun Biol on 6 May 2024 by Fujita, Y., Kadota, T., et al.
Fig.1.E
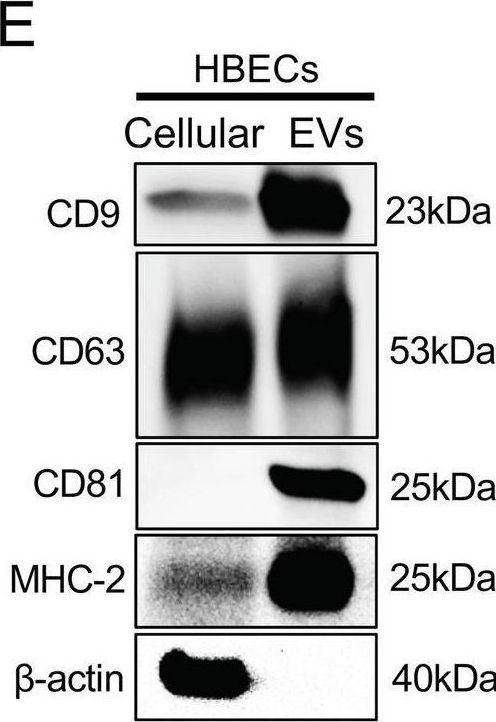
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Communications Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In iScience on 18 August 2023 by Bebelman, M. P., Setiawan, I. M., et al.
Fig.2.E
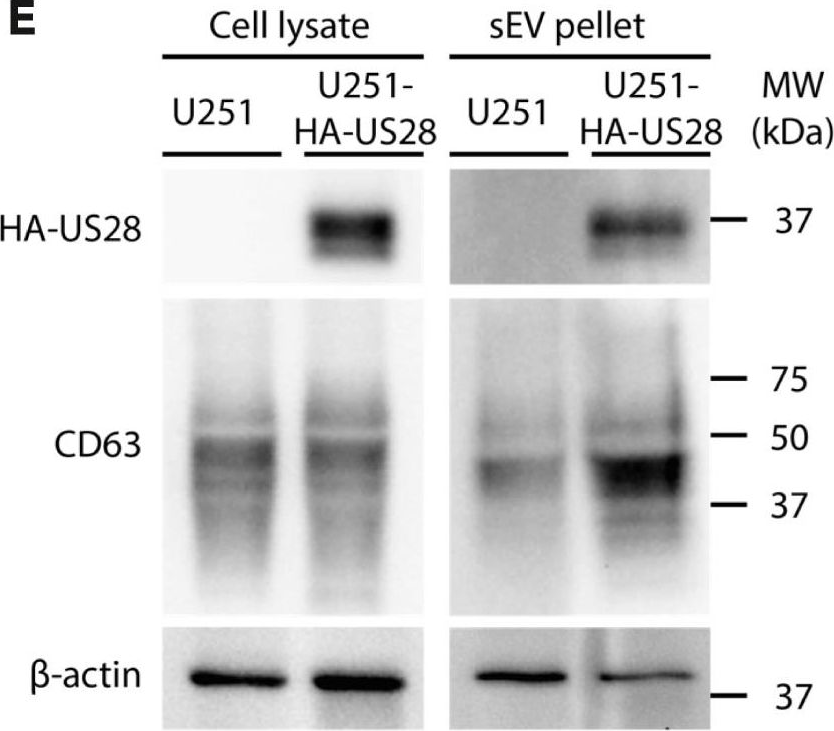
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from IScience by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
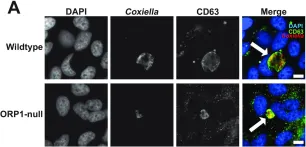
In mSphere on 22 June 2023 by Schuler, B., Sladek, M., et al.
Fig.2.A
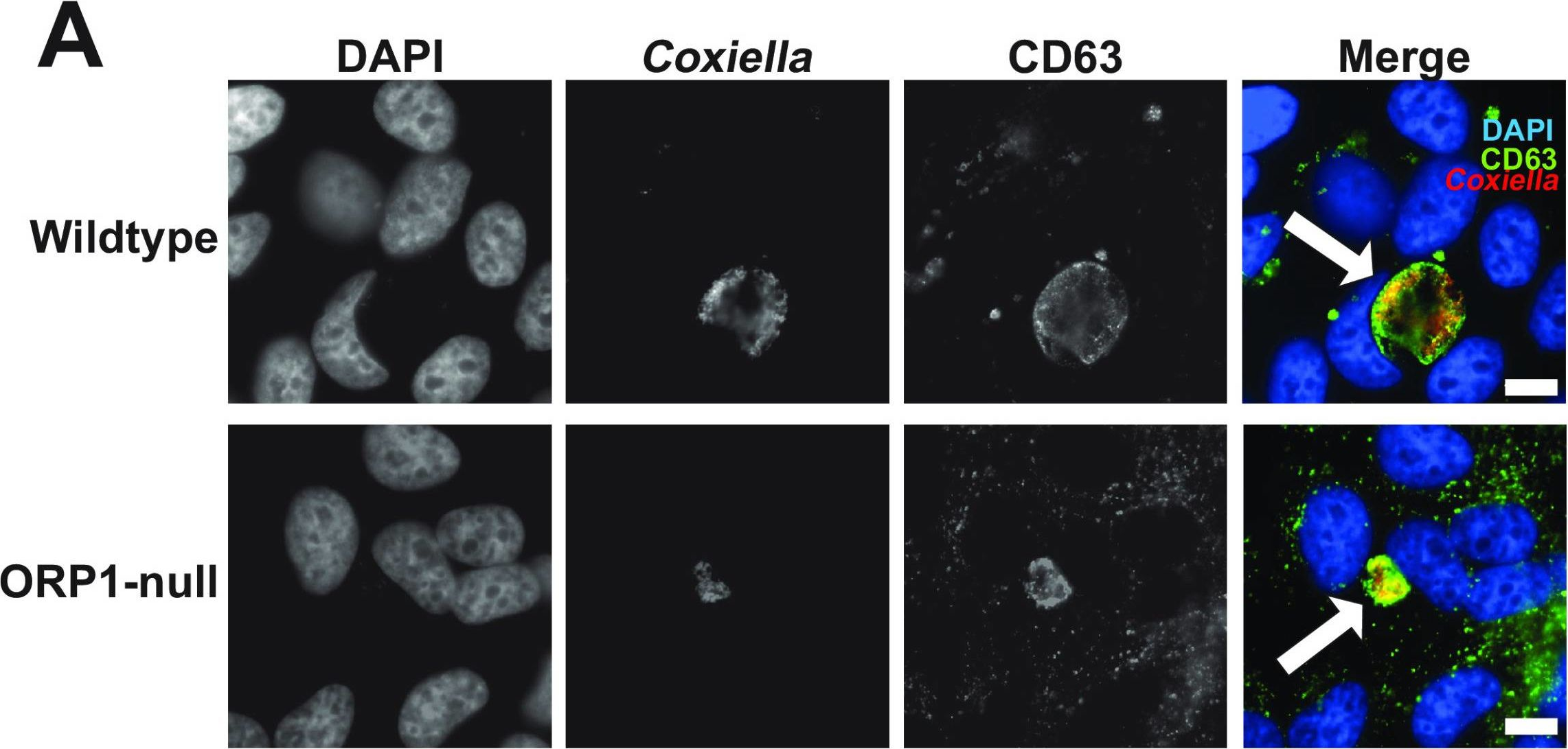
-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from MSphere by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
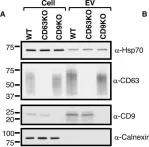
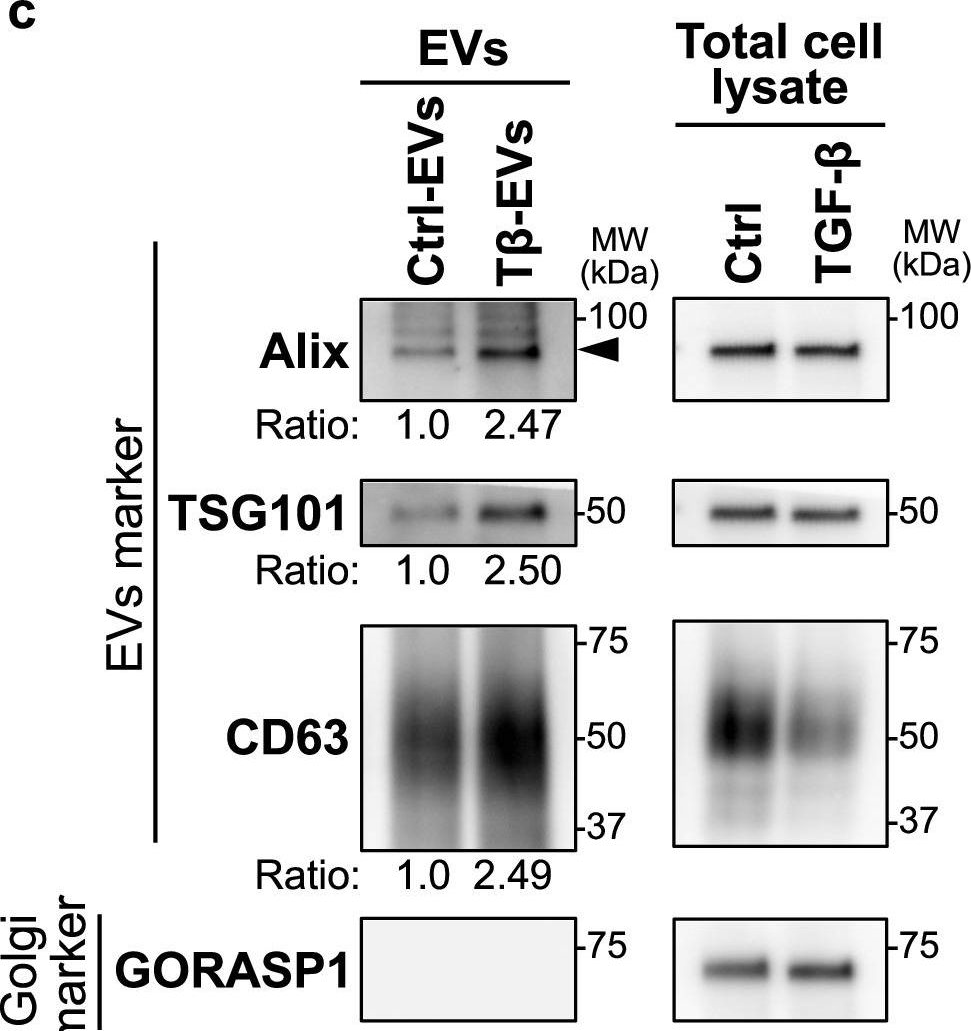
In Commun Biol on 17 May 2023 by Tognoli, M. L., Dancourt, J., et al.
Fig.2.A
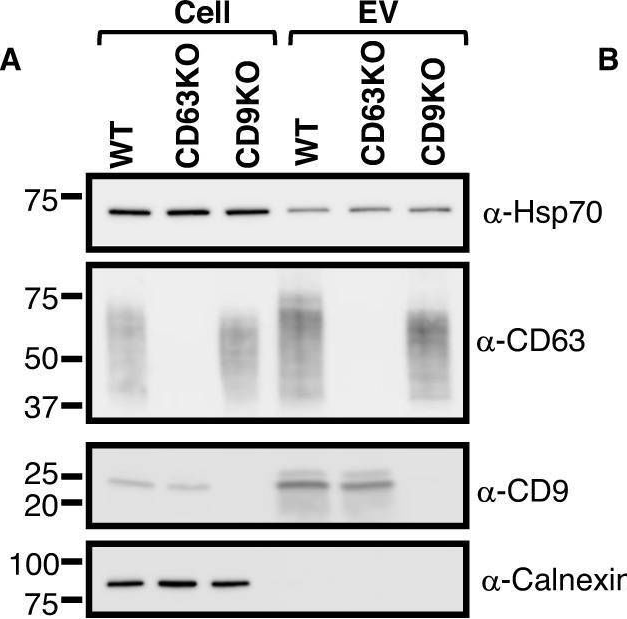
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Communications Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In Commun Biol on 17 May 2023 by Tognoli, M. L., Dancourt, J., et al.
Fig.1.B
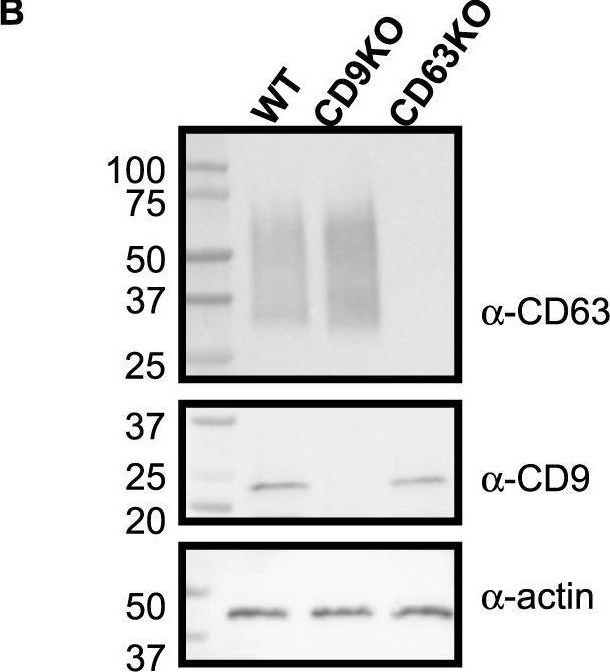
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Communications Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In Commun Biol on 17 May 2023 by Tognoli, M. L., Dancourt, J., et al.
Fig.1.A
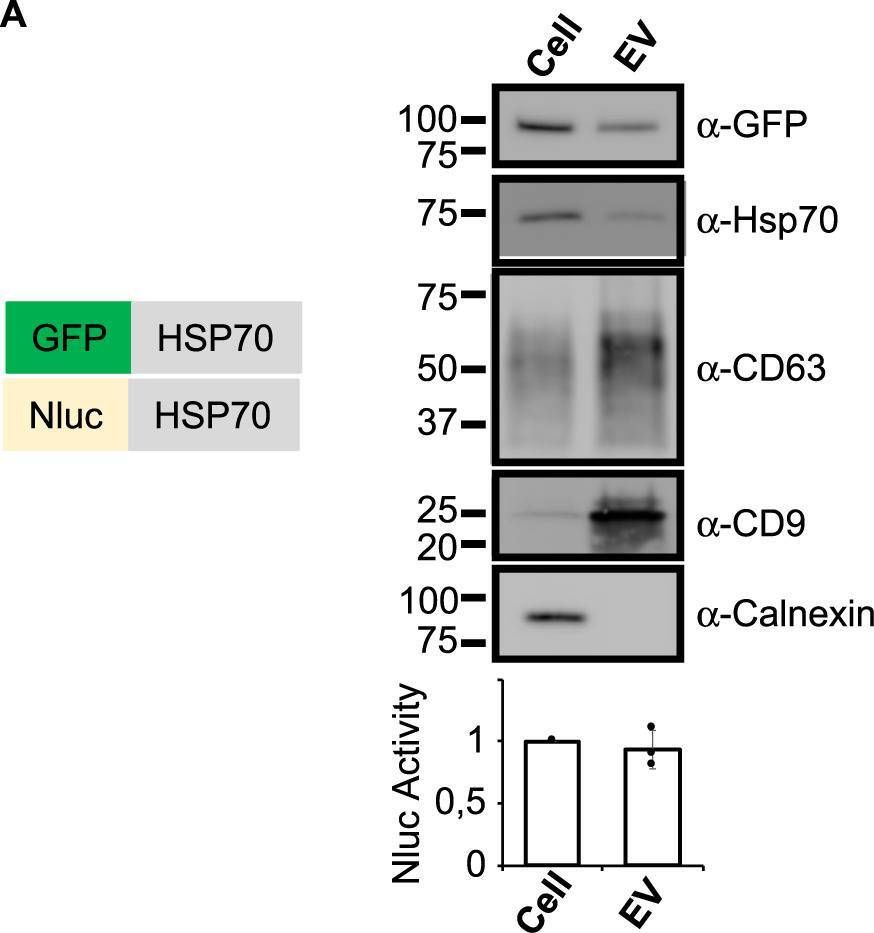
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Communications Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
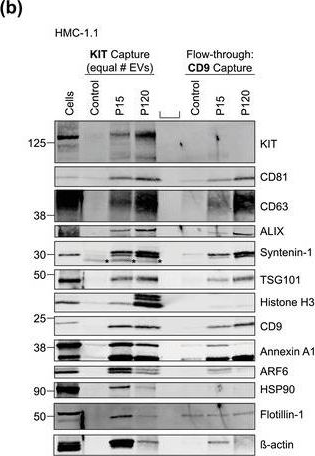
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 March 2023 by Marie, P. P., Fan, S. J., et al.
Fig.6.D
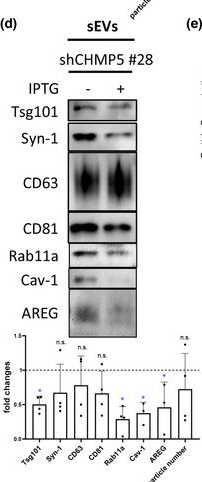
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 March 2023 by Marie, P. P., Fan, S. J., et al.
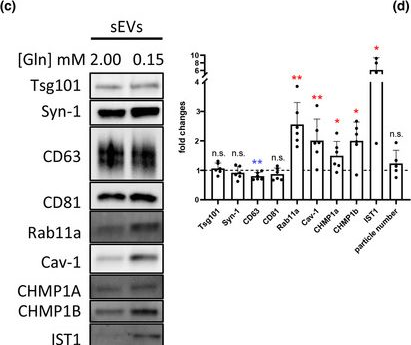
Fig.6.F
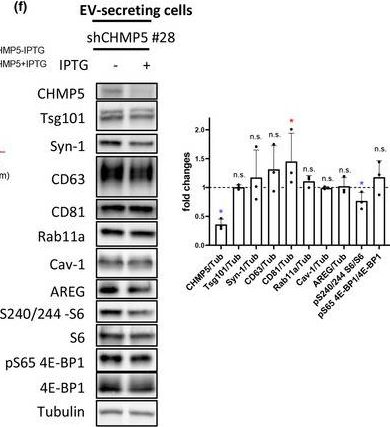
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 March 2023 by Marie, P. P., Fan, S. J., et al.
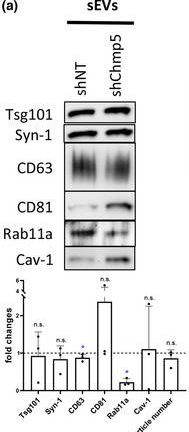
Fig.6.B
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 March 2023 by Marie, P. P., Fan, S. J., et al.
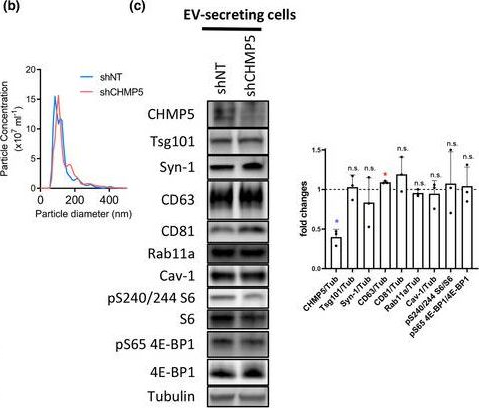
Fig.6.A
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 March 2023 by Marie, P. P., Fan, S. J., et al.
Fig.1.C
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In Blood Cancer Discov on 6 January 2023 by Gargiulo, E., Viry, E., et al.
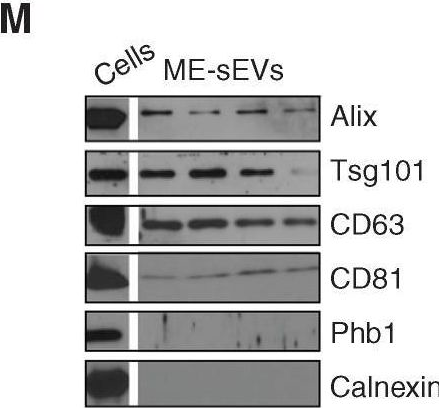
Fig.1.M
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Blood Cancer Discovery by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In Sci Rep on 22 December 2022 by Petit, I., Levy, A., et al.
Fig.1.A
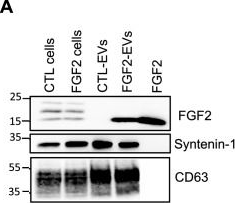
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Scientific Reports by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In Sci Rep on 22 December 2022 by Petit, I., Levy, A., et al.
Fig.1.C
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Scientific Reports by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In Inflamm Regen on 4 September 2022 by Kobayashi, M., Fujiwara, K., et al.
Fig.2.C
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Inflammation and Regeneration by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
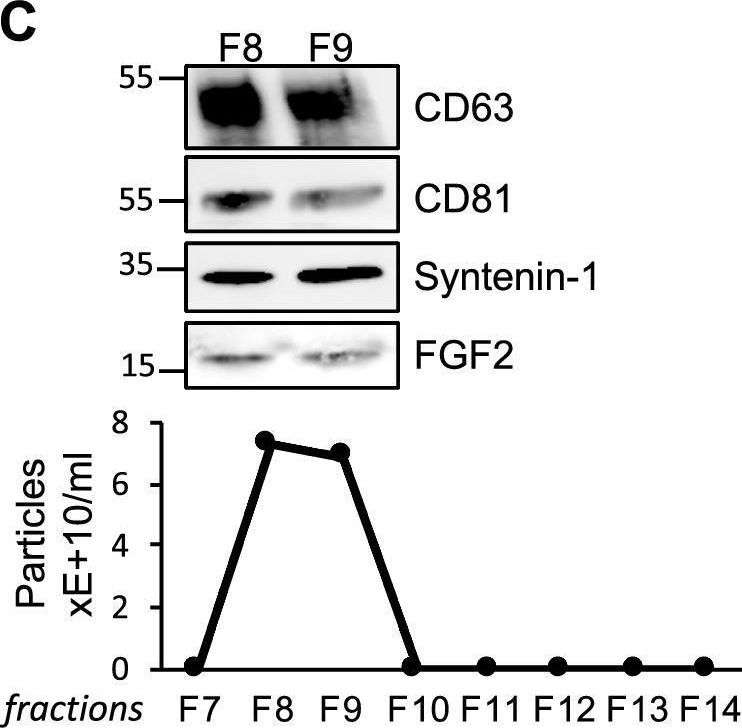
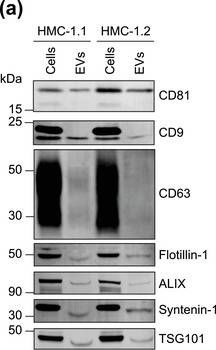
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.5.B
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.2.B
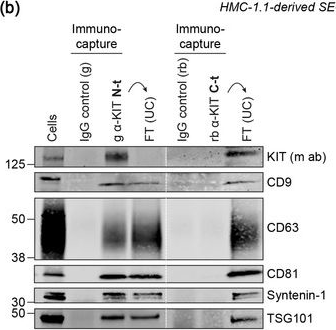
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.2.A
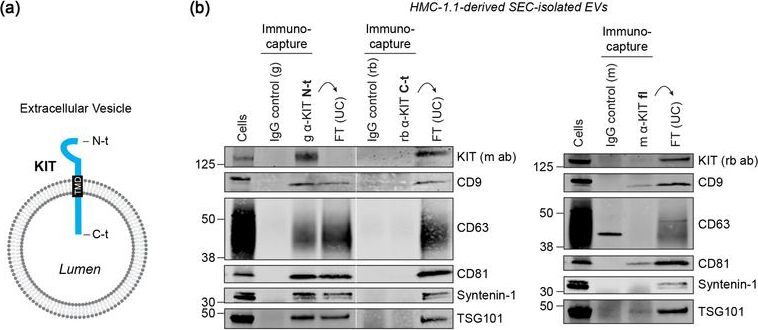
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.1.F
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.1.A
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94
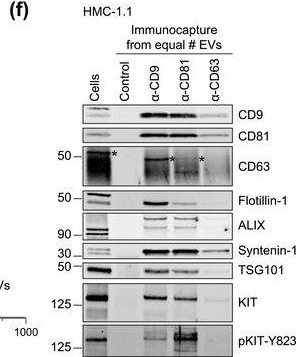
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.8.C
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Journal of Extracellular Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 94