In vitro human liver models are critical to mitigate species-specific differences observed for toxicology, disease modeling, and regenerative medicine. Interactions with mesenchyme (i.e., fibroblasts) can promote phenotypic functions of primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) in culture; however, using liver-derived fibroblasts remains elusive. Portal fibroblasts (PFs) around the portal triad influence bile duct formation during development, but their role in regulating homeostatic hepatic functions remains unknown. Here, we show that human liver PFs induce long-term phenotypic functions in PHHs at higher levels than activated hepatic stellate cells across 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional culture formats. While PF-conditioned media induces some hepatic functions, partly via insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 signaling, direct contact is necessary to induce optimal functional levels. Inhibiting Notch signaling reduces progenitor-like characteristics of PHHs and further enhances functionality. Overall, this work demonstrates a unique role for PFs in modulating hepatic functions and provides all-human and all-liver coculture strategies for downstream applications.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 30
Liver portal fibroblasts induce the functions of primary human hepatocytes in vitro.
In Communications Biology on 9 May 2025 by Brown, G. E., Bodke, V. V., et al.
-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Toxicology in Vitro : An International Journal Published in Association With BIBRA on 1 December 2022 by Kato, Y., Lim, A. Y., et al.
Establishing the functionality, reproducibility, robustness, and reliability of microphysiological systems is a critical need for adoption of these technologies. A high throughput microphysiological system for liver studies was recently proposed in which induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes (iHeps) and non-parenchymal cells (endothelial cells and THP-1 cells differentiated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate into macrophage-like cells) were co-cultured in OrganoPlate® 2-lane 96 devices. The goal of this study was to evaluate this platform using additional cell types and conditions and characterize its utility and reproducibility. Primary human hepatocytes or iHeps, with and without non-parenchymal cells, were cultured for up to 17 days. Image-based cell viability, albumin and urea secretion into culture media, CYP3A4 activity and drug metabolism were assessed. The iHeps co-cultured with non-parenchymal cells demonstrated stable cell viability and function up to 17 days; however, variability was appreciable both within and among studies. The iHeps in monoculture did not form clusters and lost viability and function over time. The primary human hepatocytes in monoculture also exhibited low cell viability and hepatic function. Metabolism of various drugs was most efficient when iHeps were co-cultured with non-parenchymal cells. Overall, we found that the OrganoPlate® 2-lane 96 device, when used with iHeps and non-parenchymal cells, is a functional liver microphysiological model; however, the high-throughput nature of this model is somewhat dampened by the need for replicates to compensate for high variability.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Cancers on 18 July 2022 by Kim, D., Kim, J. S., et al.
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) reside within the tumor microenvironment, facilitating cancer progression and metastasis via direct and indirect interactions with cancer cells and other stromal cell types. CAFs are composed of heterogeneous subpopulations of activated fibroblasts, including myofibroblastic, inflammatory, and immunosuppressive CAFs. In this study, we sought to identify subpopulations of CAFs isolated from human lung adenocarcinomas and describe their transcriptomic and functional characteristics through single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and subsequent bioinformatics analyses. Cell trajectory analysis of combined total and THY1 + CAFs revealed two branching points with five distinct branches. Based on Gene Ontology analysis, we denoted Branch 1 as "immunosuppressive", Branch 2 as "neoantigen presenting", Branch 4 as "myofibroblastic", and Branch 5 as "proliferative" CAFs. We selected representative branch-specific markers and measured their expression levels in total and THY1 + CAFs. We also investigated the effects of these markers on CAF activity under coculture with lung cancer cells. This study describes novel subpopulations of CAFs in lung adenocarcinoma, highlighting their potential value as therapeutic targets.
-
Cancer Research
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 19 March 2022 by Watanabe, F., Hollingsworth, E. W., et al.
The intrinsic genetic program of glioblastoma (GBM) stem cells is critical for tumor evolution and recurrence. We recently identified intrinsic phenotypes and immune-like genetic programs of GBM organoids (GBMO) 1 from patient derived glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs), replicating genomic, metabolic, and cellular aspects of GBM in vivo . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), a ligand-activated transcription factor, is a key regulator of infiltrating immune cells in gliomas 2, 3 and associated with poor prognosis, but its role in GSC biology is unknown 2 . Here, we show that AHR is a patient-specific regulator of the glioma intrinsic gene program in GSCs and GSC-derived GBMO that are enriched for AHR. We find that AHR is required for GSC self-renewal, GBMO expansion, radial glia-like cell proliferation, and expression of immune mediators seen in the mesenchymal subtype. CRISPR-Cas9 genetic ablation and pharmacological inhibition revealed that AHR regulates genes linked to intrinsic immunity, proliferation, and migration in GBMO. Genomic analysis of GBMO treated with AHR inhibitors identified expression signatures and candidate markers associated with survival of gliomas. Our work defines the glioma intrinsic function of AHR in a model of early GBM formation, offering a rationale for clinical exploration of a potential ‘two-hit’ target of both GBM cells and infiltrating immune cells in patients with GBM expressing high levels of AHR.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 9 October 2021 by Watanabe, F., Hollingsworth, E. W., et al.
h4>Summary/h4> Glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) are highly self-renewing, resistant to therapy, and are able to form lethal tumors 1, 2 . Tumor organoids have been developed to study tumor evolution 1–4 , and while GSCs can form organoids for glioblastoma multiforme, our understanding of their intrinsic immune, metabolic, genetic, and molecular programs is limited. To address this, we deeply characterized GSC-derived GBM organoids using a modified protocol (GBMOsm) from several patient-derived GSCs and found they develop into complex 3D tissues with unique self-organization, cancerous metabolic states, and burdensome genetic landscapes. We discovered that GBMOsc recapitulate the presence of two important cell populations thought to drive GBM progression, SATB2 + and HOPX + progenitors. Despite being devoid of immune cells, transcriptomic analysis across GBMOsc revealed an immune-like molecular program, enriched in cytokine, antigen presentation and processing, T-cell receptor inhibitors, and interferon genes. We determined that SATB2 + and HOPX + populations contribute to this immune and interferon landscape in GBM in vivo and GBMOsm. Our work deepens our understanding of the intrinsic molecular and cellular architecture of GSC-derived GBMO and defines a novel GBMOsc intrinsic immune-like program.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
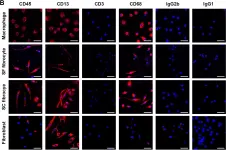
In PLoS One on 23 March 2010 by Curnow, S. J., Fairclough, M., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1