Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by ectopic bone formation. The anti-inflammatory function of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor has been reported in bone metabolism, but its utility in AS has not previously been investigated.
We assessed DPP4 level in serum, synovial fluid, and facet joint tissue of AS patients. Additionally, we investigated the effect of a DPP4 inhibitor in an experimental AS model using curdlan-injected SKG mice. Following curdlan injection, SKG mice were orally administered a DPP4 inhibitor three times per week for 5 weeks and observed clinical arthritis scores, and analyzed by micro-CT. Furthermore, osteoclast precursor cells (OPCs) from curdlan-injected SKG mice were treated with DPP4 inhibitor and evaluated the inhibitory effects of this treatment in vitro.
Soluble DPP4 level was elevated in the serum and synovial fluid of patients with AS compared to those in the control group. Expression of DPP4 increased gradually during human osteoclastogenesis and was high in mature osteoclasts. Oral administration of a DPP4 inhibitor resulted in a decrease in thickness of the hind paw, clinical arthritis scores, and enthesitis at the ankle in curdlan-injected SKG mice compared to the vehicle group. Micro-CT data revealed a significant reduction in inflammation-induced low bone density in the DPP4 inhibitor group. Moreover, treatment with a DPP4 inhibitor significantly reduced osteoclast differentiation of OPC in addition to decreasing expression of osteoclast differentiation markers.
Our findings suggest that inhibiting DPP4 may have a therapeutic effect on inflammation-mediated ectopic bone formation in AS patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 60
In Arthritis Research & Therapy on 25 February 2025 by Lee, S. H., Lee, K. H., et al.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) on 10 February 2025 by Hu, G., Whitaker, A. L., et al.
Glutathione (GSH) is the most abundant antioxidant in the cell, and it is responsible for neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can promote osteoclast differentiation and stimulate bone resorption and are some of the primary drivers of bone loss with aging and loss of sex steroids. Despite this, the role of GSH biosynthesis during osteoclastogenesis remains controversial. Here, we show that the requirements for GSH biosynthesis during osteoclastogenesis in vitro and in vivo are unique. Using a metabolomics approach, we discovered that both oxidative stress and GSH biosynthesis increase during osteoclastogenesis. Inhibiting GSH biosynthesis in vitro via the pharmacological or genetic inhibition of glutamate cysteine ligase (GCLC) prevented osteoclast differentiation. Conversely, the genetic ablation of GCLC in myeloid cells using LysMCre resulted in a decrease in bone mass in both male and female mice. The decreased bone mass of the LysMCre;Gclcfl/fl mice was attributed to increased osteoclast numbers and elevated bone resorption. Collectively, our data provide strong genetic evidence that GSH biosynthesis is essential for the regulation of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in mice. Moreover, these findings highlight the necessity of complementing in vitro studies with in vivo genetic studies.
Cellular signatures in human blood track bone mineral density in postmenopausal women.
In JCI Insight on 22 November 2024 by Kaneko, K., Tsai, J., et al.
Osteoclasts are the sole bone-resorbing cells and are formed by the fusion of osteoclast precursor cells (OCPs) derived from myeloid lineage cells. Animal studies reveal that circulating OCPs (cOCPs) in blood travel to bone and fuse with bone-resident osteoclasts. However, the characteristics of human cOCPs and their association with bone diseases remain elusive. We have identified and characterized human cOCPs and found a positive association between cOCPs and osteoclast activity. Sorted cOCPs have a higher osteoclastogenic potential than other myeloid cells and effectively differentiate into osteoclasts. cOCPs exhibit distinct morphology and transcriptomic signatures. The frequency of cOCPs in the blood varies among treatment-naive postmenopausal women and has an inverse correlation with lumbar spine bone density and a positive correlation with serum CTX, a bone resorption marker. The increased cOCPs in treatment-naive patients with osteoporosis were significantly diminished by denosumab, a widely used antiresorptive therapy. Our study reveals the distinctive identity of human cOCPs and the potential link between the dynamic regulation of cOCPs and osteoporosis and its treatment. Taken together, our study enhances our understanding of human cOCPs and highlights a potential opportunity to measure cOCPs through a simple blood test, which could potentially identify high-risk individuals.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
Glutaminolysis provides nucleotides and amino acids to regulate osteoclast differentiation in mice.
In EMBO Reports on 1 October 2024 by Hu, G., Yu, Y., et al.
Osteoclasts are bone resorbing cells that are essential to maintain skeletal integrity and function. While many of the growth factors and molecular signals that govern osteoclastogenesis are well studied, how the metabolome changes during osteoclastogenesis is unknown. Using a multifaceted approach, we identified a metabolomic signature of osteoclast differentiation consisting of increased amino acid and nucleotide metabolism. Maintenance of the osteoclast metabolic signature is governed by elevated glutaminolysis. Mechanistically, glutaminolysis provides amino acids and nucleotides which are essential for osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in vitro. Genetic experiments in mice found that glutaminolysis is essential for osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vivo. Highlighting the therapeutic implications of these findings, inhibiting glutaminolysis using CB-839 prevented ovariectomy induced bone loss in mice. Collectively, our data provide strong genetic and pharmacological evidence that glutaminolysis is essential to regulate osteoclast metabolism, promote osteoclastogenesis and modulate bone resorption in mice.
© 2024. The Author(s).
In The Journal of Immunology on 1 November 2023 by Ng, C., Qin, Y., et al.
TNF plays a crucial role in inflammation and bone resorption in various inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, its direct ability to drive macrophages to differentiate into osteoclasts is limited. Although RBP-J is recognized as a key inhibitor of TNF-mediated osteoclastogenesis, the precise mechanisms that restrain TNF-induced differentiation of macrophages into osteoclasts are not fully elucidated. In this study, we identified that the Notch ligand Jagged1 is a previously unrecognized RBP-J target. The expression of Jagged1 is significantly induced by TNF mainly through RBP-J. The TNF-induced Jagged1 in turn functions as a feedback inhibitory regulator of TNF-mediated osteoclastogenesis. This feedback inhibition of osteoclastogenesis by Jagged1 does not exist in RANKL-induced mouse osteoclast differentiation, as RANKL does not induce Jagged1 expression. The Jagged1 level in peripheral blood monocytes/osteoclast precursors is decreased in RA compared with the nonerosive inflammatory disease systemic lupus erythematosus, suggesting a mechanism that contributes to increased osteoclast formation in RA. Moreover, recombinant Jagged1 suppresses human inflammatory osteoclastogenesis. Our findings identify Jagged1 as an RBP-J direct target that links TNF and Notch signaling pathways and restrains TNF-mediated osteoclastogenesis. Given that Jagged1 has no effect on TNF-induced expression of inflammatory genes, its use may present a new complementary therapeutic approach to mitigate inflammatory bone loss with little impact on the immune response in disease conditions.
Copyright © 2023 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
-
WB
-
Immunology and Microbiology
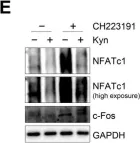
In Front Oncol on 28 March 2023 by Sarabia-Sánchez, M. A., Moreno-Londoño, A. P., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
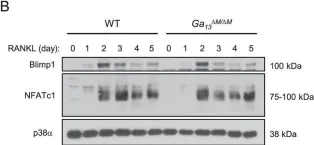
In iScience on 17 March 2023 by Giampaolo, S., Chiarolla, C. M., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from iScience by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
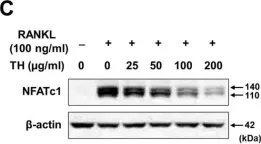
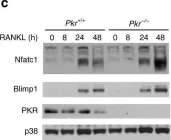
In Nutrients on 18 October 2022 by Heo, J., Kim, M., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nutrients by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
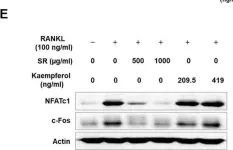
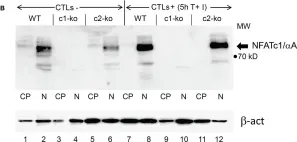
In Front Pharmacol on 22 January 2022 by Lee, S., Kim, M., et al.
Fig.12.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Pharmacol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
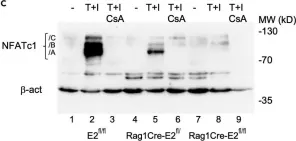
In Cells on 10 December 2021 by Kim, S. Y., Oh, Y., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Cells on 10 December 2021 by Kim, S. Y., Oh, Y., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Cells on 10 December 2021 by Kim, S. Y., Oh, Y., et al.
Fig.6.G

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Cells on 10 December 2021 by Kim, S. Y., Oh, Y., et al.
Fig.6.H

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Cells on 10 December 2021 by Kim, S. Y., Oh, Y., et al.
Fig.6.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Sci Rep on 12 March 2019 by Nakano, S., Inoue, K., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Nat Commun on 5 October 2018 by Inoue, K., Deng, Z., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Front Immunol on 28 June 2018 by Baur, J., Otto, C., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Front Immunol on 28 June 2018 by Baur, J., Otto, C., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In Oncotarget on 15 September 2017 by Chai, R. C., McDonald, M. M., et al.
Fig.3.F

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
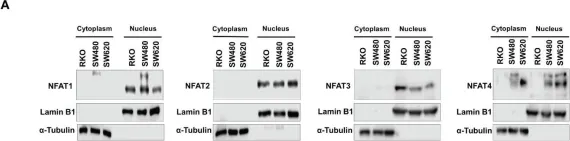
In Nat Commun on 11 September 2017 by Klein-Hessling, S., Muhammad, K., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16
In PLoS One on 21 August 2013 by Khor, E. C., Abel, T., et al.
Fig.8.C

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 16