Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a severe diffuse progressive fibrosing interstitial disease leading to respiratory failure and death in the absence of organ transplantation. Substantial evidence has confirmed the pivotal role of fibroblasts in the progression of IPF, yet effective therapeutic options are scarce. Single-cell transcriptomics profiling revealed that among the diverse fibroblast subsets, FAP1+ alveolar fibroblasts (AFs) are pivotal for the progression of IPF. On the basis of these findings, we developed FAP1-targeting chimeric antigen receptor cytotoxic effector regulatory T (CAR-cTregs) cells, which leverage the targeted killing advantage of the currently trending CAR-based immunotherapy for tumors and incorporate the immunosuppressive functions of Tregs to mitigate the inflammation caused by both the disease itself and CAR-T-cell infusion. Accordingly, CAR-cTregs were constructed to effectively eliminate FAP1+ fibroblasts in vitro. This cytotoxic effect can be abrogated by inhibitors of the granzyme-perforin pathway. In the bleomycin-induced PF model, CAR-cTregs were found to reverse fibrosis characterized by diminished recruitment of fibrocytes and improved remodeling of epithelial cells. Together, our results demonstrate that CAR-cTregs can serve as a promising therapeutic option for IPF and provide a novel strategy for treating multiple chronic inflammatory diseases by inducing both cytotoxicity and immunosuppression.
Product Citations: 108
In JCI Insight on 8 July 2025 by Jiang, Y. H., Zhou, M., et al.
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
IGF1R Promotes Th17/Treg Cell Development in Experimental Autoimmune Prostatitis.
In Journal of Inflammation Research on 5 May 2025 by Guan, Y., Yue, S., et al.
Chronic prostatitis is a common urological disorder in young and middle-aged men, characterized by frequent relapses and an unknown etiology. We investigated the potential function of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) -related ligands in chronic prostatitis in the current study.
In this study, we established the chronic experimental autoimmune prostatitis mouse model H&E staining was used to assess immune cell infiltration in prostate tissue, while RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses were performed to validate gene and protein expression differences across groups, respectively. Immunofluorescence staining was utilized to determine the spatial distribution of key proteins. Flow cytometry was conducted to analyze the proportions of immune cell populations in different experimental groups. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) was employed to knock down Igflr, and ELISA was used to measure cytokine levels in the peripheral blood of mice. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05, and all tests were conducted as two-tailed. Data analysis was performed using R software (version 4.2.2).
We successful established the EAP model and discovered that the expression of IGF1R, content of IGF1-related ligands, was highest in prostate tissue and CD4+ T cell subset. Furthermore, protein expression levels of IGF1R were also validated that upregulated in mouse prostate tissue. Colocalization of immunofluorescence suggested that IGF1R protein is highly expressed on CD4+ T cells. Stimulation with desIGF1, a truncated analogue of IGF1, resulted in the significantly increased prostate inflammation and pain scores observed in the EAP+desIGF1 group mouse compared to other groups In vitro study further suggested that desIGF1 could increase the proportion of Th17 cells while decreasing the proportion of Treg cells. In the EAP+AAV-shIgf1r group, the knock down function of igf1r led to the alleviative prostate inflammation and response frequency of pain behavior test. We found that calcium ion associated pathways are active in EAP by bioinformatics, and further validated that PKC-β protein with significantly increased expression noted in the EAP+desIGF1 group, and decreased in the EAP+AAV-shIgf1r group. We also found that the proportion of Th17 cells increased after activation of PKC- β by flow cytometry.
These findings support that PKC-β associated pathways mediated by IGF1/IGF1R axis may impact Th17 cell differentiation and exacerbating prostate inflammation in EAP mouse, providing new molecular targets for the clinical therapeutic strategy.
© 2025 Guan et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Local Exosome Inhibition Potentiates Mild Photothermal Immunotherapy Against Breast Cancer.
In Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) on 1 January 2025 by Chen, Q., Li, Y., et al.
Limited immune infiltration within the tumor microenvironment (TME) hampers the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. To enhance immune infiltration, mild photothermal therapy (PTT) is often combined with immunotherapy. However, the impact of mild PTT on the TME remains unclear. The bioinformatics analyses reveal that mild PTT amplifies immune cell infiltration and stimulates T-cell activity. Notably, it accelerates the release of tumor cell-derived exosomes (TEX) and upregulates PD-L1 expression on both tumor cells and TEX. Consequently, it is proposed that locally inhibiting TEX release is crucial for overcoming the adverse effects of mild PTT, thereby enhancing ICB therapy. Thus, a multi-stage drug delivery system is designed that concurrently delivers photosensitizers (reduced graphene oxide nanosheets, NRGO), anti-PD-L1 antibodies, and exosome inhibitors (sulfisoxazole). The system employs a temperature-sensitive lipid gel as the primary carrier, with NRGO serving as a secondary carrier that supports photothermal conversion and incorporation of sulfisoxazole. Importantly, controlled drug release is achieved using near-infrared radiation. The findings indicate that this local combination therapy remodels the immunosuppressive TME through exosome inhibition and enhanced immune cell infiltration, while also boosting T-cell activity to trigger systemic antitumor immunity, showcasing the remarkable efficacy of this combination strategy in eradicating cold tumors.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Death & Disease on 18 December 2024 by Zheng, Z. Y., Lin, W., et al.
Effectively interfering with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) function in tumor cells and simultaneously activating an anti-tumor immune microenvironment to attack the tumor cells are promising strategies for cancer treatment. However, precise ER-stress induction is still a huge challenge. In this study, we synthesized a near-infrared (NIR) probe, NIR-715, which induces tumor cell death and inhibits tumor growth without causing apparent side effects. NIR-715 triggers severe ER stress and immunogenic cell death (ICD) after visible light exposure. NIR-715 induced ICD-associated HMGB1 release in vitro and anti-tumor immune responses, including increased cytotoxic T lymphocyte (GZMB+ CD8+ T cell) infiltration and decreased numbers of exhausted T lymphocytes (PD-L1+ CD8+ T cell). These findings suggest that NIR-715 may be a novel agent for "cold" tumor photodynamic therapy (PDT). Schematic illustration of NIR-715 photodynamic therapy for visible light-triggered, endoplasmic reticulum-targeting antitumor therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
In Theranostics on 31 October 2024 by Li, X., Chen, M., et al.
The endogenous immunomodulator adenosine (ADO) was expected to be potentialized as an efficacious mediator to combat psoriasis. However, its efficacy is severely hindered by its poor metabolic stability and insufficient accumulation at the dermatological lesions. Methods: In this study, a biomineralized in situ catalytic nanoreactor was delicately customized by encapsulating ADO precursor (adenosine monophosphate, AMP) within the internal porous skeleton of zeolitic imidazolate framework-90, followed by the biomineralization of the AMP catabolic enzyme on the outer layer. The nanocrystals were then incorporated into a dissolving microneedles patch, which was designed to deliver drugs with precision into the cutaneous lesion and enhance the efficacy of psoriasis treatment. Results: Upon penetration into the skin, the nanoreactors were released and underwent a gradual collapse of their structure, releasing AMP when exposed to the acidic microenvironment. Meanwhile, the acidic pH could trigger an in situ catalytic reaction to continuously produce ADO. This system yielded remarkable results in a psoriasis-like mouse model. The mechanism study demonstrated that this system could substantially reshape the inflammatory ecosystem by inhibiting the keratinocyte hyperplasia, reducing inflammatory cytokine expression, and regulating the infiltration of immune cells. Conclusion: The in situ catalytic nanoreactor integrated microneedle patch is a promising modular platform for co-delivery of prodrugs and their catabolic enzymes, offering a potential solution for various diseases.
© The author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
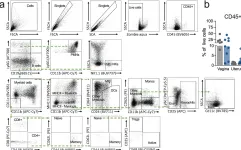
In Nat Commun on 3 February 2024 by Mercado-Evans, V., Mejia, M. E., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
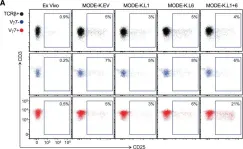
In Cell on 22 September 2016 by Di Marco Barros, R., Roberts, N. A., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cell by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
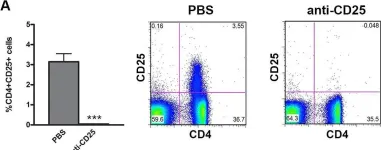
In PLoS One on 25 June 2015 by van Herwijnen, M. J., van der Zee, R., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
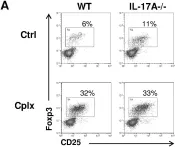
In PLoS One on 23 October 2013 by Vokaer, B., Charbonnier, L. M., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4