Cyclophosphamide (CTX) is the first-line medication for the treatment of breast cancer, although it potentially leads to severe ovarian dysfunction and even premature ovarian failure (POF). However, the mechanism of CTX-induced POF remains unclear. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy has been wildly used for treating numerous diseases. Therefore, our study aims to elucidate the underlying mechanism of CTX-induced POF and to explore the therapeutic effect of human urine stem cells (hUSCs) in POF.
CTX-induced POF or ovarian granulosa cell (GCs) apoptosis were treated with hUSCs and their exosomes in vitro and in vivo. Morphological, histological, and functional alternations were examined using multiple approaches. The effector molecules of hUSC-derived exosomes (hUSC-Exo) were determined by differential expression analysis in the ovaries. The target genes of miRNA were accessed by transcriptome sequencing in GCs, and the underlying mechanisms were further elucidated.
hUSCs remarkably inhibited CTX-induced apoptosis and promoted the proliferation of GCs, respectively. In addition, we observed that miR-27b-3p was highly expressed in hUSC-Exo and markedly suppressed CTX-induced GC apoptosis by specifically inhibiting the expression of SLC1A4, a serine transporter, in ovarian GCs, which, in turn, elevated the concentration of the intracellular serine by inhibiting the outflux of cellular serine. More importantly, the knockdown of SLC1A4 or simple supplementation of serine suppressed CTX-induced apoptosis of GCs. Finally, we demonstrated that CTX-induced apoptosis of ovarian GCs was essential for POF by reducing the intracellular serine concentration via elevating the expression of SLC1A4, whereas hUSCs protected against CTX-induced POF via miR-27b-3p/SLC1A4/serine axis-mediated activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
Our study suggests that hUSC-based cell therapy or simple supplementation of serine may provide an efficient therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of CTX-induced POF clinically.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 77
In Cellular Molecular Biology Letters on 19 February 2025 by Gu, H. C., Wang, L. F., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Protocol for differentiation of monocytes and macrophages from human induced pluripotent stem cells.
In STAR Protocols on 20 September 2024 by Emmerich, K., Calcaterra, F., et al.
Study of disease-relevant immune cells, namely monocytes and macrophages, is limited based on availability of primary tissue, a limitation that can be remedied using human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) technology. Here, we present a protocol for differentiation of monocytes and macrophages from hiPSCs. We describe steps for hiPSC maintenance, mesoderm lineage induction, hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) commitment and expansion, and myeloid lineage induction. We then detail procedures for monocyte formation and functional macrophage formation and polarization. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Chen et al.1.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Cells on 17 August 2024 by Dayoub, A. S., Acharya, E., et al.
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) has a dual-phase disease pathology; in phase 1, hyperoxia-induced vaso-obliteration occurs in the retinal vasculature due to increased oxidative stress (OS) and inflammation, followed by phase 2, where hypoxia increases the overproduction of growth factors, inducing retinal neovascularization. Toll-like receptor 2 and -4 (TLR2 and TLR4) overactivation, hyper-inflammation, macrophages, and neutrophil infiltration contribute to the developing ROP. AVR-121 and AVR-123 are novel classes of small-molecule dual inhibitors of TLR2/4 tested in a human leukemia monocytic cell line (THP-1) and cord-blood-derived mononuclear cells (CBMCs). Both compounds inhibited TLR2/4 signaling-related inflammatory cytokines in THP-1 cells and inhibited VEGF-induced neovascularization in human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs), which are hallmarks of ROP. In an oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) murine model, the intraperitoneal injection of AVR-123 in the hyperoxia phase (P7-P12) or a nanosuspension eyedrop of AVR-123 in the hypoxic phase (P12-P17) significantly reduced vaso-obliteration, angiogenesis, and inflammatory cytokine profiles while not inhibiting the necessary growth factor VEGF in the juvenile mouse eyes. The results are consistent with our hypothesis that targeting the dual TLR2/4 pathway will reduce inflammation, angiogenesis, and vaso-obliteration in vitro and in vivo and reduce cytotoxic immune cells. AVR-123 has the potential to be developed as a therapy for ROP.
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cells on 30 November 2023 by Ivory, K., Angotti, R., et al.
All allergic responses to food indicate the failure of immunological tolerance, but it is unclear why cow's milk and egg (CME) allergies resolve more readily than reactivity to peanuts (PN). We sought to identify differences between PN and CME allergies through constitutive immune status and responses to cognate and non-cognate food antigens. Children with confirmed allergy to CME (n = 6) and PN (n = 18) and non-allergic (NA) (n = 8) controls were studied. Constitutive secretion of cytokines was tested in plasma and unstimulated mononuclear cell (PBMNC) cultures. Blood dendritic cell (DC) subsets were analyzed alongside changes in phenotypes and soluble molecules in allergen-stimulated MNC cultures with or without cytokine neutralization. We observed that in allergic children, constitutively high plasma levels IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-10 but less IL-12p70 than in non-allergic children was accompanied by the spontaneous secretion of sCD23, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12p70, IFN-γ and TNF-α in MNC cultures. Furthermore, blood DC subset counts differed in food allergy. Antigen-presenting cell phenotypic abnormalities were accompanied by higher B and T cell percentages with more Bcl-2 within CD69+ subsets. Cells were generally refractory to antigenic stimulation in vitro, but IL-4 neutralization led to CD152 downregulation by CD4+ T cells from PN allergic children responding to PN allergens. Canonical discriminant analyses segregated non-allergic and allergic children by their cytokine secretion patterns, revealing differences and areas of overlap between PN and CME allergies. Despite an absence of recent allergen exposure, indication of in vivo activation, in vitro responses independent of challenging antigen and the presence of unusual costimulatory molecules suggest dysregulated immunity in food allergy. Most importantly, higher Bcl-2 content within key effector cells implies survival advantage with the potential to mount abnormal responses that may give rise to the manifestations of allergy. Here, we put forward the hypothesis that the lack of apoptosis of key immune cell types might be central to the development of food allergic reactions.
-
Cell Biology
In IScience on 17 November 2023 by Chen, G., Calcaterra, F., et al.
The C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5) expressed on immune cells supports inflammatory responses by directing cells to the inflammation site. CCR5 is also a major coreceptor for macrophage tropic human immunodeficiency viruses (R5-HIV-1) and its variants can confer protection from HIV infection, making it an ideal candidate to target for therapy. We developed a stepwise protocol that differentiates induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from individuals homozygous for the CCR5Δ32 variant and healthy volunteers into myeloid lineage induced monocytes (iMono) and macrophages (iMac). By characterizing iMono and iMac against their primary counterparts, we demonstrated that CCR5Δ32 homozygous cells are endowed with similar pluripotent potential for self-renewal and differentiation as iPSC lines generated from non-variant individuals while also showing resistance to HIV infection. In conclusion, these cells are a platform to investigate CCR5 pathophysiology in HIV-positive and negative individuals and to help develop novel therapies.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
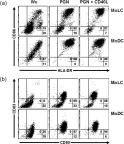
In Int J Mol Sci on 19 March 2019 by Gramlich, R., Aliahmadi, E., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
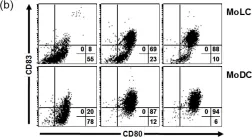
In Int J Mol Sci on 19 March 2019 by Gramlich, R., Aliahmadi, E., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2