The triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) arginine-47-histidine (R47H) mutation is a significant risk for Alzheimer's disease (AD) with unclear mechanisms. Previous studies focused on microglial amyloid-β (Aβ) phagocytosis with less attention on the impact of TREM2R47H mutation on blood monocytes.
Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) models were used to assess the contribution of blood monocytes carrying TREM2R47H mutation to AD.
Aβ phagocytosis was compromised in mouse monocytes carrying the TREM2R47H mutation. Transplantation of bone marrow cells (BMCs) carrying TREM2R47H mutation increased cerebral Aβ burden and aggravated AD-type pathologies. Moreover, the replacement of TREM2R47H-BMCs restored monocytic Aβ phagocytosis, lowered Aβ levels in the blood and brain, and improved cognitive function.
Our study reveals that blood monocytes carrying the TREM2R47H mutation substantially contribute to the pathogenesis of AD, and correcting the TREM2R47H mutation in BMCs would be a potential therapeutic approach for those carrying this mutation.
TREM2R47H mutation compromises the Aβ phagocytosis of blood monocytes. Blood monocytes carrying TREM2R47H mutation contribute substantially to AD pathogenesis. Correction of the TREM2R47H mutation in bone marrow cells ameliorates AD pathologies and cognitive impairments.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Product Citations: 64
In Alzheimer's Dementia : the Journal of the Alzheimer's Association on 1 February 2025 by Yu, Z. Y., Liu, J., et al.
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Neuroscience
In Molecular Medicine on 31 December 2024 by Chen, H., Li, Y., et al.
Partial stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) targeting hypoxic regions of large tumors (SBRT-PATHY) has been shown to enhance the efficacy of tumor radiotherapy by harnessing the radiation-induced immune response. This approach suggests that reducing the irradiation target volume not only achieves effective anti-tumor effects but also minimizes damage to surrounding normal tissues. In this study, we evaluated the antitumor efficacy of reduced-tumour-area radiotherapy (RTRT) , and explored the relationship between tumor control and immune preservation and the molecular mechanisms underlying of them.
In mouse breast cancer models, we compared the anti-tumor effects of RTRT and conventional radiotherapy (CNRT) by assessing tumor growth, metastasis, and survival rates. Additionally, we evaluated the peritumoral tissue damage and the immune microenvironment. The maturation of dendritic cells (DCs) and DNA damage induced by irradiated tumor cells were also assessed in vitro.
In pre-clinical models, both RTRT and CNRT significantly inhibited primary tumor growth when compared to non-irradiated controls, with no significant difference between RTRT and CNRT. However, RTRT significantly extended survival times in mice, and increased the likelihood of inducing abscopal effects, thereby providing potential for better control of distant metastases. Further investigations revealed that the enhanced efficacy of RTRT may be attributed to the preservation of lymphocytes within the peritumoral tissue, as well as reduced damage to the surrounding skin and circulating lymphocytes. In vitro assays demonstrated that RTRT induced DNA damage and dsDNA in tumor cells, activating the cGAS-STING pathway. RTRT also triggered the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which synergistically amplified the anti-tumor immune response.
Our findings suggested that appropriately narrowing the irradiation target volume effectively killed tumor cells while reducing damage to surrounding tissues, and preserving peritumoral lymphocytes. This approach improved the safety of radiotherapy while maintaining its efficacy in tumor control and provided an opportunity for combining high-dose radiotherapy with immunotherapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
Branched actin networks in innate immune cells mediate host microbiota homeostasis
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 18 July 2024 by Vasconcellos, L. R. C., Huang, S. C. M., et al.
Assembly of branched actin networks, driven by the Arp2/3 complex are essential for the function and integrity of the immune system. Patients with loss-of-function mutations in the ARPC5 subunit of the Arp2/3 complex develop inflammation and immunodeficiency after birth, leading to early mortality. However, the mechanistic basis for these phenotypes remains obscure. Here we demonstrate that loss of Arpc5 in the murine hematopoietic system, but not the corresponding Arpc5l isoform causes early-onset intestinal inflammation. This condition is initiated by microbiota breaching the ileal mucosa, leading to local and systemic inflammation. Macrophage and neutrophils infiltrate into the ileum, but in the absence of Arpc5 fail to restrict microbial invasion. Loss of Arpc5 compromises the ability of macrophages to phagocytose and kill intra-cellular bacteria. Our results underscore the indispensable role of Arpc5, but not Arpc5l containing Arp2/3 complexes in mononuclear phagocytes function and host-microbiota homeostasis. One-Sentence Summary Arpc5 containing Arp2/3 complexes are essential for host-microbiota homeostasis
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Parasites & Vectors on 2 July 2024 by Chen, J., Zhang, C., et al.
Toxoplasma gondii infection affects a significant portion of the global population, leading to severe toxoplasmosis and, in immunocompromised patients, even death. During T. gondii infection, disruption of gut microbiota further exacerbates the damage to intestinal and brain barriers. Therefore, identifying imbalanced probiotics during infection and restoring their equilibrium can regulate the balance of gut microbiota metabolites, thereby alleviating tissue damage.
Vimentin gene knockout (vim-/-) mice were employed as an immunocompromised model to evaluate the influence of host immune responses on gut microbiota balance during T. gondii infection. Behavioral experiments were performed to assess changes in cognitive levels and depressive tendencies between chronically infected vim-/- and wild-type (WT) mice. Fecal samples were subjected to 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequencing, and serum metabolites were analyzed to identify potential gut probiotics and their metabolites for the treatment of T. gondii infection.
Compared to the immunocompetent WT sv129 mice, the immunocompromised mice exhibited lower levels of neuronal apoptosis and fewer neurobehavioral abnormalities during chronic infection. 16S rRNA sequencing revealed a significant decrease in the abundance of probiotics, including several species of Lactobacillus, in WT mice. Restoring this balance through the administration of Lactobacillus murinus and Lactobacillus gasseri significantly suppressed the T. gondii burden in the intestine, liver, and brain. Moreover, transplantation of these two Lactobacillus spp. significantly improved intestinal barrier damage and alleviated inflammation and neuronal apoptosis in the central nervous system. Metabolite detection studies revealed that the levels of various Lactobacillus-related metabolites, including indole-3-lactic acid (ILA) in serum, decreased significantly after T. gondii infection. We confirmed that L. gasseri secreted much more ILA than L. murinus. Notably, ILA can activate the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway in intestinal epithelial cells, promoting the activation of CD8+ T cells and the secretion of interferon-gamma.
Our study revealed that host immune responses against T. gondii infection severely disrupted the balance of gut microbiota, resulting in intestinal and brain damage. Lactobacillus spp. play a crucial role in immune regulation, and the metabolite ILA is a promising therapeutic compound for efficient and safe treatment of T. gondii infection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Ebola virus-induced eye sequelae: a murine model for evaluating glycoprotein-targeting therapeutics.
In EBioMedicine on 1 June 2024 by Lee, H. N., Xu, B., et al.
Ebola virus disease (EVD) survivors experience ocular sequelae including retinal lesions, cataracts, and vision loss. While monoclonal antibodies targeting the Ebola virus glycoprotein (EBOV-GP) have shown promise in improving prognosis, their effectiveness in mitigating ocular sequelae remains uncertain.
We developed and characterized a BSL-2-compatible immunocompetent mouse model to evaluate therapeutics targeting EBOV-GP by inoculating neonatal mice with vesicular stomatitis virus expressing EBOV-GP (VSV-EBOV). To examine the impact of anti-EBOV-GP antibody treatment on acute retinitis and ocular sequelae, VSV-EBOV-infected mice were treated with polyclonal antibodies or monoclonal antibody preparations with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC-mAb) or neutralizing activity (NEUT-mAb).
Treatment with all anti-EBOV-GP antibodies tested dramatically reduced viremia and improved survival. Further, all treatments reduced the incidence of cataracts. However, NEUT-mAb alone or in combination with ADCC-mAb reduced viral load in the eyes, downregulated the ocular immune and inflammatory responses, and minimized retinal damage more effectively.
Anti-EBOV-GP antibodies can improve survival among EVD patients, but improved therapeutics are needed to reduce life altering sequelae. This animal model offers a new platform to examine the acute and long-term effect of the virus in the eye and the relative impact of therapeutic candidates targeting EBOV-GP. Results indicate that even antibodies that improve systemic viral clearance and survival can differ in their capacity to reduce acute ocular inflammation, and long-term retinal pathology and corneal degeneration.
This study was partly supported by Postgraduate Research Fellowship Awards from ORISE through an interagency agreement between the US DOE and the US FDA.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
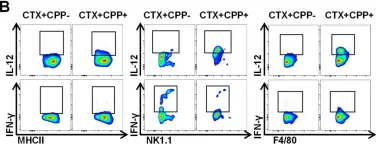
In Nutrients on 9 September 2020 by Sun, P., Kim, Y., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nutrients by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
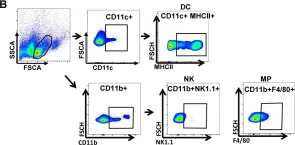
In Nutrients on 9 September 2020 by Sun, P., Kim, Y., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nutrients by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2