AAV-PHP.eB depends on endothelial cells to highly transduce the central nervous system (CNS) and is widely used for intravenous gene therapy. However, the transduction profile and therapeutic efficiency after endothelial cell injury such as ischemic stroke is largely unknown. In this study, we tested the transduction profiles of AAV-PHP.eB and developed intravenous NeuroD1 gene therapy to treat ischemic stroke in mice. We found that AAV-PHP.eB-GFP control virus crossed the BBB and infected brain cells efficiently in normal brain. However, after stroke, AAV-PHP.eB-GFP control virus was highly restricted in the blood vessels. Surprisingly, after switching to therapeutic vector AAV-PHP.eB-NeuroD1-GFP, the viral vector successfully crossed blood vessels and infected brain cells. Using Tie2-cre transgenic mice, we demonstrated that NeuroD1 regulated endothelial gene expression to modulate AAV-PHP.eB transduction. Following the changes of signaling pathways in endothelial cells, NeuroD1 effectively protected BBB integrity, attenuated neuroinflammation, inhibited neuron apoptosis and rescued motor deficits after ischemic stroke. Moreover, NeuroD1 over-expression in brain cells further promoted neural regeneration. These results indicate that intravenous gene therapy using AAV-PHP.eB for ischemic stroke differs from intracranial gene therapy and NeuroD1 intravenous delivery using AAV-PHP.eB efficiently rescue both vascular damage and neuronal loss, providing an advancing therapeutic treatment for stroke.
Product Citations: 45
In Aging and Disease on 20 December 2023 by He, X., Wang, X., et al.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cardiovascular biology
In Cytotherapy on 1 September 2023 by Chang, Q., Fujio, M., et al.
While distraction osteogenesis (DO) achieves substantial bone regeneration, prolonged fixation may lead to infections. Existing stem cell and physical therapies have limitations, requiring the development of novel therapeutic approaches. Here, we evaluated high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) as a novel therapeutic target for DO treatment.
Micro-computed tomography (Micro-CT) analysis and histological staining of samples obtained from tibial DO model mice was performed. Transwell migration, wound healing, and proliferation assays were also performed on cultured human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) and human umbilival vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Tube formation assay was performed on HUVECs, whereas osteogenic differentiation assay was performed on hMSCs.
Micro-CT analysis and histological staining of mouse samples revealed that HMGB1 promotes bone regeneration during DO via the recruitment of PDGFRα and Sca-1 positve (PαS+) cells and endothelial progenitor cells. Furthermore, HMGB1 accelerated angiogenesis during DO, promoted the migration and osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs as well as the proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of HUVECs in vitro.
Our findings suggest that HMGB1 has a positive influence on endogenous stem/progenitor cells, representing a novel therapeutic target for the acceleration of DO-driven bone regeneration.
Copyright © 2023 International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Nature Communications on 5 January 2023 by Sastourné-Arrey, Q., Mathieu, M., et al.
Fibro-adipogenic progenitors (FAPs) play a crucial role in skeletal muscle regeneration, as they generate a favorable niche that allows satellite cells to perform efficient muscle regeneration. After muscle injury, FAP content increases rapidly within the injured muscle, the origin of which has been attributed to their proliferation within the muscle itself. However, recent single-cell RNAseq approaches have revealed phenotype and functional heterogeneity in FAPs, raising the question of how this differentiation of regenerative subtypes occurs. Here we report that FAP-like cells residing in subcutaneous adipose tissue (ScAT), the adipose stromal cells (ASCs), are rapidly released from ScAT in response to muscle injury. Additionally, we find that released ASCs infiltrate the damaged muscle, via a platelet-dependent mechanism and thus contribute to the FAP heterogeneity. Moreover, we show that either blocking ASCs infiltration or removing ASCs tissue source impair muscle regeneration. Collectively, our data reveal that ScAT is an unsuspected physiological reservoir of regenerative cells that support skeletal muscle regeneration, underlining a beneficial relationship between muscle and fat.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Cell Reports on 6 September 2022 by Wei, X., Zhang, L., et al.
Functional implication of stromal heterogeneity in the prostate remains incompletely understood. Using lineage tracing and light-sheet imaging, we show that some fibroblast cells at the mouse proximal prostatic ducts and prostatic urethra highly express Lgr5. Genetic ablation of these anatomically restricted stromal cells, but not nonselective ablation of prostatic stromal cells, rapidly induces prostate epithelial turnover and dedifferentiation that are reversed following spontaneous restoration of the Lgr5+ stromal cells. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis indicates that ablating the Lgr5+ stromal cells activates a mechanosensory response. Ablating the Lgr5+ stromal cells impairs the control of prostatic ductal outlet, increases prostate tissue stiffness, and activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Suppressing MAPK overrides the elevated epithelial proliferation. In summary, the Lgr5+ stromal cells regulate prostate tissue homeostasis and maintain its functional integrity in a long-distance manner. Our study implies that the cells at organ junctions most likely control organ homeostasis by sustaining a balanced mechanoforce.Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Scientific Reports on 19 November 2021 by Prideaux, M., Wright, C. S., et al.
Mesenchymal progenitors differentiate into several tissues including bone, cartilage, and adipose. Targeting these cells in vivo is challenging, making mesenchymal progenitor cell lines valuable tools to study tissue development. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be isolated from humans and animals; however, obtaining homogenous, responsive cells in a reproducible fashion is challenging. As such, we developed two mesenchymal progenitor cell (MPC) lines, MPC1 and MPC2, generated from bone marrow of male C57BL/6 mice. These cells were immortalized using the temperature sensitive large T-antigen, allowing for thermal control of proliferation and differentiation. Both MPC1 and MPC2 cells are capable of osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic differentiation. Under osteogenic conditions, both lines formed mineralized nodules, and stained for alizarin red and alkaline phosphatase, while expressing osteogenic genes including Sost, Fgf23, and Dmp1. Sost and Dmp1 mRNA levels were drastically reduced with addition of parathyroid hormone, thus recapitulating in vivo responses. MPC cells secreted intact (iFGF23) and C-terminal (cFGF23) forms of the endocrine hormone FGF23, which was upregulated by 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D (1,25D). Both lines also rapidly entered the adipogenic lineage, expressing adipose markers after 4 days in adipogenic media. MPC cells were also capable of chondrogenic differentiation, displaying increased expression of cartilaginous genes including aggrecan, Sox9, and Comp. With the ability to differentiate into multiple mesenchymal lineages and mimic in vivo responses of key regulatory genes/proteins, MPC cells are a valuable model to study factors that regulate mesenchymal lineage allocation as well as the mechanisms that dictate transcription, protein modification, and secretion of these factors.
© 2021. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In PLoS One on 24 June 2016 by Kim, J. H., Hong, S. J., et al.
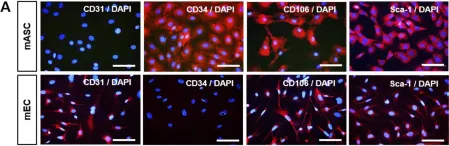
Fig.1.A
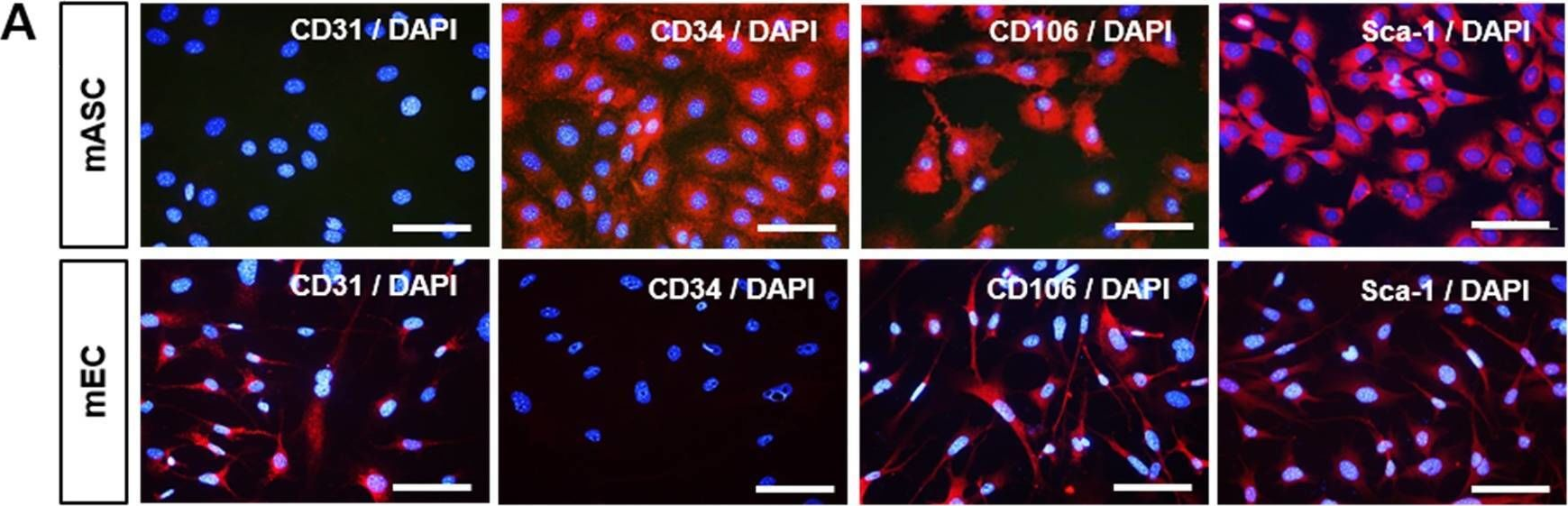
-
ICC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS ONE by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1