Breast cancer (BC) is commonly labeled a "cold tumor" due to its dense population of immunosuppressive cells, particularly M2-like macrophages, which contribute to its resistance to therapy. Thus, there is a pressing need to shift the macrophage polarization towards M1 and revitalize the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) to improve BC prognosis. In this study, we leveraged published RNA-sequencing data and performed multiplex immunohistochemistry on clinical specimens to identify NR4A3 as a promising biomarker for favorable outcomes in BC. High NR4A3 expression correlates with an inflamed TIME, characterized by heightened T-cell infiltration and activation. NR4A3 was preferentially expressed in macrophages and fostered M1-like macrophage polarization through direct binding to p65, thereby enhancing NF-κB transcriptional activity. Overexpression of Nr4a3 in tumor-infiltrating macrophages significantly inhibited the growth of E0771 tumors in a syngeneic mouse model, accompanied by increased T-cell infiltration and elevated production of functional cytokines. Conversely, suppression of Nr4a3 in macrophages compromised T-cell recruitment and diminished their anti-tumor capabilities. Consistent with these findings, co-culture experiments involving human T cells and NR4A3-overexpressing THP1 cells further demonstrated enhanced T-cell functionality. Collectively, our findings uncover a novel role for NR4A3 in macrophage polarization and TIME remodeling, offering a potential biomarker for favorable BC prognosis and a therapeutic target to enhance immunotherapy efficacy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 65
In NPJ Breast Cancer on 7 July 2025 by Qian, Y. Y., Jin, N., et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Epidermal maintenance of Langerhans cells relies on autophagy-regulated lipid metabolism.
In The Journal of Cell Biology on 3 February 2025 by Arbogast, F., Sal-Carro, R., et al.
Macroautophagy (often-named autophagy), a catabolic process involving autophagy-related (Atg) genes, prevents the accumulation of harmful cytoplasmic components and mobilizes energy reserves in long-lived and self-renewing cells. Autophagy deficiency affects antigen presentation in conventional dendritic cells (DCs) without impacting their survival. However, previous studies did not address epidermal Langerhans cells (LCs). Here, we demonstrate that deletion of either Atg5 or Atg7 in LCs leads to their gradual depletion. ATG5-deficient LCs showed metabolic dysregulation and accumulated neutral lipids. Despite increased mitochondrial respiratory capacity, they were unable to process lipids, eventually leading them to ferroptosis. Finally, metabolically impaired LCs upregulated proinflammatory transcripts and showed decreased expression of neuronal interaction receptors. Altogether, autophagy represents a critical regulator of lipid storage and metabolism in LCs, allowing their maintenance in the epidermis.
© 2024 Arbogast et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
In Immunity on 12 September 2023 by Brown, H., Komnick, M. R., et al.
Lymph nodes (LNs) are critical sites for shaping tissue-specific adaptive immunity. However, the impact of LN sharing between multiple organs on such tailoring is less understood. Here, we describe the drainage hierarchy of the pancreas, liver, and the upper small intestine (duodenum) into three murine LNs. Migratory dendritic cells (migDCs), key in instructing adaptive immune outcome, exhibited stronger pro-inflammatory signatures when originating from the pancreas or liver than from the duodenum. Qualitatively different migDC mixing in each shared LN influenced pancreatic β-cell-reactive T cells to acquire gut-homing and tolerogenic phenotypes proportional to duodenal co-drainage. However, duodenal viral infections rendered non-intestinal migDCs and β-cell-reactive T cells more pro-inflammatory in all shared LNs, resulting in elevated pancreatic islet lymphocyte infiltration. Our study uncovers immune crosstalk through LN co-drainage as a powerful force regulating pancreatic autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Neonatal imprinting of alveolar macrophages via neutrophil-derived 12-HETE.
In Nature on 1 February 2023 by Pernet, E., Sun, S., et al.
Resident-tissue macrophages (RTMs) arise from embryonic precursors1,2, yet the developmental signals that shape their longevity remain largely unknown. Here we demonstrate in mice genetically deficient in 12-lipoxygenase and 15-lipoxygenase (Alox15-/- mice) that neonatal neutrophil-derived 12-HETE is required for self-renewal and maintenance of alveolar macrophages (AMs) during lung development. Although the seeding and differentiation of AM progenitors remained intact, the absence of 12-HETE led to a significant reduction in AMs in adult lungs and enhanced senescence owing to increased prostaglandin E2 production. A compromised AM compartment resulted in increased susceptibility to acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide and to pulmonary infections with influenza A virus or SARS-CoV-2. Our results highlight the complexity of prenatal RTM programming and reveal their dependency on in trans eicosanoid production by neutrophils for lifelong self-renewal.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Identification of dendritic cell-T cell interactions driving immune responses to food
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 27 October 2022 by Canesso, M. C., Castro, T. B., et al.
The intestinal immune system must concomitantly tolerate food and commensals and protect against pathogens. Dendritic cells (DCs) orchestrate these immune responses by presenting luminal antigens and inducing functional differentiation of CD4 + T cells into regulatory (pTreg) or pro-inflammatory (Th) subsets. However, the exact nature of the DCs inducing tolerance or inflammation to dietary antigens has been difficult to define. Using an intestine-adapted Labeling Immune Partnerships by SorTagging Intercellular Contacts (LIPSTIC) combined with single-cell transcriptomics, we characterized DCs presenting dietary antigens in the context of tolerance or infection. At steady-state, migratory cDC1 and cDC2 DCs, but not resident DCs, were found to present dietary antigen to cognate CD4 + T cells. Whereas cDC2s promoted T cell activation, only cDC1s induced their differentiation into pTregs. Infection with the helminth Strongyloides venezuelensis abrogated cDC1 presentation of dietary antigens, preventing pTreg and oral tolerance induction. In contrast, Heligmosomoides polygyrus infection only partially affected cDC1s, allowing oral tolerance to be maintained. An expanded population of cDC2s that induced type-2 immunity during both helminth infections did not present dietary antigens, demonstrating that compartmentalized presentation of luminal antigens can prevent food-specific Th2 responses during inflammatory conditions. Our data uncover novel cellular mechanisms by which tolerance to food is induced and can be disrupted during infections.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
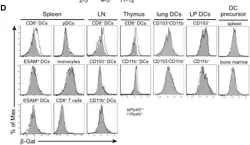
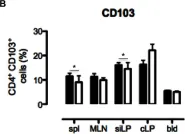
In Front Immunol on 28 February 2019 by Zwick, M., Ulas, T., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
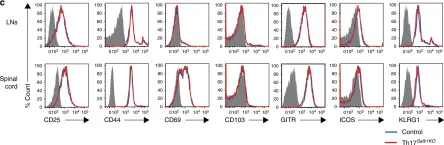
In Nat Commun on 1 February 2019 by Yasuda, K., Kitagawa, Y., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
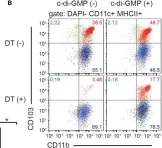
In Front Immunol on 6 June 2018 by Liu, S., Xia, Q., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
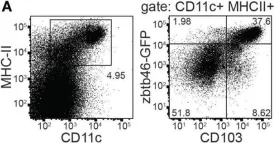
In Front Immunol on 6 June 2018 by Liu, S., Xia, Q., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In PLoS One on 19 June 2013 by Radulovic, K., Rossini, V., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5