Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) contains inflammatory cues that enable peripheral immune surveillance of the central nervous system (CNS). While some cranial nerves allow for CSF efflux, the immune environment around CSF-interfacing cranial nerves during neuroinflammation is still poorly understood. Using a mouse model of multiple sclerosis [experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)] and CNS Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection (CNS-Mtb), we examined immune responses around olfactory nerve bundles near the cribriform plate, a key CSF efflux route. During neuroinflammation, we found increased perineural immune cells that had access to intracranial injected beads, dye, and bacteria. Additionally, we identified osseous channels connecting the environment surrounding olfactory nerves to bone marrow in the cribriform plate (cpBM). Notably, the cpBM undergoes myelopoiesis during EAE, has access to components of intracranial drainage, and is vulnerable to Mtb bacteria invasion during CNS-Mtb infection. Our findings improve the understanding of how the environments of CSF-interfacing cranial nerves and bone marrow are altered within the skull during neuroinflammatory disease.
Product Citations: 31
In Science Advances on 27 June 2025 by Laaker, C., Kovács, K. G., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
T cells use focal adhesions to pull themselves through confined environments.
In The Journal of Cell Biology on 7 October 2024 by Caillier, A., Oleksyn, D., et al.
Immune cells are highly dynamic and able to migrate through environments with diverse biochemical and mechanical compositions. Their migration has classically been defined as amoeboid under the assumption that it is integrin independent. Here, we show that activated primary Th1 T cells require both confinement and extracellular matrix proteins to migrate efficiently. This migration is mediated through small and dynamic focal adhesions that are composed of the same proteins associated with canonical mesenchymal cell focal adhesions, such as integrins, talin, and vinculin. These focal adhesions, furthermore, localize to sites of contractile traction stresses, enabling T cells to pull themselves through confined spaces. Finally, we show that Th1 T cells preferentially follow tracks of other T cells, suggesting that these adhesions modify the extracellular matrix to provide additional environmental guidance cues. These results demonstrate not only that the boundaries between amoeboid and mesenchymal migration modes are ambiguous, but that integrin-mediated focal adhesions play a key role in T cell motility.
© 2024 Caillier et al.
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
T cells Use Focal Adhesions to Pull Themselves Through Confined Environments
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 19 October 2023 by Caillier, A., Oleksyn, D., et al.
Immune cells are highly dynamic and able to migrate through environments with diverse biochemical and mechanical composition. Their migration has classically been defined as amoeboid under the assumption that it is integrin-independent. Here we show that activated primary Th1 T cells require both confinement and extracellular matrix protein to migrate efficiently. This migration is mediated through small and dynamic focal adhesions that are composed of the same proteins associated with canonical mesenchymal focal adhesions, such as integrins, talin, and vinculin. These focal adhesions, furthermore, localize to sites of contractile traction stresses, enabling T cells to pull themselves through confined spaces. Finally, we show that Th1 T cell preferentially follows tracks of other T cells, suggesting that these adhesions are modifying the extracellular matrix to provide additional environmental guidance cues. These results demonstrate not only that the boundaries between amoeboid and mesenchymal migration modes are ambiguous, but that integrin-mediated adhesions play a key role in T cell motility. Graphical Abstract
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
mAb therapy controls CNS-resident lyssavirus infection via a CD4 T cell-dependent mechanism.
In EMBO Molecular Medicine on 11 October 2023 by Mastraccio, K. E., Huaman, C., et al.
Infections with rabies virus (RABV) and related lyssaviruses are uniformly fatal once virus accesses the central nervous system (CNS) and causes disease signs. Current immunotherapies are thus focused on the early, pre-symptomatic stage of disease, with the goal of peripheral neutralization of virus to prevent CNS infection. Here, we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of F11, an anti-lyssavirus human monoclonal antibody (mAb), on established lyssavirus infections. We show that a single dose of F11 limits viral load in the brain and reverses disease signs following infection with a lethal dose of lyssavirus, even when administered after initiation of robust virus replication in the CNS. Importantly, we found that F11-dependent neutralization is not sufficient to protect animals from mortality, and a CD4 T cell-dependent adaptive immune response is required for successful control of infection. F11 significantly changes the spectrum of leukocyte populations in the brain, and the FcRγ-binding function of F11 contributes to therapeutic efficacy. Thus, mAb therapy can drive potent neutralization-independent T cell-mediated effects, even against an established CNS infection by a lethal neurotropic virus.
© 2023 Commonwealth of Australia and The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Immunology on 1 April 2023 by Lo, W. L., Kuhlmann, M., et al.
Mature T cells must discriminate between brief interactions with self-peptides and prolonged binding to agonists. The kinetic proofreading model posits that certain T-cell antigen receptor signaling nodes serve as molecular timers to facilitate such discrimination. However, the physiological significance of this regulatory mechanism and the pathological consequences of disrupting it are unknown. Here we report that accelerating the normally slow phosphorylation of the linker for activation of T cells (LAT) residue Y136 by introducing an adjacent Gly135Asp alteration (LATG135D) disrupts ligand discrimination in vivo. The enhanced self-reactivity of LATG135D T cells triggers excessive thymic negative selection and promotes T-cell anergy. During Listeria infection, LATG135D T cells expand more than wild-type counterparts in response to very weak stimuli but display an imbalance between effector and memory responses. Moreover, despite their enhanced engagement of central and peripheral tolerance mechanisms, mice bearing LATG135D show features associated with autoimmunity and immunopathology. Our data reveal the importance of kinetic proofreading in balancing tolerance and immunity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
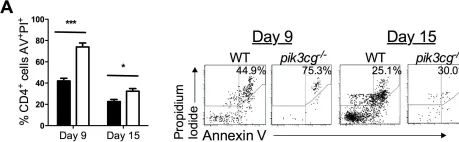
In PLoS One on 3 October 2012 by Comerford, I., Litchfield, W., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1