Aurora A kinase, a cell division regulator, is frequently overexpressed in various cancers, provoking genome instability and resistance to antimitotic chemotherapy. Localization and enzymatic activity of Aurora A are regulated by its interaction with the spindle assembly factor TPX2. We have used fragment-based, structure-guided lead discovery to develop small molecule inhibitors of the Aurora A-TPX2 protein-protein interaction (PPI). Our lead compound, CAM2602, inhibits Aurora A:TPX2 interaction, binding Aurora A with 19 nM affinity. CAM2602 exhibits oral bioavailability, causes pharmacodynamic biomarker modulation, and arrests the growth of tumor xenografts. CAM2602 acts by a novel mechanism compared to ATP-competitive inhibitors and is highly specific to Aurora A over Aurora B. Consistent with our finding that Aurora A overexpression drives taxane resistance, these inhibitors synergize with paclitaxel to suppress the outgrowth of pancreatic cancer cells. Our results provide a blueprint for targeting the Aurora A-TPX2 PPI for cancer therapy and suggest a promising clinical utility for this mode of action.
Product Citations: 24
Selective Aurora A-TPX2 Interaction Inhibitors Have In Vivo Efficacy as Targeted Antimitotic Agents.
In Journal of Medicinal Chemistry on 12 September 2024 by Stockwell, S. R., Scott, D. E., et al.
-
Chemistry
In Journal of Cancer on 1 July 2024 by Wu, Y., Dai, S., et al.
Purpose: Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz is a widely used classical traditional Chinese herbal medicine, that has shown remarkable efficacy in cancers. Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most common malignant tumor globally. Interferon (IFN)-γ, a prominent cytokine involved in anti-tumor immunity that has cytostatic, pro-apoptotic, and immune-stimulatory properties for the detection and removal of transformed cells. Atractylenolides-II (AT-II) belongs to the lactone compound that is derived from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz with anti-cancer activity. However, whether AT-II combined with IFN-γ modulates CRC progression and the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. The present study aimed to elucidate the efficacy and pharmaceutical mechanism of action of AT-II combined with IFN-γ synergistically against CRC by regulating the NF-kB p65/PD-L1 signaling pathway. Methods: HT29 and HCT15 cells were treated with AT-II and IFN-γ alone or in combination and cell viability, migration, and invasion were then analyzed using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and Transwell assays, respectively. Furthermore, the underlying mechanism was investigated through western blot assay. The role of AT-II combined with IFN-γ on tumor growth and lung metastases was estimated in vivo. Finally, the population of lymphocytes in tumor tissues of lung metastatic C57BL/6 mice and the plasma cytokine levels were confirmed by flow cytometry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Results: AT-II or the combination IFN-γ significantly inhibited the growth and migration abilities of CRC cells in vitro and in vivo. The biological mechanisms behind the beneficial effects of AT-II combined with IFN-γ were also measured and inhibition of p38 MAPK, FAK, Wnt/β-catenin, Smad, and NF-kB p65/PD-L1 pathways was observed. Moreover, AT-II combined with IFN-γ significantly inhibited HCT15 xenograft tumor growth and lung metastases in C57BL/6 mice, which was accompanied by lymphocyte infiltration into the tumor tissues and inflammatory response inactivation. Conclusions: The results showed that the AT-II in combination with IFN-γ could be used as a potential strategy for tumor immunotherapy in CRC. More importantly, the mechanism by which AT-II suppressed CRC progressions was by inhibiting the NF-kB p65/PD-L1 signal pathway.
© The author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
Plasma Glycomic Markers of Accelerated Biological Aging During Chronic HIV Infection
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 10 August 2023 by Giron, L. B., Liu, Q., et al.
ABSTRACT People with HIV (PWH) experience an increased vulnerability to premature aging and inflammation-associated comorbidities, even when HIV replication is suppressed by antiretroviral therapy (ART). However, the factors that contribute to or are associated with this vulnerability remain uncertain. In the general population, alterations in the glycomes of circulating IgGs trigger inflammation and precede the onset of aging-associated diseases. Here, we investigate the IgG glycomes of cross-sectional and longitudinal samples from 1,216 women and men, both living with virally suppressed HIV and those without HIV. Our glycan-based machine learning models indicate that living with chronic HIV significantly accelerates the accumulation of pro-aging-associated glycomic alterations. Consistently, PWH exhibit heightened expression of senescence-associated glycan-degrading enzymes compared to their controls. These glycomic alterations correlate with elevated markers of inflammatory aging and the severity of comorbidities, potentially preceding the development of such comorbidities. Mechanistically, HIV-specific antibodies glycoengineered with these alterations exhibit reduced anti-HIV IgG-mediated innate immune functions. These findings hold significant potential for the development of glycomic-based biomarkers and tools to identify and prevent premature aging and comorbidities in people living with chronic viral infections.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
TRAPnSeq allows high-throughput profiling of antigen-specific antibody-secreting cells.
In Cell Rep Methods on 24 July 2023 by Asrat, S., Devlin, J. C., et al.
Following activation by cognate antigen, B cells undergo fine-tuning of their antigen receptors and may ultimately differentiate into antibody-secreting cells (ASCs). While antigen-specific B cells that express surface receptors (B cell receptors [BCRs]) can be readily cloned and sequenced following flow sorting, antigen-specific ASCs that lack surface BCRs cannot be easily profiled. Here, we report an approach, TRAPnSeq (antigen specificity mapping through immunoglobulin [Ig] secretion TRAP and Sequencing), that allows capture of secreted antibodies on the surface of ASCs, which in turn enables high-throughput screening of single ASCs against large antigen panels. This approach incorporates flow cytometry, standard microfluidic platforms, and DNA-barcoding technologies to characterize antigen-specific ASCs through single-cell V(D)J, RNA, and antigen barcode sequencing. We show the utility of TRAPnSeq by profiling antigen-specific IgG and IgE ASCs from both mice and humans and highlight its capacity to accelerate therapeutic antibody discovery from ASCs.
© 2023 The Authors.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Engineering of immunoinstructive extracellular matrices for enhanced osteoinductivity.
In Bioactive Materials on 1 June 2023 by García-García, A., Pigeot, S., et al.
The increasing recognition of the contribution of the immune system to activate and prime regeneration implies that tissue engineering strategies and biomaterials design should target regulation of early immunological processes. We previously proposed the cell-based engineering and devitalization of extracellular matrices (ECMs) as a strategy to generate implant materials delivering custom-defined signals. Here, in the context of bone regeneration, we aimed at enhancing the osteoinductivity of such ECMs by enriching their immunomodulatory factors repertoire. Priming with IL1β a cell line overexpressing BMP-2 enabled engineering of ECMs preserving osteoinductive signals and containing larger amounts of angiogenic (VEGF) and pro-inflammatory molecules (IL6, IL8 and MCP1). Upon implantation, these IL1β-induced materials enhanced processes typical of the inflammatory phase (e.g., vascular invasion, osteoclast recruitment and differentiation), leading to 'regenerative' events (e.g., M2 macrophage polarization) and ultimately resulting in faster and more efficient bone formation. These results bear relevance towards the manufacturing of potent off-the-shelf osteoinductive materials and outline the broader paradigm of engineering immunoinstructive implants to enhance tissue regeneration.
© 2022 The Authors.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
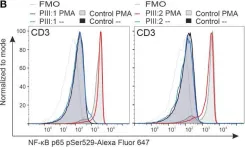
In Front Immunol on 6 December 2022 by Pernaa, N., Keskitalo, S., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1