In humans, Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV) infection typically presents as a self-limiting febrile illness but can cause severe complications. Neurological disease manifestations are particularly concerning as they are associated with increased mortality and long-term morbidity. This study demonstrated that vaccination with live attenuated RVFV was effective in preventing central nervous system (CNS) disease in the CC057/Unc mouse model of late-onset RVF encephalitis. Vaccine candidates (ΔNSs and ΔNSsΔNSm) were safe and immunogenic and elicited both RVFV-specific humoral and cellular immunity. Vaccinated mice survived percutaneous wild-type (WT) RVFV challenge and were protected from CNS disease. Naïve mice that received passive transfer of serum from vaccinated animals 2 days post-WT challenge were protected against late-onset encephalitis. These data demonstrate that humoral immunity is sufficient to protect against RVF encephalitis in CC057/Unc mice and suggest the potential of these vaccine candidates to prevent CNS disease in humans.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 36
In NPJ Vaccines on 2 July 2025 by Mueller Brown, K., Barbeau, D. J., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Science Advances on 27 June 2025 by Laaker, C., Kovács, K. G., et al.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) contains inflammatory cues that enable peripheral immune surveillance of the central nervous system (CNS). While some cranial nerves allow for CSF efflux, the immune environment around CSF-interfacing cranial nerves during neuroinflammation is still poorly understood. Using a mouse model of multiple sclerosis [experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)] and CNS Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection (CNS-Mtb), we examined immune responses around olfactory nerve bundles near the cribriform plate, a key CSF efflux route. During neuroinflammation, we found increased perineural immune cells that had access to intracranial injected beads, dye, and bacteria. Additionally, we identified osseous channels connecting the environment surrounding olfactory nerves to bone marrow in the cribriform plate (cpBM). Notably, the cpBM undergoes myelopoiesis during EAE, has access to components of intracranial drainage, and is vulnerable to Mtb bacteria invasion during CNS-Mtb infection. Our findings improve the understanding of how the environments of CSF-interfacing cranial nerves and bone marrow are altered within the skull during neuroinflammatory disease.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
In Nature Communications on 23 July 2024 by Leekha, A., Saeedi, A., et al.
Immunization programs against SARS-CoV-2 with commercial intramuscular vaccines prevent disease but are less efficient in preventing infections. Mucosal vaccines can provide improved protection against transmission, ideally for different variants of concern (VOCs) and related sarbecoviruses. Here, we report a multi-antigen, intranasal vaccine, NanoSTING-SN (NanoSTING-Spike-Nucleocapsid), eliminates virus replication in both the lungs and the nostrils upon challenge with the pathogenic SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC. We further demonstrate that NanoSTING-SN prevents transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VOC (BA.5) to vaccine-naïve hamsters. To evaluate protection against other sarbecoviruses, we immunized mice with NanoSTING-SN. We showed that immunization affords protection against SARS-CoV, leading to protection from weight loss and 100% survival in mice. In non-human primates, animals immunized with NanoSTING-SN show durable serum IgG responses (6 months) and nasal wash IgA responses cross-reactive to SARS-CoV-2 (XBB1.5), SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV antigens. These observations have two implications: (1) mucosal multi-antigen vaccines present a pathway to reducing transmission of respiratory viruses, and (2) eliciting immunity against multiple antigens can be advantageous in engineering pan-sarbecovirus vaccines.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Veterinary Research
In mBio on 31 October 2023 by Kim, D., Kim, E., et al.
Dabie bandavirus (DBV) is an emerging tick-borne virus that causes severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in infected patients. Human SFTS symptoms progress from fever, fatigue, and muscle pain to the depletion of white blood cells and platelets with fatality rates up to 30%. The recent spread of its vector tick to over 20 states in the United States increases the potential for outbreaks of the SFTS beyond the East Asia. Thus, the development of vaccine to control this rapidly emerging virus is a high priority. In this study, we applied self-assembling ferritin (FT) nanoparticle to enhance the immunogenicity of DBV Gn head domain (GnH) as a vaccine target. Mice immunized with the GnH-FT nanoparticle vaccine induced potent antibody responses and cellular immunity. Immunized aged ferrets were fully protected from the lethal challenge of DBV. Our study describes the GnH-FT nanoparticle vaccine candidate that provides protective immunity against the emerging DBV infection.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Communications (London, England) on 1 October 2023 by Zhang, B., Wang, C. M., et al.
The efficacy of anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) immunotherapy in various cancers, including gastric cancer (GC), needs to be potentiated by more effective targeting to enhance therapeutic efficacy or identifying accurate biomarkers to predict clinical responses. Here, we attempted to identify molecules predicting or/and promoting anti-PD-1 therapeutic response in advanced GC (AGC).
The transcriptome of AGC tissues from patients with different clinical responses to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy and GC cells was analyzed by RNA sequencing. The protein and mRNA levels of the major facilitator superfamily domain containing 2A (MFSD2A) in GC cells were assessed via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. Additionally, the regulation of anti-PD-1 response by MFSD2A was studied in tumor-bearing mice. Cytometry by Time-of-Flight, multiple immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry assays were used to explore immunological responses. The effects of MFSD2A on lipid metabolism in mice cancer tissue and GC cells was detected by metabolomics.
Higher expression of MFSD2A in tumor tissues of AGC patients was associated with better response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Moreover, MFSD2A expression was lower in GC tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues, and its expression was inversely correlated with GC stage. The overexpression of MFSD2A in GC cells enhanced the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in vivo by reprogramming the tumor microenvironment (TME), characterized by increased CD8+ T cell activation and reduced its exhaustion. MFSD2A inhibited transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) release from GC cells by suppressing cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2)-prostaglandin synthesis, which consequently reprogrammed TME to promote anti-tumor T cell activation.
MFSD2A potentially serves as a predictive biomarker for anti-PD-1 immunotherapy response in AGC patients. MFSD2A may be a promising therapeutic target to potentiate the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by reprogramming the TME to promote T cells activation.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
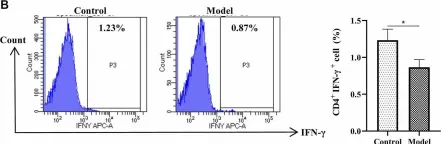
In Front Pharmacol on 7 June 2022 by Zhou, Y., Wang, T., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Pharmacol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1