Adenosine (Ado) mediates immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment and exhausted CD8+ CAR-T cells express CD39 and CD73, which mediate proximal steps in Ado generation. Here, we sought to enhance CAR-T cell potency by knocking out CD39, CD73, or adenosine receptor 2a (A2aR) but observed only modest effects. In contrast, overexpression of Ado deaminase (ADA-OE), which metabolizes Ado to inosine (INO), induced stemness and enhanced CAR-T functionality. Similarly, CAR-T cell exposure to INO augmented function and induced features of stemness. INO induced profound metabolic reprogramming, diminishing glycolysis, increasing mitochondrial and glycolytic capacity, glutaminolysis and polyamine synthesis, and reprogrammed the epigenome toward greater stemness. Clinical scale manufacturing using INO generated enhanced potency CAR-T cell products meeting criteria for clinical dosing. These results identify INO as a potent modulator of CAR-T cell metabolism and epigenetic stemness programming and deliver an enhanced potency platform for cell manufacturing.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 8
Inosine induces stemness features in CAR-T cells and enhances potency.
In Cancer Cell on 12 February 2024 by Klysz, D. D., Fowler, C., et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Immunity on 13 December 2022 by Lukhele, S., Rabbo, D. A., et al.
Type I and II interferons (IFNs) stimulate pro-inflammatory programs that are critical for immune activation, but also induce immune-suppressive feedback circuits that impede control of cancer growth. Here, we sought to determine how these opposing programs are differentially induced. We demonstrated that the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 2 (IRF2) was expressed by many immune cells in the tumor in response to sustained IFN signaling. CD8+ T cell-specific deletion of IRF2 prevented acquisition of the T cell exhaustion program within the tumor and instead enabled sustained effector functions that promoted long-term tumor control and increased responsiveness to immune checkpoint and adoptive cell therapies. The long-term tumor control by IRF2-deficient CD8+ T cells required continuous integration of both IFN-I and IFN-II signals. Thus, IRF2 is a foundational feedback molecule that redirects IFN signals to suppress T cell responses and represents a potential target to enhance cancer control.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Mass cytometry immunostaining protocol for multiplexing clinical samples.
In STAR Protocols on 16 September 2022 by Gadalla, R., Boukhaled, G. M., et al.
This is a cytometry by time-of-flight (CyTOF) staining protocol for hematopoietic-derived cells, that leverages live-cell barcoding using receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C (CD45) antibodies conjugated to metal isotopes in combination with DNA-based palladium barcoding to multiplex up to 40 samples. In this protocol, DNA-based barcoding is performed before surface and intracellular immunostaining, which reduces the batch effects that result from day-to-day variations in staining and instrument sensitivity. This protocol also reduces antibody consumption and eliminates the need for repeated instrument adjustment.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Humanized Mouse as a Tool to Predict Immunotoxicity of Human Biologics.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 17 November 2020 by Yong, K. S. M., Her, Z., et al.
Advancements in science enable researchers to constantly innovate and create novel biologics. However, the use of non-human animal models during the development of biologics impedes identification of precise in vivo interactions between the human immune system and treatments. Due to lack of this understanding, adverse effects are frequently observed in healthy volunteers and patients exposed to potential biologics during clinical trials. In this study, we evaluated and compared the effects of known immunotoxic biologics, Proleukin®/IL-2 and OKT3 in humanized mice (reconstituted with human fetal cells) to published clinical outcomes. We demonstrated that humanized mice were able to recapitulate in vivo pathological changes and human-specific immune responses, such as elevated cytokine levels and modulated lymphocytes and myeloid subsets. Given the high similarities of immunological side effects observed between humanized mice and clinical studies, this model could be used to assess immunotoxicity of biologics at a pre-clinical stage, without placing research participants and/or patients at risk.
Copyright © 2020 Yong, Her, Tan, Tan, Liu, Lai, Heng, Fan, Chang, Wang, Chan, Chen and Chen.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Cell on 11 February 2019 by Gide, T. N., Quek, C., et al.
Cancer immunotherapies provide survival benefits in responding patients, but many patients fail to respond. Identifying the biology of treatment response and resistance are a priority to optimize drug selection and improve patient outcomes. We performed transcriptomic and immune profiling on 158 tumor biopsies from melanoma patients treated with anti-PD-1 monotherapy (n = 63) or combined anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 (n = 57). These data identified activated T cell signatures and T cell populations in responders to both treatments. Further mass cytometry analysis identified an EOMES+CD69+CD45RO+ effector memory T cell phenotype that was significantly more abundant in responders to combined immunotherapy compared with non-responders (n = 18). The gene expression profile of this population was associated with longer progression-free survival in patients treated with single agent and greater tumor shrinkage in both treatments.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
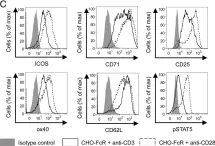
In J Immunol on 15 September 2015 by Gardner, D. H., Jeffery, L. E., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from J Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1