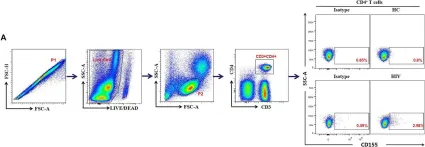
The application of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibodies has brought significant benefits to patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, not all patients respond to PD-1 immune therapy. The aim of this study was to identify response biomarkers to predict the efficacy of chemotherapy combined with anti-PD-1 therapy in NSCLC patients.
Thirty-two NSCLC patients receiving chemotherapy combined with anti-PD-1 therapy were recruited, and peripheral blood samples were collected before and after treatment. Flow cytometry was used to detect the proportions of circulating T-cell subsets, and cytokines in the blood serum were detected via ELISA.
The results revealed that, among the CR/PR group (CR, complete response; PR, partial response; n = 22), the proportions of CD3+TIM-3+PD-1+, CD3+CD4+TIM-3+PD-1+, and CD3+CD8+TIM-3+PD-1+, CD3+γδT+PD-1+, CD3+γδT+Vδ1+PD-1+, and CD3+γδT+Vδ2+PD-1+T cells were lower after treatment, with no significant differences found between the stable disease (SD) and progressive disease (PD) groups (n = 10). Some proinflammatory cytokines are highly expressed in patients with NSCLC.
This study suggests that monitoring changes in immune biomarkers in the circulating cells of NSCLC patients may help differentiate CR/PR patients from SD/PD patients, providing a potential new approach for assessing the efficacy of chemotherapy combined with anti-PD-1 therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Cao, Zhang, Guo, Wu, Guo, Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Li, Yang, He, Bai, Lv, Xie, Huang, Xiao, Deng, Li, Zhu, Jia, Yin and Wang.
Product Citations: 78
In Frontiers in Immunology on 1 May 2025 by Cao, J., Zhang, Y., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy : CII on 17 April 2025 by D'Alterio, C., Rea, G., et al.
The MITO-END3 trial compared carboplatin and paclitaxel (CP) with avelumab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel (CPA) as first-line treatment in endometrial cancer (EC) patients and demonstrated a significant interaction between avelumab response and mismatch repair status. To investigate prognostic/predictive biomarker, 29 MITO-END3-EC patients were evaluated at pretreatment (B1) and at the end of CP/CPA treatment (B2) for peripheral myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and Tregs. At B2, effector Tregs frequency was significantly higher in patients treated with CPA as compared to CP (p = 0.038). Both treatments (CP/CPA) induced significant decrease in peripheral M-MDSC (- 5.41%) in TCGA 2-MSI-high as compared to TCGA-category 4 tumors (p = 0.004). In accordance, both treatments induced M-MDSCs (+ 5.34%) in MSS patients as compared to MSI-high patients (p = 0.001). Moreover, in a subgroup of patients, primary tumors were highly infiltrated by M-MDSCs in MSS as compared to MSI-high ECs. A post hoc analysis displayed higher frequency of M-MDSCs (p = 0.020) and lower frequency of CD4+ (p < 0.005) at pretreatment in EC patients as compared to healthy donors. In conclusion, the peripheral evaluation of MDSCs and Tregs correlated with molecular features in EC treated with CP/CPA and may add insights in identifying EC patients responder to first-line chemo/chemo-immunotherapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 28 March 2025 by Jin, C., Chen, R., et al.
B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell immunotherapy has shown promising results in the treatment of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (R/RMM). This study presents the updated long-term outcomes from our center.
Between July 30, 2018, and September 27, 2023, 141 patients with R/RMM who received BCMA CAR-T therapy were enrolled. Patients underwent conditioning chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and fludarabine, followed by BCMA CAR-T cell infusion at a median dose of 2.36×106 cells/kg. The study evaluated overall response rates, long-term efficacy, safety profiles, and their associations with clinical and disease characteristics.
At a median follow-up of 20.2 months, the safety profile of the therapy was manageable. Grade 3/4 cytokine release syndrome occurred in 36.2% of patients, with no cases of severe neurotoxicity reported. 1-month post-infusion, grade ≥3 anemia persisted in 39.6% of patients, while neutropenia (43.3%) and thrombocytopenia (52.2%) were observed. The objective response rate (ORR) among evaluable patients was 94.8%, with 50.7% achieving a complete response (CR). The 4-year progression-free survival and overall survival rates were 37.4% (95% CI, 29.1% to 48.1%) and 63.2% (95% CI, 54.8% to 72.8%), respectively, with survival curves showing gradual flattening over time. Patients with a history of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and those with extramedullary disease demonstrated significantly inferior efficacy and survival outcomes. Peak CAR-T cell expansion was positively correlated with ORR (p<0.001) and CR (p<0.001). Notably, patients with prior ASCT exhibited significantly lower CAR-T cell expansion compared with those without prior ASCT (p<0.001). Immunophenotypic analysis of infused CAR-T cells demonstrated impaired fitness in patients who received ASCT in the past year.
BCMA CAR-T therapy in patients with R/RMM results in significant and sustained responses, with a manageable safety profile on a large scale. Prior ASCT and extramedullary disease represent adverse prognostic factors. Patients with a history of ASCT demonstrate limited peak CAR-T cell expansion.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Single cell suppression profiling of human regulatory T cells.
In Nature Communications on 3 February 2025 by Søndergaard, J. N., Tulyeu, J., et al.
Regulatory T cells (Treg) play an important role in regulating immune homeostasis in health and disease. Traditionally their suppressive function has been assayed by mixing purified cell populations, which does not provide an accurate picture of a physiologically relevant response. To overcome this limitation, we here develop 'single cell suppression profiling of human Tregs' (scSPOT). scSPOT uses a 52-marker CyTOF panel, a cell division detection algorithm, and a whole PBMC system to assess the effect of Tregs on all other cell types simultaneously. In this head-to-head comparison, we find Tregs having the clearest suppressive effects on effector memory CD8 T cells through partial division arrest, cell cycle inhibition, and effector molecule downregulation. Additionally, scSPOT identifies a Treg phenotypic split previously observed in viral infection and propose modes of action by the FDA-approved drugs Ipilimumab and Tazemetostat. scSPOT is thus scalable, robust, widely applicable, and may be used to better understand Treg immunobiology and screen for therapeutic compounds.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
LINE1 modulate human T cell function by regulating protein synthesis during the life span.
In Science Advances on 11 October 2024 by Burattin, F. V., Vadalà, R., et al.
The molecular mechanisms responsible for the heightened reactivity of quiescent T cells in human early life remain largely elusive. Our previous research identified that quiescent adult naïve CD4+ T cells express LINE1 (long interspersed nuclear elements 1) spliced in previously unknown isoforms, and their down-regulation marks the transition to activation. Here, we unveil that neonatal naïve T cell quiescence is characterized by enhanced energy production and protein synthesis. This phenotype is associated with the absence of LINE1 expression attributed to tonic T cell receptor/mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling and (polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 (PTBP1)-mediated LINE1 splicing suppression. The absence of LINE1 expression primes these cells for rapid execution of the activation program by directly regulating protein synthesis. LINE1 expression progressively increases in childhood and adults, peaking in elderly individuals, and, by decreasing protein synthesis, contributes to immune senescence in aging. Our study proposes LINE1 as a critical player of human T cell function across the human life span.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Front Immunol on 27 October 2018 by Yin, X., Liu, T., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1