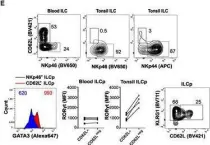
Human CD117+ CRTH2neg innate lymphoid cells (ILC) comprise multipotent precursors (ILCp), which are able to differentiate into subtypes in response to different signals received in peripheral tissues. NKp46+ ILCp have been reported to associate with ILC3 whereas KLRG1+ ILCp with ILC2, although the latter can also generate other ILC subsets, thus, maintaining a substantial plasticity. We here showed that CD62L is expressed by ILCp exclusively within KLRG1+ population and its expression marks a loss of their broad differentiation potential. Analysis of cytokine production and relevant markers demonstrated that CD62L+ ILCp mainly differentiate into ILC2 whereas CD62Lneg counterpart can also differentiate into other ILC subsets depending on the signals they receive. Remarkably, in peripheral blood of psoriatic patients, where ILC3 are usually enriched, CD62L+ ILC were drastically reduced, whereas CD62Lneg ILC2 upregulated both RORγt and NKp46, thus, suggesting an ongoing conversion to ILC3. Therefore, CD62L now emerges as a potential marker to identify a skewing toward type 2 among ILCp.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Product Citations: 13
In European Journal of Immunology on 1 July 2021 by Campana, S., De Pasquale, C., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancers on 16 July 2020 by Kim, N., Kim, M. Y., et al.
The BCR-ABL1 fusion gene generating an oncogenic tyrosine kinase is a hallmark of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), which can be successfully targeted by BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). However, treatment-free remission has been achieved in a minority of patients due to evolving TKI resistance and intolerance. Primary or acquired resistance to the approved TKIs and progression to blast crisis (BC), thus, remain a major clinical challenge that requires alternative therapeutic strategies. Here, we first demonstrate that donor natural killer (NK) cells prepared using a protocol adopted in clinical trials can efficiently eliminate CML-BC blasts, with TKI resistance regardless of BCR-ABL1 mutations, and preferentially target CD34+CD38- leukemic stem cells (LSC), a potential source of disease relapse. Mechanistically, the predominant expression of PVR, a ligand for the NK cell-activating DNAM-1 receptor, in concert with ICAM-1, a ligand for NK cell adhesion, confer this susceptibility to NK cells, despite the lack of ligands for NKG2D, a principal NK cell activating receptor, as an immune evasion mechanism. With these mechanistic insights, our findings provide a proof-of-concept that donor NK cell-based therapy is a viable strategy for overcoming TKI resistance in CML, particularly the advanced, multi-TKI-resistant CML with dismal outcome.
-
Cancer Research
Human NK cell receptor KIR2DS4 detects a conserved bacterial epitope presented by HLA-C.
In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on 25 June 2019 by Sim, M. J. W., Rajagopalan, S., et al.
Natural killer (NK) cells have an important role in immune defense against viruses and cancer. Activation of human NK cell cytotoxicity toward infected or tumor cells is regulated by killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) that bind to human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I). Combinations of KIR with HLA-I are genetically associated with susceptibility to disease. KIR2DS4, an activating member of the KIR family with poorly defined ligands, is a receptor of unknown function. Here, we show that KIR2DS4 has a strong preference for rare peptides carrying a Trp at position 8 (p8) of 9-mer peptides bound to HLA-C*05:01. The complex of a peptide bound to HLA-C*05:01 with a Trp at p8 was sufficient for activation of primary KIR2DS4+ NK cells, independent of activation by other receptors and of prior NK cell licensing. HLA-C*05:01+ cells that expressed the peptide epitope triggered KIR2DS4+ NK cell degranulation. We show an inverse correlation of the worldwide allele frequency of functional KIR2DS4 with that of HLA-C*05:01, indicative of functional interaction and balancing selection. We found a highly conserved peptide sequence motif for HLA-C*05:01-restricted activation of human KIR2DS4+ NK cells in bacterial recombinase A (RecA). KIR2DS4+ NK cells were stimulated by RecA epitopes from multiple human pathogens, including Helicobacter, Chlamydia, Brucella, and Campylobacter. We predict that over 1,000 bacterial species could activate NK cells through KIR2DS4, and propose that human NK cells also contribute to immune defense against bacteria through recognition of a conserved RecA epitope presented by HLA-C*05:01.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Cell on 13 December 2018 by André, P., Denis, C., et al.
Checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, only a minority of patients respond to these immunotherapies. Here, we report that blocking the inhibitory NKG2A receptor enhances tumor immunity by promoting both natural killer (NK) and CD8+ T cell effector functions in mice and humans. Monalizumab, a humanized anti-NKG2A antibody, enhanced NK cell activity against various tumor cells and rescued CD8+ T cell function in combination with PD-x axis blockade. Monalizumab also stimulated NK cell activity against antibody-coated target cells. Interim results of a phase II trial of monalizumab plus cetuximab in previously treated squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck showed a 31% objective response rate. Most common adverse events were fatigue (17%), pyrexia (13%), and headache (10%). NKG2A targeting with monalizumab is thus a novel checkpoint inhibitory mechanism promoting anti-tumor immunity by enhancing the activity of both T and NK cells, which may complement first-generation immunotherapies against cancer.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Research on 1 December 2018 by Sun, H., Xu, J., et al.
: We previously reported that deficiencies in natural killer (NK)-cell number and function play an important role in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon remain obscure. In this study, we analyzed the expression of CD160 on intrahepatic NK cells by evaluating peritumoral and intratumoral tissues of 279 patients with HCC and 20 healthy livers. We observed reduced expression of CD160 on intratumoral NK cells, and patients with lower CD160 cell densities within tumors exhibited worse disease and a higher recurrence rate. High-resolution microarray and gene set enrichment analysis of flow cytometry-sorted primary intrahepatic CD160+ and CD160- NK cells of healthy livers indicated that human CD160+ NK cells exhibited functional activation, high IFNγ production, and NK-mediated immunity. In addition, global transcriptomic analysis of sorted peritumoral and intratumoral CD160+ NK cells revealed that intratumoral CD160+ NK cells are more exhausted than peritumoral CD160+ NK cells and produce less IFNγ. High levels of TGFβ1 interfered with production of IFNγ by CD160+ NK cells, blocking of which specifically restored IFNγ production in CD160+ NK cells to normal levels. These findings indicate that reduced numbers of CD160+ NK cells, together with the functional impairment of CD160+ NK cells by TGFβ1, contribute to tumor immune escape. In addition, restoring the expression of CD160 and blocking TGFβ1 appear a promising therapeutic strategy against liver cancer. SIGNIFICANCE: These findings show that reduced number and function of CD160+ NK cells in the tumor microenvironment contributes to immune escape of HCC; blocking TGFβ1 restores IFNγ production of CD160+ NK cells.Graphical Abstract: http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/canres/78/23/6581/F1.large.jpg.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Cancer Research
In Eur J Immunol on 1 July 2021 by Campana, S., De Pasquale, C., et al.
Fig.1.M

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Eur J Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1