Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) resists immunotherapy due to its immunosuppressive microenvironment. Sarcoma homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) inhibits T cell receptor signaling, and its pharmacological inhibition is limited by poor selectivity and membrane permeability. Here, we generated CRISPR-edited SHP-1-knockout (KO) CD8+ T cells to enhance adoptive therapy against HCC. Single-cell RNA sequencing of HCC patient T cells revealed elevated SHP-1 in exhausted subsets. SHP-1-KO T cells exhibited increased effector memory T cells (TEM) proportions and enhanced IFN-γ/Granzyme B/perforin secretion, improving cytotoxicity against HCC lines. In humanized PDX models, SHP-1-KO T cells demonstrated superior tumor-killing activity. Transcriptomics identified upregulated lipid metabolism pathways, with HMGCR as a hub gene. Combining SHP-1-KO T cells with simvastatin (HMGCR inhibitor) synergistically amplified anti-HCC efficacy. This study proposes a dual strategy combining SHP-1-targeted cell therapy and metabolic modulation to overcome immunotherapy resistance, offering a translatable approach for HCC treatment.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Product Citations: 89
In IScience on 18 April 2025 by Liu, H., Ge, W., et al.
-
Cancer Research
In Molecular Therapy. Methods Clinical Development on 13 March 2025 by Hsieh, H. J., Urak, R., et al.
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling is involved in the growth of normal and cancer cells and is crucial for T cell activation. Previously, we have shown that AKT Inhibitor VIII, a selective AKT-1/2 inhibitor, during chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell manufacturing, improves CAR T cell function in preclinical models. Although AKT Inhibitor VIII could enhance CAR T cell function, AKT Inhibitor VIII is not a clinical-grade compound. However, pan-AKT inhibitors have been applied against cancers with PIK3CA/AKT/PTEN alterations in clinical trials. We evaluated ex vivo and in vivo strategies of enhancing CAR T cell therapeutic effect using the pan-AKT inhibitor capivasertib. We found that ex vivo 0.25 μM capivasertib treatment during the period of T cell stimulation during manufacture enhanced the antitumor activity of CAR T cells in B cell lymphoma mouse models. Mechanistically, capivasertib changed gene and protein expression patterns related to the functions of memory and effector CAR T cells. Furthermore, in vivo combination therapy of capivasertib and CD19-specific CAR T cells led to improved early response to and persistence of functional CAR T cells in mice bearing PTEN-deficient lymphoma cells compared to CAR T cells alone. Capivasertib exerts a similar function to AKT Inhibitor VIII in modulating CAR T cells, and combining CAR T cell therapy with capivasertib both ex vivo and in vivo offers the potential to improve patient outcomes. Since PTEN deficiency is common in cancer and is the main mechanism for capivasertib function, combination therapy may provide an alternative solution for the challenges of CAR T cell therapy.
© 2025 The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Immunology on 1 February 2025 by Song, F., Tsahouridis, O., et al.
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR T cells) with T stem (TSCM) cell-like phenotypic characteristics promote sustained antitumor effects. We performed an unbiased and automated high-throughput screen of a kinase-focused compound set to identify kinase inhibitors (KIs) that preserve human TSCM cell-like CAR T cells. We identified three KIs, UNC10225387B, UNC10225263A and UNC10112761A, that combined in vitro increased the frequency of CD45RA+CCR7+TCF1hi TSCM cell-like CAR T cells from both healthy donors and patients with cancer. KI-treated CAR T cells showed enhanced antitumor effects both in vitro and in vivo in mouse tumor models. The KI cocktail maintains TSCM cell-like phenotype preferentially in CAR T cells originating from naive T cells and causes transcriptomic changes without arresting T cell activation or modulating the chromatin organization. Specific kinases, ITK, ADCK3, MAP3K4 and CDK13, targeted by the KI cocktail in a dose-dependent manner are directly associated with the preservation of TSCM cell-like CAR T cells. Knockdown of these kinases individually or in combination enriches for TSCM cell-like CAR T cells, but only CAR T cells generated in the presence of the KI cocktail show robust expansion and differentiation on stimulation with tumor cells. Overall, transient pharmacological inhibition of strategically targeted kinases maintains stem-like features in CAR T cells and improves their antitumor activity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In IScience on 20 December 2024 by Mathews, J. A., Borovsky, D. T., et al.
Natural killer (NK) cell activity is influenced by cytokines and microenvironment factors, resulting in remarkably diverse functions, by contributing to inflammatory responses or serving as rheostats of adaptive immunity. Using single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), we identified a TGFβ1 highCD56brightNK cell population associated with hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients protected from acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). We further define a role for the combination of interleukin-2 (IL-2) and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) in promoting a regulatory phenotype in NK cells. "Induced" regulatory NK cells produce high amounts of TGF-β1, inhibited T cells, could promote naive T cells differentiation into regulatory T cells, and exhibited a unique transcriptional program that includes expression of IKZF2 (HELIOS) and ZNF683 (HOBIT). This phenotype was not stable, and "induced" regulatory NK cells lost the ability to secrete TGF-β1 upon exposure to different cytokines. These findings define protective CD56brightNK cells post-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and demonstrate the combination of IL-2 and TGF-β1 promotes regulatory activity in NK cells.
© 2024 The Author(s).
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases on 1 October 2024 by Luo, X., Li, J., et al.
This study investigates changes in immune cell subsets in peripheral blood of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients with colitis or terminal ileitis. It aims to explore the connection between changes in lymphocyte subsets and gut inflammation, providing insights for early detection.
Overall, 50 AS patients undergoing colonoscopy were enrolled. Flow cytometry was employed to analyze lymphocyte subsets, including T and B cells, in peripheral blood. Disease activity was assessed using CRP, ESR, BASDAI, ASDAS-CRP, and ASDAS-ESR.
Compared to AS patients without gut inflammation, those with colorectal inflammation showed a significant increase in total T cells (p < .05), an increase in exhausted CD4+ T cells (p < .05), and a decrease in Th2 cells and total Tc cells (p < .05). Notably, in AS patients with terminal ileitis, there was an increase in total B cells and classic switched B cells (p < .05), with a decrease in double-positive T cells (p < .05). However, no significant differences were observed in the distribution of Tfh-cell subpopulations (Tfh1, Tfh2, Tfh17) and Tc-cell subpopulations (Tc1, Tc2, Tc17) between AS patients with either colorectal inflammation or terminal ileitis (p > .05). We explored the relationship between disease activity scores, ESR, CRP, and lymphocyte subsets, but found no statistically significant correlation between them.
Distinct immune patterns may exist in AS with different types of intestinal inflammation. Colitis in AS is primarily characterized by a significant increase in exhausted CD4+ T cells, along with a decrease in Th2 cells. In contrast, terminal ileum inflammation in AS is marked by an increase in total B cells and classic switched B cells. These findings offer new insights for early detection and therapeutic intervention.
© 2024 Asia Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
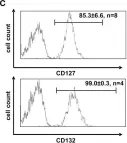
In Front Immunol on 25 February 2015 by Ziegler, H., Welker, C., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1