The application of CAR T therapy has significantly improved the efficacy of hematological tumors. However, there are still some challenges in the treatment of solid tumors, mainly because the complex immune microenvironment affects the proliferation of T cells, making T cells unable to function well. IL-15 has been reported to be a cytokine that can activate T cells and promote the proliferation and survival of T cells, especially CD8+ T cells. The complex formed by the high-affinity binding of IL-15 and IL-15Rα can bind to IL-2/IL-15Rβ/γ heterodimer on the surface of T cells, thereby activating downstream signaling pathways in T cells. In this study, we explored the activity of NKG2D-CAR T expressing IL-15/IL-15Rα complex (IL15C) on pancreatic cancer. The results of in vitro experiments showed that CAR T cells expressing IL15C had a stronger killing effect on tumor cells and showed a dose-dependent effect. In addition, the proliferation and anti-apoptosis levels of CAR T cells were enhanced after the co-expression of IL15C. IL15C regulates the function of T cells by activating the JAK/STAT5 signaling pathway of T cells. In vivo experiments showed that IL15C-NKG2D-CAR T cells could better inhibit tumor growth than the control group. This study provides a new idea for improving the efficacy of CAR T cells in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Jin, Guo, Hui, Ji, Huang, Xue, Gao, Ren, Lin, Zhou and Jiang.
Product Citations: 19
In Frontiers in Immunology on 8 July 2025 by Chen, Y., Jin, C., et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Immunology Research on 1 October 2024 by Dong, B., Obermajer, N., et al.
Cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocyte (CTL) recognition of non-mutated tumor-associated antigens (TAA), present on cancer cells and also in healthy tissues, is an important element of cancer immunity, but the mechanism of its selectivity for cancer cells and opportunities for its enhancement remain elusive. In this study, we found that CTL expression of the NK receptors (NKR) DNAM1 and NKG2D was associated with the effector status of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and long-term survival of patients with melanoma. Using MART1 and NY-ESO-1 as model TAAs, we demonstrated that DNAM1 and NKG2D regulate T-cell receptor (TCR) functional avidity and set the threshold for TCR activation of human TAA-specific CTLs. Superior co-stimulatory effects of DNAM1 over CD28 involved enhanced TCR signaling, CTL killer function, and polyfunctionality. Double transduction of human CTLs with TAA-specific TCR and NKRs resulted in strongly enhanced antigen sensitivity, without a reduction in antigen specificity and selectivity of killer function. In addition, the elevation of NKR ligand expression on cancer cells due to chemotherapy also increased CTL recognition of cancer cells expressing low levels of TAAs. Our data help explain the ability of self-antigens to mediate tumor rejection in the absence of autoimmunity and support the development of dual-targeting adoptive T-cell therapies that use NKRs to enhance the potency and selectivity of recognition of TAA-expressing cancer cells.
©2024 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Cancer Research
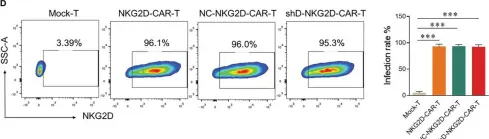
shRNA-mediated gene silencing of HDAC11 empowers CAR-T cells against prostate cancer.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 5 June 2024 by Zhang, H., Yao, J., et al.
Epigenetic mechanisms are involved in several cellular functions, and their role in the immune system is of prime importance. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are an important set of enzymes that regulate and catalyze the deacetylation process. HDACs have been proven beneficial targets for improving the efficacy of immunotherapies. HDAC11 is an enzyme involved in the negative regulation of T cell functions. Here, we investigated the potential of HDAC11 downregulation using RNA interference in CAR-T cells to improve immunotherapeutic outcomes against prostate cancer. We designed and tested four distinct short hairpin RNA (shRNA) sequences targeting HDAC11 to identify the most effective one for subsequent analyses. HDAC11-deficient CAR-T cells (shD-NKG2D-CAR-T) displayed better cytotoxicity than wild-type CAR-T cells against prostate cancer cell lines. This effect was attributed to enhanced activation, degranulation, and cytokine release ability of shD-NKG2D-CAR-T when co-cultured with prostate cancer cell lines. Our findings reveal that HDAC11 interference significantly enhances CAR-T cell proliferation, diminishes exhaustion markers PD-1 and TIM3, and promotes the formation of T central memory TCM populations. Further exploration into the underlying molecular mechanisms reveals increased expression of transcription factor Eomes, providing insight into the regulation of CAR-T cell differentiation. Finally, the shD-NKG2D-CAR-T cells provided efficient tumor control leading to improved survival of tumor-bearing mice in vivo as compared to their wild-type counterparts. The current study highlights the potential of HDAC11 downregulation in improving CAR-T cell therapy. The study will pave the way for further investigations focused on understanding and exploiting epigenetic mechanisms for immunotherapeutic outcomes.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Yao, Ajmal, Farooq and Jiang.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
FTO negatively regulates the cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells.
In EMBO Reports on 5 April 2023 by Kim, S. M., Oh, S. C., et al.
N6 -Methyladenosine (m6 A) is the most abundant epitranscriptomic mark and plays a fundamental role in almost every aspect of mRNA metabolism. Although m6 A writers and readers have been widely studied, the roles of m6 A erasers are not well-understood. Here, we investigate the role of FTO, one of the m6 A erasers, in natural killer (NK) cell immunity. We observe that FTO-deficient NK cells are hyperactivated. Fto knockout (Fto-/- ) mouse NK cells prevent melanoma metastasis in vivo, and FTO-deficient human NK cells enhance the antitumor response against leukemia in vitro. We find that FTO negatively regulates IL-2/15-driven JAK/STAT signaling by increasing the mRNA stability of suppressor of cytokine signaling protein (SOCS) family genes. Our results suggest that FTO is an essential modulator of NK cell immunity, providing a new immunotherapeutic strategy for allogeneic NK cell therapies.
© 2023 The Authors.
-
FC/FACS
In Biomedicines on 20 March 2023 by Huang, S., Tan, Y. Q., et al.
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a chronic T cell-mediated inflammatory disease. Interferon (IFN)-γ has been suggested to be vital for the OLP immune responses. A prominent innate-like lymphocyte subset, γδ T cells, span the innate-adaptive continuum and exert immune effector functions by producing a wide spectrum of cytokines, including IFN-γ. The involvement and mechanisms of γδ T cells in the pathogenesis of OLP remain obscure. The expression of γδ T cells in lesion tissues and in the peripheral blood of OLP patients was determined via flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Human leukocyte antigen-DR (HLA-DR), cluster of differentiation (CD) 69, Toll-like receptors (TLRs), natural killer group 2, member D (NKG2D) and IFN-γ were detected in γδ T cells of OLP patients using flow cytometry. Additionally, the involvement of stimulator of the interferon genes (STING)-TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) pathway in γδ T cells was evaluated by multi-color immunofluorescence. Western blotting was employed to investigate the regulatory mechanisms of γδ T cells in OLP. γδ T cells were significantly upregulated in the lesion tissues, whereas their peripheral counterparts were downregulated in OLP patients. Meanwhile, increased frequencies of local CD69+ and NKG2D+ γδ T cells and peripheral HLA-DR+ and TLR4+ γδ T cells were detected in OLP. Furthermore, significant co-localization of STING and TBK1 was observed in the γδ T cells of OLP lesions. In addition, enhanced IFN-γ and interleukin (IL)-17A were positively associated with the activated STING-TBK1 pathway and γδ T cells in OLP. Taken together, the upregulated STING-TBK1 pathway in activated γδ T cells might participate in the regulation of immune responses in OLP.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Front Immunol on 5 June 2024 by Zhang, H., Yao, J., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1