Lentiviral vector (LV)-mediated ex vivo gene therapy for haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) has delivered on the promise of a 'one-and-done' treatment for several genetic diseases1. However, ex vivo manipulation and patient conditioning before transplantation are major hurdles that could be overcome by an in vivo approach. Here we demonstrate that in vivo gene delivery to HSPCs after systemic LV administration is enabled by the substantial trafficking of these cells from the liver to the bone marrow in newborn mice. We improved gene-transfer efficiency using a phagocytosis-shielded LV, successfully reaching bona fide HSPCs capable of long-term multilineage output and engraftment after serial transplantation, as confirmed by clonal tracking. HSPC mobilization further increased gene transfer, extending the window of intervention, although permissiveness to LV transduction declined with age. We successfully tested this in vivo strategy in mouse models of adenosine deaminase deficiency, autosomal recessive osteopetrosis and Fanconi anaemia. Interestingly, in vivo gene transfer provided a selective advantage to corrected HSPCs in Fanconi anaemia, leading to near-complete haematopoietic reconstitution and prevention of bone marrow failure. Given that circulating HSPCs in humans are also most abundant shortly after birth, in vivo HSPC gene transfer holds strong translational potential across multiple diseases.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 106
In vivo haemopoietic stem cell gene therapy enabled by postnatal trafficking.
In Nature on 28 May 2025 by Milani, M., Fabiano, A., et al.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
An engineered palivizumab IgG2 subclass for synthetic gp130 and fas-mediated signaling.
In The Journal of Biological Chemistry on 1 March 2025 by Wittich, C., Ettich, J., et al.
Recently, we phenocopied interleukin (IL-)6 signaling using the dimerized single-chain variable fragment (scFv) derived from the respiratory syncytial virus IgG1-antibody palivizumab (PscFvLHFc) to activate a palivizumab antiidiotypic nanobody (AIPVHH)-gp130 receptor fusion protein. Palivizumab was unable to activate STAT3 signaling, so we aimed to create a similar ligand capable of triggering this pathway. Here, we created three variants of the ligand called PscFvLH0Fc, PscFvLH4Fc and PscFvLH8Fc by shortening the spacer region connecting PscFvLH and Fc from 23 amino acids in PscFvLHFc to 0 amino acids or expanding it by rigid linkers of four or eight alpha helical loops, respectively. The rigid-linker ligands had completely altered cellular activation patterns via AIPVHHgp130 fusion proteins. Deleting the extracellular stalk region between transmembrane and AIPVHH in the synthetic receptors AIP2VHHgp130Δstalk and AIP3VHHgp130Δstalk to increase rigidity and enhanced the biological activity of the short spacer PscFvFc ligands. Since scFv constructs are less stable than antibodies and have not been Food and Drug Administration approved, we looked for different antibody backbones. Transferring palivizumab's variable region to a more rigid and hence more agonistic IgG2 backbone (PIgG2) maintained affinity while improving agonistic properties activating cells expressing AIP2VHHgp130Δstalk and AIP3VHHgp130Δstalk but not their full-length counterparts. Furthermore, we engineered a tetravalent palivizumab variant (PscFvPIgG2) capable of inducing higher-order receptor clustering, activating Fas-induced apoptosis. In summary, we engineered a fully-synthetic cytokine/cytokine receptor pair based on the IgG2-variant of palivizumab and the AIPVHHgp130Δstalk variants opening avenues for therapeutic applications using nonphysiological targets in immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
Inhibition of Atg7 in intestinal epithelial cells drives resistance against Citrobacter rodentium.
In Cell Death & Disease on 19 February 2025 by Cune, D., Pitasi, C. L., et al.
Autophagy, a cytoprotective mechanism in intestinal epithelial cells, plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis. Beyond its cell-autonomous effects, the significance of autophagy in these cells is increasingly acknowledged in the dynamic interplay between the microbiota and the immune response. In the context of colon cancer, intestinal epithelium disruption of autophagy has been identified as a critical factor influencing tumor development. This disruption modulates the composition of the gut microbiota, eliciting an anti-tumoral immune response. Here, we report that Atg7 deficiency in intestinal epithelial cells shapes the intestinal microbiota leading to an associated limitation of colitis induced by Citrobacter rodentium infection. Mice with an inducible, intestinal epithelial-cell-specific deletion of the autophagy gene, Atg7, exhibited enhanced clearance of C. rodentium, mitigated hyperplasia, and reduced pathogen-induced goblet cell loss. This protective effect is linked to a higher proportion of neutrophils and phagocytic cells in the early phase of infection. At later stages, it is associated with the downregulation of pro-inflammatory pathways and an increase in Th17 and Treg responses-immune responses known for their protective roles against C. rodentium infection, modulated by specific gut microbiota. Fecal microbiota transplantation and antibiotic treatment approaches revealed that the Atg7-deficiency-shapped microbiota, especially Gram-positive bacteria, playing a central role in driving resistance to C. rodentium infection. In summary, our findings highlight that inhibiting autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells contributes to maintaining homeostasis and preventing detrimental intestinal inflammation through microbiota-mediated colonization resistance against C. rodentium. This underscores the central role played by autophagy in shaping the microbiota in promoting immune-mediated resistance against enteropathogens.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
In IScience on 16 August 2024 by Wenzek, C., Siemes, D., et al.
The immune system has emerged as an important target of thyroid hormones (THs); however, the role of TH in T cells has so far remained elusive. In this study, we assessed the effect of TH receptor α (TRα) signaling on activation and function of T cells. Our findings show that lack of canonical TRα action not only increased the frequency of regulatory T cells (Treg) but propelled an activated and migratory Treg phenotype and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation in Treg. Conversely, canonical TRα action reduced activation of the NF-κB pathway previously shown to play a pivotal role in Treg differentiation and function. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that TRα impacts T cell differentiation and phenotype. Given the well-known interaction of inflammation, immune responses, and TH axis in e.g., severe illness, altered TH-TRα signaling may have an important role in regulating T cell responses during disease.
© 2024 The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
FLASH Bragg-peak irradiation with a therapeutic carbon ion beam: first in vivo results
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 16 July 2024 by Tinganelli, W., Sokol, O., et al.
Background and purpose In recent years, ultra-high dose rate (UHDR) irradiation has emerged as a promising innovative approach to cancer treatment. Characteristic feature of this regimen, commonly referred to as FLASH effect, demonstrated primarily for electrons, photons or protons, is the improved normal tissue sparing, while the tumor control is similar to the one of the conventional dose-rate (CDR) treatments. The FLASH mechanism is, however, unknown. One major question is whether this effect is maintained when using densely ionizing (high-LET) heavy nuclei. Materials and Methods Here we report the effects of 20 Gy UHDR heavy ion irradiation in clinically relevant conditions, i.e., at high-LET in the spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP) of a 12 C beam using an osteosarcoma mouse model. Results We show that UHDR irradiation was less toxic in the normal tissue compared to CDR while maintaining tumor control. The immune activation was also comparable in UHDR and CDR groups. We observed that the gut microbiome was altered in mice injected with the tumor compared to healthy animals, but both UHDR and CDR exposures steered the metagenome toward a balanced state. Conclusions The results show that the FLASH effect is safe and effective in heavy ion therapy and provide an important benchmark for the current mechanistic FLASH models. Highlights - FLASH irradiation with SOBP carbon ions spares normal tissue in mouse - Tumor control, immune response, and gut microbioma changes are induced at the same extent both at conventional and ultra-high dose rate - FLASH carbon ion irradiation is a safe and effective alternative to conventional radiotherapy.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Int J Mol Sci on 27 April 2023 by Martins, A. C., Lima, I. S., et al.
Fig.1.G

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
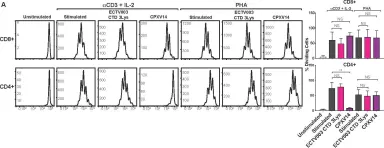
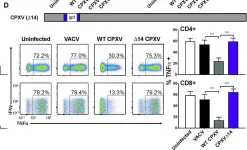
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
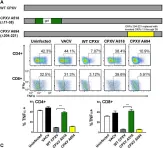
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
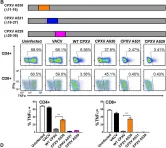
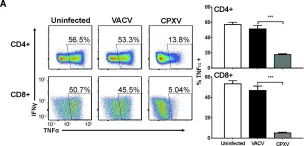
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
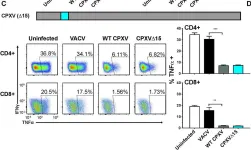
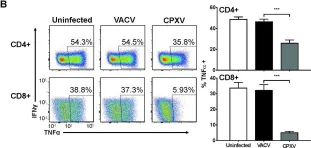
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
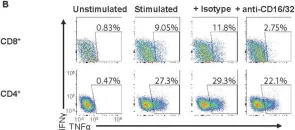
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
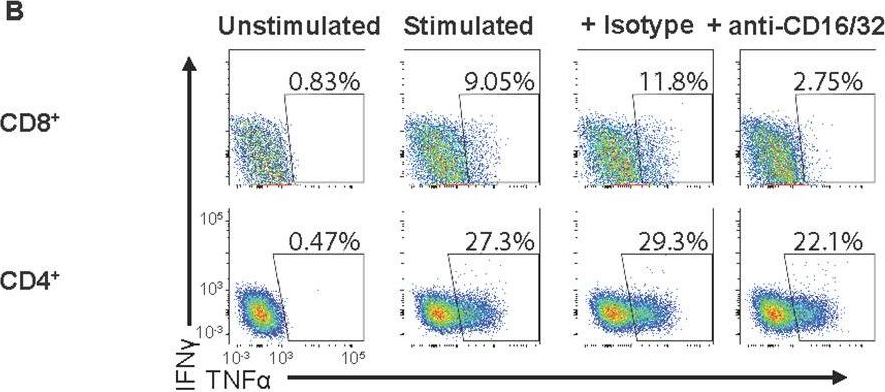
In PLoS Pathog on 1 September 2022 by Iyer, R. F., Edwards, D. M., et al.
Fig.5.B
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9