Lentiviral vector (LV)-mediated ex vivo gene therapy for haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) has delivered on the promise of a 'one-and-done' treatment for several genetic diseases1. However, ex vivo manipulation and patient conditioning before transplantation are major hurdles that could be overcome by an in vivo approach. Here we demonstrate that in vivo gene delivery to HSPCs after systemic LV administration is enabled by the substantial trafficking of these cells from the liver to the bone marrow in newborn mice. We improved gene-transfer efficiency using a phagocytosis-shielded LV, successfully reaching bona fide HSPCs capable of long-term multilineage output and engraftment after serial transplantation, as confirmed by clonal tracking. HSPC mobilization further increased gene transfer, extending the window of intervention, although permissiveness to LV transduction declined with age. We successfully tested this in vivo strategy in mouse models of adenosine deaminase deficiency, autosomal recessive osteopetrosis and Fanconi anaemia. Interestingly, in vivo gene transfer provided a selective advantage to corrected HSPCs in Fanconi anaemia, leading to near-complete haematopoietic reconstitution and prevention of bone marrow failure. Given that circulating HSPCs in humans are also most abundant shortly after birth, in vivo HSPC gene transfer holds strong translational potential across multiple diseases.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 36
In vivo haemopoietic stem cell gene therapy enabled by postnatal trafficking.
In Nature on 1 July 2025 by Milani, M., Fabiano, A., et al.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Single-cell profiling of MC1R-inhibited melanocytes.
In Pigment Cell Melanoma Research on 1 March 2024 by Berns, H. M., Watkins-Chow, D. E., et al.
The human red hair color (RHC) trait is caused by increased pheomelanin (red-yellow) and reduced eumelanin (black-brown) pigment in skin and hair due to diminished melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) function. In addition, individuals harboring the RHC trait are predisposed to melanoma development. While MC1R variants have been established as causative of RHC and are a well-defined risk factor for melanoma, it remains unclear mechanistically why decreased MC1R signaling alters pigmentation and increases melanoma susceptibility. Here, we use single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) of melanocytes isolated from RHC mouse models to define a MC1R-inhibited Gene Signature (MiGS) comprising a large set of previously unidentified genes which may be implicated in melanogenesis and oncogenic transformation. We show that one of the candidate MiGS genes, TBX3, a well-known anti-senescence transcription factor implicated in melanoma progression, binds both E-box and T-box elements to regulate genes associated with melanogenesis and senescence bypass. Our results provide key insights into further mechanisms by which melanocytes with reduced MC1R signaling may regulate pigmentation and offer new candidates of study toward understanding how individuals with the RHC phenotype are predisposed to melanoma.
© 2023 The Authors. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
-
Cancer Research
In Science Advances on 14 July 2023 by Pikkupeura, L. M., Bressan, R. B., et al.
During intestinal organogenesis, equipotent epithelial progenitors mature into phenotypically distinct stem cells that are responsible for lifelong maintenance of the tissue. While the morphological changes associated with the transition are well characterized, the molecular mechanisms underpinning the maturation process are not fully understood. Here, we leverage intestinal organoid cultures to profile transcriptional, chromatin accessibility, DNA methylation, and three-dimensional (3D) chromatin conformation landscapes in fetal and adult epithelial cells. We observed prominent differences in gene expression and enhancer activity, which are accompanied by local changes in 3D organization, DNA accessibility, and methylation between the two cellular states. Using integrative analyses, we identified sustained Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) transcriptional activity as a major gatekeeper of the immature fetal state. We found the YAP-associated transcriptional network to be regulated at various levels of chromatin organization and likely to be coordinated by changes in extracellular matrix composition. Together, our work highlights the value of unbiased profiling of regulatory landscapes for the identification of key mechanisms underlying tissue maturation.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
In Science Advances on 14 July 2023 by Hansen, S. L., Larsen, H. L., et al.
Generation of functionally mature organs requires exquisite control of transcriptional programs governing cell state transitions during development. Despite advances in understanding the behavior of adult intestinal stem cells and their progeny, the transcriptional regulators that control the emergence of the mature intestinal phenotype remain largely unknown. Using mouse fetal and adult small intestinal organoids, we uncover transcriptional differences between the fetal and adult state and identify rare adult-like cells present in fetal organoids. This suggests that fetal organoids have an inherent potential to mature, which is locked by a regulatory program. By implementing a CRISPR-Cas9 screen targeting transcriptional regulators expressed in fetal organoids, we establish Smarca4 and Smarcc1 as important factors safeguarding the immature progenitor state. Our approach demonstrates the utility of organoid models in the identification of factors regulating cell fate and state transitions during tissue maturation and reveals that SMARCA4 and SMARCC1 prevent precocious differentiation during intestinal development.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Nature Communications on 28 November 2022 by Takano, J., Ito, S., et al.
Polycomb group proteins (PcG), polycomb repressive complexes 1 and 2 (PRC1 and 2), repress lineage inappropriate genes during development to maintain proper cellular identities. It has been recognized that PRC1 localizes at the replication fork, however, the precise functions of PRC1 during DNA replication are elusive. Here, we reveal that a variant PRC1 containing PCGF1 (PCGF1-PRC1) prevents overloading of activators and chromatin remodeling factors on nascent DNA and thereby mediates proper deposition of nucleosomes and correct downstream chromatin configurations in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). This function of PCGF1-PRC1 in turn facilitates PRC2-mediated repression of target genes such as Hmga2 and restricts premature myeloid differentiation. PCGF1-PRC1, therefore, maintains the differentiation potential of HSPCs by linking proper nucleosome configuration at the replication fork with PcG-mediated gene silencing to ensure life-long hematopoiesis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
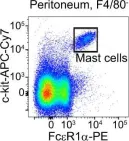
In Nat Commun on 18 November 2022 by Matsumura, T., Totani, H., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1