Exploring the impact of persistent mutations in SARS-CoV-2 variants and reduced immunity on breakthrough infections (BTIs) is crucial, particularly in understanding how antigen-specific memory B cells (MBCs) respond to new variants. We followed 107 participants who received the ancestral inactivated vaccine and experienced one or two Omicron BTIs over six months. Using flow cytometry, SARS-CoV-2 antigen probes, single-cell RNA sequencing, and B cell receptor (BCR) profiling, we assessed MBCs and immune diversity. Our findings revealed that although neutralizing antibody levels decreased over time, the number of specific MBCs remained stable and matured progressively. Notably, pre-existing Omicron-specific MBCs played a key role in preventing secondary Omicron infections. Differential gene analysis showed enrichment in antigen processing and immune regulation pathways, while clonal lineage analysis revealed more B cell expansion and V(D)J gene-specific rearrangements in high neutralization samples. These results emphasize MBCs' critical role in long-term immunity and inform future vaccination strategies.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Product Citations: 90
In IScience on 18 April 2025 by Chu, Q., Li, K., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Temperature-based MHC class-I multimer peptide exchange for human HLA-A, B and C
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 23 December 2024 by Pothast, C. R., Derksen, I., et al.
T cell recognition of specific antigens presented by major histocompatibility complexes class-I (MHC-I) can play an important role during immune responses against pathogens and cancer cells. Detection of T cell immunity is based on assessing the presence of antigen-specific cytotoxic CD8+ T cells using MHC class-I (MHC-I) multimer technology. Previously we have designed conditional peptides for HLA-A*02:01, H-2K b and HLA-E that form stable peptide-MHC-I-complexes at low temperatures and dissociate when exposed to a defined elevated temperature. The resulting conditional MHC-I complex can easily and without additional handling be exchanged with a peptide of interest, allowing to exchange peptides in a ready-to-use multimer and a high-throughput manner. Here we present data that this peptide-exchange technology is a general applicable, ready-to-use and fast approach to load many different peptides in MHC-I multimers for alleles of the HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C loci. We describe the development of conditional peptides for HLA-A*03:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-B*07:02 and HLA-C*07:02 that only form stable peptide-MHC-I complexes at low temperatures, allowing peptide exchange at higher defined temperature. We document the ease and flexibility of this technology by monitoring CD8+ T cell responses to virus-specific peptide-MHC complexes in patients. Graphical abstract Highlights T cell immunity relies on antigen-specific CD8+ T cells recognizing peptide MHC-I complexes. Establishing temperature-based peptide exchange across multiple HLA alleles, resulting in a robust, easy, and fast system to generate peptide MHC-I complexes. Temperature-based MHC class-I multimer demonstrate applicability across major MHC-I gene families for monitoring CD8+ T cell responses. Easy high-throughput peptide exchange potential, enhancing clinical utility of MHC multimer technology.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Protocol to construct humanized mice with adult CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
In STAR Protocols on 20 September 2024 by Yu, C. I., Maser, R., et al.
Humanized mice, defined as mice with human immune systems, have become an emerging model to study human hematopoiesis, infectious disease, and cancer. Here, we describe the techniques to generate humanized NSGF6 mice using adult human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). We describe steps for constructing and monitoring the engraftment of humanized mice. We then detail procedures for tissue processing and immunophenotyping by flow cytometry to evaluate the multilineage hematopoietic differentiation. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Yu et al.1.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
In Journal of Virology on 13 June 2024 by Rahmberg, A. R., Markowitz, T. E., et al.
Human and simian immunodeficiency viruses (HIV and SIV) are lentiviruses that reverse transcribe their RNA genome with subsequent integration into the genome of the target cell. How progressive infection and administration of antiretrovirals (ARVs) longitudinally influence the transcriptomic and epigenetic landscape of particular T cell subsets, and how these may influence the genetic location of integration are unclear. Here, we use RNAseq and ATACseq to study the transcriptomics and epigenetic landscape of longitudinally sampled naïve and memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in two species of non-human primates prior to SIV infection, during chronic SIV infection, and after administration of ARVs. We find that SIV infection leads to significant alteration to the transcriptomic profile of all T cell subsets that are only partially reversed by administration of ARVs. Epigenetic changes were more apparent in animals with longer periods of untreated SIV infection and correlated well with changes in corresponding gene expression. Known SIV integration sites did not vary due to SIV status but did contain more open chromatin in rhesus macaque memory T cells, and the expression of proteasome-related genes at the pre-SIV timepoint correlated with subsequent viremia.IMPORTANCEChronic inflammation during progressive human and simian immunodeficiency virus (HIV and SIV) infections leads to significant co-morbidities in infected individuals with significant consequences. Antiretroviral (ARV)-treated individuals also manifest increased levels of inflammation which are associated with increased mortalities. These data will help guide rational development of modalities to reduce inflammation observed in people living with HIV and suggest mechanisms underlying lentiviral integration site preferences.
-
FC/FACS
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland) on 6 April 2024 by Castro, F. O. F., Guilarde, A. O., et al.
This study evaluated the influence of cannabis and/or cocaine use in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- and cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific T-cell responses of people with HIV (PWH).
There was a higher percentage of IL-17-producing HIV-Gag-specific CD8+ T-cells in all drug users than that in PWH non-drug users. Stratifying the drug-user groups, increased percentages of IL-17-producing HIV-Gag-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells were found in PWH cannabis plus cocaine users compared to PWH non-drug users. In response to CMV, there were higher percentage of IL-17-producing CMV-specific CD8+ T-cell in PWH cocaine users than that in PWH non-drug users. Considering all drug users together, there was a higher percentage of SEB-stimulated IL-17-producing CD4+ T-cells than that in PWH non-drug users, whereas cannabis users had higher percentages of IL-17-producing CD4+ T-cells compared to non-drug users.
Cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 37 PWH undergoing antiretroviral therapy (ART) using cannabis (10), cocaine (7), or cannabis plus cocaine (10) and non-drug users (10) were stimulated with HIV-1 Gag or CMV-pp65 peptide pools, or staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) and evaluated for IFN-γ- and/or IL-17A-producing CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells using flow cytometry.
Cannabis plus cocaine use increased HIV-specific IL-17 producing T-cells and cocaine use increased IL-17 CMV-specific CD8+ T-cell responses which could favor the inflammatory conditions associated with IL-17 overproduction.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Plant Science
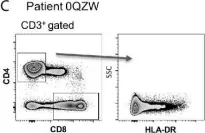
In Front Immunol on 18 May 2021 by Baumgaertner, P., Sankar, M., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1