Intraperitoneal cellular immunotherapy with CAR-redirected lymphocytes is an intriguing approach to target peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC) from ovarian cancer (OC), which is currently evaluated in clinical trials. PC displays a composite structure with floating tumor cells within ascites and solid-like masses invading the peritoneum. Therefore, a comprehensive experimental model is crucial to optimize CAR-cell therapies in such a peculiar environment. Here, we explored the activity of cytokine-induced killer lymphocytes (CIK), redirected by CAR against mesothelin (MSLN-CAR.CIK), within reductionistic 3D models resembling the structural complexity of both liquid and solid components of PC. MSLN-CAR.CIK effectively killed and were functionally efficient against OC targets. In a "floating-like" 3D context with floating OC spheroids, both tumor localization and killing by MSLN-CAR.CIK were significantly boosted by fluid flow. In a "solid-like" context, MSLN-CAR.CIK were recruited through the extracellular matrix on embedded tumor aggregates, with variable kinetics depending on the effector-target distance. Furthermore, MSLN-CAR.CIK penetrated the inner levels of OC spheroids exerting effective tumor killing. Our findings provide currently unknown therapeutically relevant information on intraperitoneal approaches with CAR.CIK, supporting further developments and improvements for clinical studies in the context of locoregional cell therapy approaches for patients with PC from OC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 23
In Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy : CII on 2 November 2024 by Galvagno, F., Leuci, V., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Redox Biology on 1 November 2024 by Heirman, P., Verswyvel, H., et al.
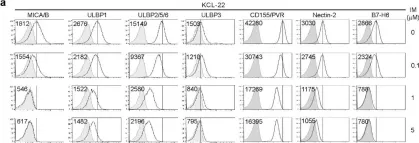
Non-thermal plasma (NTP) shows promise as a potent anti-cancer therapy with both cytotoxic and immunomodulatory effects. In this study, we investigate the chemical and biological effects of NTP-induced oxidation on several key, determinant immune checkpoints of natural killer (NK) cell function. We used molecular dynamics (MD) and umbrella sampling simulations to investigate the effect of NTP-induced oxidative changes on the MHC-I complexes HLA-Cw4 and HLA-E. Our simulations indicate that these chemical alterations do not significantly affect the binding affinity of these markers to their corresponding NK cell receptor, which is supported with experimental read-outs of ligand expression on human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells after NTP application. Broadening our scope to other key ligands for NK cell reactivity, we demonstrate rapid reduction in CD155 and CD112, target ligands of the inhibitory TIGIT axis, and in immune checkpoint CD73 immediately after treatment. Besides these transient chemical alterations, the reactive species in NTP cause a cascade of downstream cellular reactions. This is underlined by the upregulation of the stress proteins MICA/B, potent ligands for NK cell activation, 24 h post treatment. Taken together, this work corroborates the immunomodulatory potential of NTP, and sheds light on the interaction mechanisms between NTP and cancer cells.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In European Journal of Immunology on 1 September 2024 by Aublin-Gex, A., Jacolin, F., et al.
Hexokinases (HKs) control the first step of glucose catabolism. A switch of expression from liver HK (glucokinase, GCK) to the tumor isoenzyme HK2 is observed in hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Our prior work revealed that HK isoenzyme switch in hepatocytes not only regulates hepatic metabolic functions but also modulates innate immunity and sensitivity to Natural Killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity. This study investigates the impact of HK2 expression and its mitochondrial binding on the resistance of human liver cancer cells to NK-cell-induced cytolysis. We have shown that HK2 expression induces resistance to NK cell cytotoxicity in a process requiring mitochondrial binding of HK2. Neither HK2 nor GCK expression affects target cells' ability to activate NK cells. In contrast, mitochondrial binding of HK2 reduces effector caspase 3/7 activity both at baseline and upon NK-cell activation. Furthermore, HK2 tethering to mitochondria enhances their resistance to cytochrome c release triggered by tBID. These findings indicate that HK2 mitochondrial binding in liver cancer cells is an intrinsic resistance factor to cytolysis and an escape mechanism from immune surveillance.
© 2024 The Author(s). European Journal of Immunology published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Cytotoxic lymphocytes target characteristic biophysical vulnerabilities in cancer.
In Immunity on 11 May 2021 by Tello-Lafoz, M., Srpan, K., et al.
Immune cells identify and destroy tumors by recognizing cellular traits indicative of oncogenic transformation. In this study, we found that myocardin-related transcription factors (MRTFs), which promote migration and metastatic invasion, also sensitize cancer cells to the immune system. Melanoma and breast cancer cells with high MRTF expression were selectively eliminated by cytotoxic lymphocytes in mouse models of metastasis. This immunosurveillance phenotype was further enhanced by treatment with immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) antibodies. We also observed that high MRTF signaling in human melanoma is associated with ICB efficacy in patients. Using biophysical and functional assays, we showed that MRTF overexpression rigidified the filamentous actin cytoskeleton and that this mechanical change rendered mouse and human cancer cells more vulnerable to cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Collectively, these results suggest that immunosurveillance has a mechanical dimension, which we call mechanosurveillance, that is particularly relevant for the targeting of metastatic disease.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Oncology Reports on 1 February 2021 by Carré, T., Thiery, J., et al.
Resistance of tumor cells to cell‑mediated cytotoxicity remains an obstacle to the immunotherapy of cancer and its molecular basis is poorly understood. To investigate the acquisition of tumor resistance to cell‑mediated cytotoxicity, resistant variants were selected following long‑term natural killer (NK) cell selection pressure. It was observed that these variants were resistant to NK cell‑mediated lysis, but were sensitive to autologous cytotoxic T lymphocytes or cytotoxic drugs. This resistance appeared to be dependent, at least partly, on an alteration of target cell recognition by NK effector cells, but did not appear to involve any alterations in the expression of KIR, DNAM1 or NKG2D ligands on resistant cells, nor the induction of protective autophagy. In the present study, in order to gain further insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying the acquired tumor resistance to NK cell‑mediated cytotoxicity, a comprehensive analysis of the variant transcriptome was conducted. Comparative analysis identified an expression profile of genes that best distinguished resistant variants from parental sensitive cancer cells, with candidate genes putatively involved in NK cell‑mediated lysis resistance, but also in adhesion, migration and invasiveness, including upregulated genes, such as POT1, L1CAM or ECM1, and downregulated genes, such as B7‑H6 or UCHL1. Consequently, the selected variants were not only resistant to NK cell‑mediated lysis, but also displayed more aggressive properties. The findings of the present study emphasized that the role of NK cells may span far beyond the mere killing of malignant cells, and NK cells may be important effectors during cancer immunoediting.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancers (Basel) on 16 July 2020 by Kim, N., Kim, M. Y., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1