With recent advances in immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), immunotherapy has become the standard treatment for various malignant tumors. Their indications and dosages have been determined empirically, taking individually conducted clinical trials into consideration, but without a standard method to evaluate them. Here we establish an advanced imaging system to visualize human PD-1 microclusters, in which a minimal T cell receptor (TCR) signaling unit co-localizes with the inhibitory co-receptor PD-1 in vitro. In these microclusters PD-1 dephosphorylates both the TCR/CD3 complex and its downstream signaling molecules via the recruitment of a phosphatase, SHP2, upon stimulation with the ligand hPD-L1. In this system, blocking antibodies for hPD-1-hPD-L1 binding inhibits hPD-1 microcluster formation, and each therapeutic antibody (pembrolizumab, nivolumab, durvalumab and atezolizumab) is characterized by a proprietary optimal concentration and combinatorial efficiency enhancement. We propose that our imaging system could digitally evaluate PD-1-mediated T cell suppression to evaluate their clinical usefulness and to develop the most suitable combinations among ICIs or between ICIs and conventional cancer treatments.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 11
In Nature Communications on 6 June 2023 by Nishi, W., Wakamatsu, E., et al.
Water channel aquaporin 4 is required for T cell receptor mediated lymphocyte activation.
In Journal of Leukocyte Biology on 1 June 2023 by Nicosia, M., Lee, J., et al.
Aquaporins are a family of ubiquitously expressed transmembrane water channels implicated in a broad range of physiological functions. We have previously reported that aquaporin 4 (AQP4) is expressed on T cells and that treatment with a small molecule AQP4 inhibitor significantly delays T cell mediated heart allograft rejection. Using either genetic deletion or small molecule inhibitor, we show that AQP4 supports T cell receptor mediated activation of both mouse and human T cells. Intact AQP4 is required for optimal T cell receptor (TCR)-related signaling events, including nuclear translocation of transcription factors and phosphorylation of proximal TCR signaling molecules. AQP4 deficiency or inhibition impairs actin cytoskeleton rearrangements following TCR crosslinking, causing inferior TCR polarization and a loss of TCR signaling. Our findings reveal a novel function of AQP4 in T lymphocytes and identify AQP4 as a potential therapeutic target for preventing TCR-mediated T cell activation.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for Leukocyte Biology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Preprint on Research Square on 17 August 2022 by Nishi, W., Wakamatsu, E., et al.
With recent advances in immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), cancer immunotherapy has become the standard treatment for various malignant tumors. Their indications and dosages have been determined on the basis of several clinical trials conducted separately. In this study, we have established an advanced imaging system to visualize “human PD-1 microclusters,” in which PD-1 actually dephosphorylates both the TCR/CD3 complex and its downstream signaling molecules via the recruitment of a phosphatase, SHP2. Furthermore, each antibody required its own concentration and gained much greater effects in combination with other antibodies against different targets. We propose that our imaging system could digitally evaluate the PD-1-mediated T cell suppression and practical effects of each ICI. Currently, numerous new ICIs are tested, and more suitable combinations of them with other ICIs or conventional cancer treatments are being explored. Our study will have a wide range of applications to clinical practice in the future.
In Communications Biology on 14 May 2021 by Takehara, T., Wakamatsu, E., et al.
The coinhibitory receptor, PD-1, is of major importance for the suppression of T cell activation in various types of immune responses. A high-resolution imaging study showed that PD-1 forms a coinhibitory signalosome, "PD-1 microcluster", with the phosphatase, SHP2, to dephosphorylate the TCR/CD3 complex and its downstream signaling molecules. Such a consecutive reaction entirely depended on PD-1-PD-L1/2 binding. PD-L2 is expressed on professional antigen-presenting cells and also on some tumor cells, which possibly explains the discrepant efficacy of immune checkpoint therapy for PD-L1-negative tumors. Here, we performed precise imaging analysis of PD-L2 forming PD-1-PD-L2 clusters associating with SHP2. PD-L2 could compete with PD-L1 for binding to PD-1, occupying the same space at TCR microclusters. The PD-1 microcluster formation was inhibited by certain mAbs with functional consequences. Thus, PD-1 microcluster formation provides a visible index for the effectiveness of anti-PD-1- or anti-PD-L1/2-mediated T cell suppression. PD-L2 may exert immune suppressive responses cooperatively with PD-L1 on the microcluster scale.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 10 February 2021 by Ye, Z., Shen, Y., et al.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are two distinct autoimmune diseases that manifest with chronic synovial inflammation. Here, we show that CD4+ T cells from patients with RA and PsA have increased expression of the pore-forming calcium channel component ORAI3, thereby increasing the activity of the arachidonic acid-regulated calcium-selective (ARC) channel and making T cells sensitive to arachidonic acid. A similar increase does not occur in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Increased ORAI3 transcription in RA and PsA T cells is caused by reduced IKAROS expression, a transcriptional repressor of the ORAI3 promoter. Stimulation of the ARC channel with arachidonic acid induces not only a calcium influx, but also the phosphorylation of components of the T cell receptor signaling cascade. In a human synovium chimeric mouse model, silencing ORAI3 expression in adoptively transferred T cells from patients with RA attenuates tissue inflammation, while adoptive transfer of T cells from healthy individuals with reduced expression of IKAROS induces synovitis. We propose that increased ARC activity due to reduced IKAROS expression makes T cells more responsive and contributes to chronic inflammation in RA and PsA.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
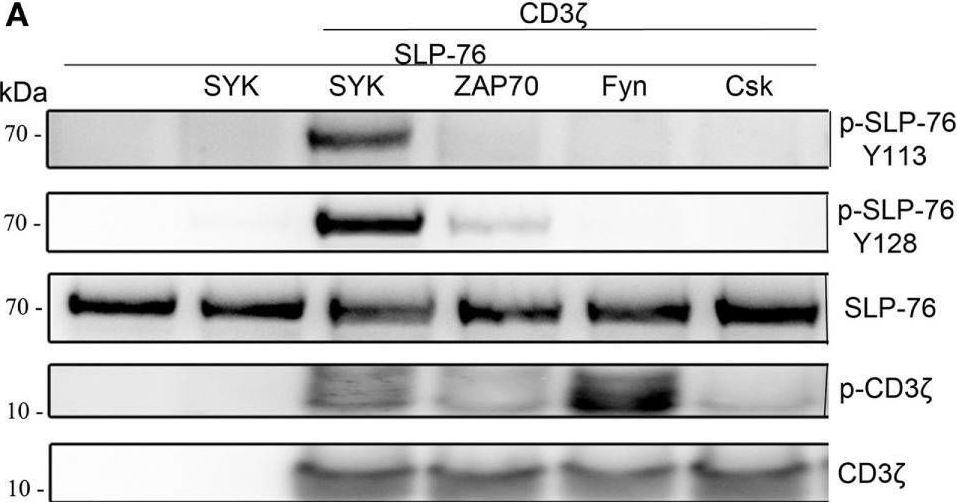
In Front Immunol on 25 July 2017 by Fasbender, F., Claus, M., et al.
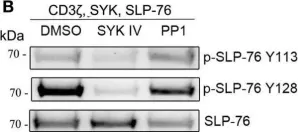
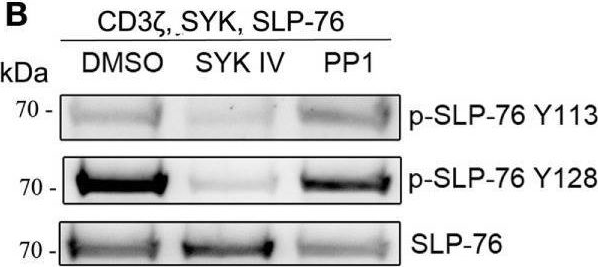
Fig.3.B
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Immunology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Front Immunol on 25 July 2017 by Fasbender, F., Claus, M., et al.
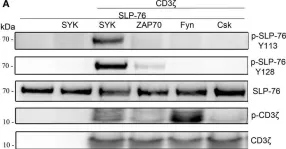
Fig.3.A
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Immunology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
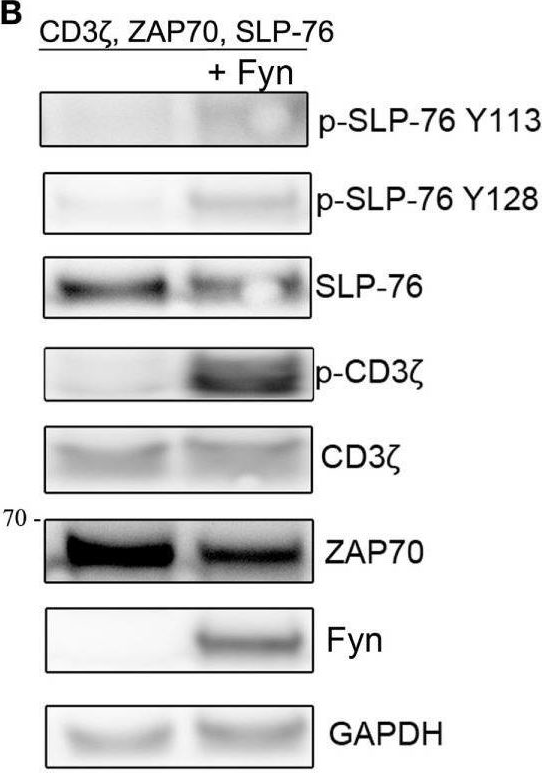
In Front Immunol on 25 July 2017 by Fasbender, F., Claus, M., et al.
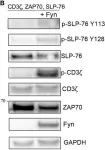
Fig.4.B
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Immunology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3