Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive breast cancer subtype and has the highest rate of recurrence1. The predominant standard of care for advanced TNBC is systemic chemotherapy with or without immunotherapy; however, responses are typically short lived1,2. Thus, there is an urgent need to develop more effective treatments. Components of the PI3K pathway represent plausible therapeutic targets; more than 70% of TNBCs have alterations in PIK3CA, AKT1 or PTEN3-6. However, in contrast to hormone-receptor-positive tumours, it is still unclear whether or how triple-negative disease will respond to PI3K pathway inhibitors7. Here we describe a promising AKT-inhibitor-based therapeutic combination for TNBC. Specifically, we show that AKT inhibitors synergize with agents that suppress the histone methyltransferase EZH2 and promote robust tumour regression in multiple TNBC models in vivo. AKT and EZH2 inhibitors exert these effects by first cooperatively driving basal-like TNBC cells into a more differentiated, luminal-like state, which cannot be effectively induced by either agent alone. Once TNBCs are differentiated, these agents kill them by hijacking signals that normally drive mammary gland involution. Using a machine learning approach, we developed a classifier that can be used to predict sensitivity. Together, these findings identify a promising therapeutic strategy for this highly aggressive tumour type and illustrate how deregulated epigenetic enzymes can insulate tumours from oncogenic vulnerabilities. These studies also reveal how developmental tissue-specific cell death pathways may be co-opted for therapeutic benefit.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 53
AKT and EZH2 inhibitors kill TNBCs by hijacking mechanisms of involution.
In Nature on 1 November 2024 by Schade, A. E., Perurena, N., et al.
Highly efficient generation of self-renewing trophoblast from human pluripotent stem cells.
In IScience on 18 October 2024 by Slamecka, J., Ryu, S., et al.
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) represent a powerful model system to study early developmental processes. However, lineage specification into trophectoderm (TE) and trophoblast (TB) differentiation remains poorly understood, and access to well-characterized placental cells for biomedical research is limited, largely depending on fetal tissues or cancer cell lines. Here, we developed novel strategies enabling highly efficient TE specification that generates cytotrophoblast (CTB) and multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast (STB), followed by the establishment of trophoblast stem cells (TSCs) capable of differentiating into extravillous trophoblast (EVT) and STB after long-term expansion. We confirmed stepwise and controlled induction of lineage- and cell-type-specific genes consistent with developmental biology principles and benchmarked typical features of placental cells using morphological, biochemical, genomics, epigenomics, and single-cell analyses. Charting a well-defined roadmap from hPSCs to distinct placental phenotypes provides invaluable opportunities for studying early human development, infertility, and pregnancy-associated diseases.
© 2024 The Author(s).
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Restraint of IFN-γ expression through a distal silencer CNS-28 for tissue homeostasis.
In Immunity on 9 May 2023 by Cui, K., Chen, Z., et al.
Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) is a key cytokine in response to viral or intracellular bacterial infection in mammals. While a number of enhancers are described to promote IFN-γ responses, to the best of our knowledge, no silencers for the Ifng gene have been identified. By examining H3K4me1 histone modification in naive CD4+ T cells within Ifng locus, we identified a silencer (CNS-28) that restrains Ifng expression. Mechanistically, CNS-28 maintains Ifng silence by diminishing enhancer-promoter interactions within Ifng locus in a GATA3-dependent but T-bet-independent manner. Functionally, CNS-28 restrains Ifng transcription in NK cells, CD4+ cells, and CD8+ T cells during both innate and adaptive immune responses. Moreover, CNS-28 deficiency resulted in repressed type 2 responses due to elevated IFN-γ expression, shifting Th1 and Th2 paradigm. Thus, CNS-28 activity ensures immune cell quiescence by cooperating with other regulatory cis elements within the Ifng gene locus to minimize autoimmunity.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
-
ChIP
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports Medicine on 21 March 2023 by Fischer, J. R., Jackson, H. W., et al.
Although breast cancer mortality is largely caused by metastasis, clinical decisions are based on analysis of the primary tumor and on lymph node involvement but not on the phenotype of disseminated cells. Here, we use multiplex imaging mass cytometry to compare single-cell phenotypes of primary breast tumors and matched lymph node metastases in 205 patients. We observe extensive phenotypic variability between primary and metastatic sites and that disseminated cell phenotypes frequently deviate from the clinical disease subtype. We identify single-cell phenotypes and spatial organizations of disseminated tumor cells that are associated with patient survival and a weaker survival association for high-risk phenotypes in the primary tumor. We show that p53 and GATA3 in lymph node metastases provide prognostic information beyond clinical classifiers and can be measured with standard methods. Molecular characterization of disseminated tumor cells is an untapped source of clinically applicable prognostic information for breast cancer.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 3 January 2023 by Wang, J., Cheng, M., et al.
Pigs are the most suitable model to study various therapeutic strategies and drugs for human beings, while knowledge about tissue- and cell type-specific transcriptomes and heterogeneity is poorly available. Here, we focused on the intestinal immunity of pigs. Through single-cell sequencing (scRNA-seq) and flow cytometry analysis of the types of immune cells in the jejunum of pigs, we found that innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) existed in the lamina propria lymphocytes (LPLs) of the jejunum. Then, through flow sorting of Live/Dead (L/D) - Lineage(LIN) - CD45 + cells and scRNA-seq, we found that ILCs in the porcine jejunum were mainly ILC3s, with a small number of ILC1s, ILC2s and NK cells. Through a gene expression map, we found that ILCs coexpressed IL-7Rα, ID2 and other genes and differentially expressed RORC, GATA3 and other genes but did not express the CD3 gene. According to their gene expression profiles, ILC3s can be divided into four subgroups, and genes such as CXCL8, CXCL2, IL-22, IL-17 and NCR2 are differentially expressed. To further detect and identify ILC3s, we prepared RORC monoclonal antibodies and verified the classification of ILCs in the porcine jejunum subgroup and the expression of related hallmark genes at the protein level by flow cytometry. For systematically characterizing of ILCs in the porcin intestines, we combined our pigs ILCs dataset with publicly available humans and mice ILCs data and identified that the humans and pigs ILCs shared more common features than that of mice in gene signatures and cell states. Our results for the first time showed in detail the gene expression of porcine jejunal ILCs, the subtype classification of ILCs and the markers of various ILCs, which provides a basis for in-depth exploration of porcine intestinal mucosal immunity. Graphical abstract
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Veterinary Research
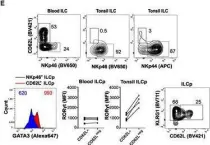
In Eur J Immunol on 1 July 2021 by Campana, S., De Pasquale, C., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Eur J Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
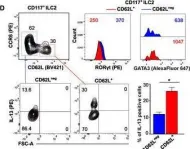
In Eur J Immunol on 1 July 2021 by Campana, S., De Pasquale, C., et al.
Fig.1.M

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Eur J Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Eur J Immunol on 1 July 2021 by Campana, S., De Pasquale, C., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Eur J Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3