The bone marrow (BM) niche is critical in regulating hematopoiesis, and sexual dimorphism and its underlying mechanism in the BM niche and its impact on hematopoiesis are not well understood. We show that male mice exhibited a higher abundance of leptin-receptor-expressing mesenchymal stromal cells (LepR-MSCs) compared with female mice. Sex-mismatched coculture and BM transplantation showed that the male BM niche provided superior support for in vitro colony formation and in vivo hematopoietic engraftment. The cotransplantation of male stromal cells significantly enhanced engraftment in female recipients. Single-cell RNA-seq revealed that the lower expression of the X-linked lysine H3K4 demethylase, Kdm5c, in male MSCs led to the increased expression of Cxcl12. In MSC-specific Kdm5c-KO mouse model, the reduction of KDM5C in female MSCs enhanced MSC quantity and function, ultimately improving engraftment to the male level. Kdm5c thus plays a role in driving sexual dimorphism in the BM niche and hematopoietic regeneration. Our study unveils a sex-dependent mechanism governing the BM niche regulation and its impact on hematopoietic engraftment. The finding offers potential implications for enhancing BM transplantation efficacy in clinical settings by harnessing the resource of male MSCs or targeting Kdm5c.
Product Citations: 45
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 21 January 2025 by Cui, X., Hou, L., et al.
Conserved role of hnRNPL in alternative splicing of epigenetic modifiers enables B cell activation.
In EMBO Reports on 1 June 2024 by Subramani, P. G., Fraszczak, J., et al.
The multifunctional RNA-binding protein hnRNPL is implicated in antibody class switching but its broader function in B cells is unknown. Here, we show that hnRNPL is essential for B cell activation, germinal center formation, and antibody responses. Upon activation, hnRNPL-deficient B cells show proliferation defects and increased apoptosis. Comparative analysis of RNA-seq data from activated B cells and another eight hnRNPL-depleted cell types reveals common effects on MYC and E2F transcriptional programs required for proliferation. Notably, while individual gene expression changes are cell type specific, several alternative splicing events affecting histone modifiers like KDM6A and SIRT1, are conserved across cell types. Moreover, hnRNPL-deficient B cells show global changes in H3K27me3 and H3K9ac. Epigenetic dysregulation after hnRNPL loss could underlie differential gene expression and upregulation of lncRNAs, and explain common and cell type-specific phenotypes, such as dysfunctional mitochondria and ROS overproduction in mouse B cells. Thus, hnRNPL is essential for the resting-to-activated B cell transition by regulating transcriptional programs and metabolism, at least in part through the alternative splicing of several histone modifiers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Immunity on 10 October 2023 by Arroyo-Diaz, N. M., Bachus, H., et al.
Lung-resident memory B cells (lung-BRMs) differentiate into plasma cells after reinfection, providing enhanced pulmonary protection. Here, we investigated the determinants of lung-BRM differentiation upon influenza infection. Kinetic analyses revealed that influenza nucleoprotein (NP)-specific BRMs preferentially differentiated early after infection and required T follicular helper (Tfh) cell help. BRM differentiation temporally coincided with transient interferon (IFN)-γ production by Tfh cells. Depletion of IFN-γ in Tfh cells prevented lung-BRM differentiation and impaired protection against heterosubtypic infection. IFN-γ was required for expression of the transcription factor T-bet by germinal center (GC) B cells, which promoted differentiation of a CXCR3+ GC B cell subset that were precursors of lung-BRMs and CXCR3+ memory B cells in the mediastinal lymph node. Absence of IFN-γ signaling or T-bet in GC B cells prevented CXCR3+ pre-memory precursor development and hampered CXCR3+ memory B cell differentiation and subsequent lung-BRM responses. Thus, Tfh-cell-derived IFN-γ is critical for lung-BRM development and pulmonary immunity, with implications for vaccination strategies targeting BRMs.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports on 28 March 2023 by Cui, X., Zhang, C., et al.
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) have the ability to self-renew and differentiate to all blood cell types. HSCs and their differentiated progeny show sex/gender differences. The fundamental mechanisms remain largely unexplored. We previously reported that latexin (Lxn) deletion increased HSC survival and repopulation capacity in female mice. Here, we find no differences in HSC function and hematopoiesis in Lxn knockout (Lxn-/-) male mice under physiologic and myelosuppressive conditions. We further find that Thbs1, a downstream target gene of Lxn in female HSCs, is repressed in male HSCs. Male-specific high expression of microRNA 98-3p (miR98-3p) contributes to Thbs1 suppression in male HSCs, thus abrogating the functional effect of Lxn in male HSCs and hematopoiesis. These findings uncover a regulatory mechanism involving a sex-chromosome-related microRNA and its differential control of Lxn-Thbs1 signaling in hematopoiesis and shed light on the process underlying sex dimorphism in both normal and malignant hematopoiesis.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
A cis-element at the Rorc locus regulates the development of type 3 innate lymphoid cells.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 28 March 2023 by Chang, D., Zhang, H., et al.
As an important early source of IL-17A and IL-22 in immune responses, type 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) are critically regulated by the transcription factor retinoic-acid-receptor-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt). Previously, we have identified a crucial role of the conserved non-coding sequence 9 (CNS9), located at +5,802 to +7,963 bp of the Rorc gene, in directing T helper 17 differentiation and related autoimmune disease. However, whether cis-acting elements regulate RORγt expression in ILC3s is unknown.
Here we show that CNS9 deficiency in mice not only decreases ILC3 signature gene expression and increases ILC1-gene expression features in total ILC3s, but also leads to generation of a distinct CD4+NKp46+ ILC3 population, though the overall numbers and frequencies of RORγt+ ILC3s are not affected. Mechanistically, CNS9 deficiency selectively decreases RORγt expression in ILC3s, which thus alters ILC3 gene expression features and promotes cell-intrinsic generation of CD4+NKp46+ ILC3 subset.
Our study thus identifies CNS9 as an essential cis-regulatory element controlling the lineage stability and plasticity of ILC3s through modulating expression levels of RORγt protein.
Copyright © 2023 Chang, Zhang, Ge, Xing, Guo, Wang and Dong.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
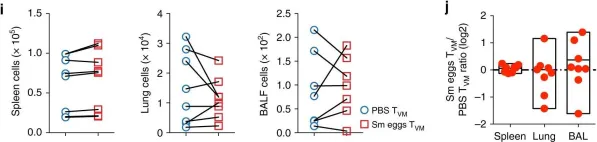
In Nat Commun on 30 October 2018 by Rolot, M., Dougall, A. M., et al.
Fig.7.I

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
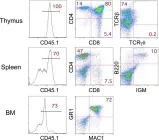
In Stem Cell Reports on 10 November 2015 by Ikawa, T., Masuda, K., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Stem Cell Reports by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2