Nonhuman primates have a key role in the evaluation of novel therapeutics including vaccine and drug development. Monitoring biochemical and hematological parameters of macaques is critical to understand toxicity and safety, but general reference intervals following standardized guidelines remain to be determined. Here we compiled multiple internal datasets to define normal ranges of classical biochemical and hematological parameters in Indian and Chinese rhesus macaques as well as cynomolgus macaques. Furthermore, the combination of hematological data with phenotypic information of cells obtained by flow cytometry enabled analyses of specific immune cell subsets. We found that vaccination generally induced transient changes at 24 h in cell frequencies accompanied by fluctuation in selected liver enzymes and metabolites. However, most parameters remained within our identified reference intervals. These deviations did not lead to noticeable side effects. Fluctuation in selected biochemical and hematological parameters was accompanied with differentiation of CD14+CD16+ intermediate monocytes and upregulation of genes associated with interleukin-1 signaling. By contrast, two animals with noticeable side effects showed sustained deviations. This study provides insights into baseline and vaccine-induced biochemical and hematological profiles of healthy macaques, facilitating the interpretation of toxicity and safety assessments in preclinical trials of novel therapies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 28
In Lab Animal on 1 June 2025 by Yan, X., Arcoverde Cerveira, R., et al.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
CD37 is a safe chimeric antigen receptor target to treat acute myeloid leukemia.
In Cell Reports Medicine on 18 June 2024 by Caulier, B., Joaquina, S., et al.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is characterized by the accumulation of immature myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the peripheral blood. Nearly half of the AML patients relapse after standard induction therapy, and new forms of therapy are urgently needed. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T therapy has so far not been successful in AML due to lack of efficacy and safety. Indeed, the most attractive antigen targets are stem cell markers such as CD33 or CD123. We demonstrate that CD37, a mature B cell marker, is expressed in AML samples, and its presence correlates with the European LeukemiaNet (ELN) 2017 risk stratification. We repurpose the anti-lymphoma CD37CAR for the treatment of AML and show that CD37CAR T cells specifically kill AML cells, secrete proinflammatory cytokines, and control cancer progression in vivo. Importantly, CD37CAR T cells display no toxicity toward hematopoietic stem cells. Thus, CD37 is a promising and safe CAR T cell AML target.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In NPJ Vaccines on 20 January 2024 by Lenart, K., Arcoverde Cerveira, R., et al.
The immune responses to Novavax's licensed NVX-CoV2373 nanoparticle Spike protein vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 remain incompletely understood. Here, we show in rhesus macaques that immunization with Matrix-MTM adjuvanted vaccines predominantly elicits immune events in local tissues with little spillover to the periphery. A third dose of an updated vaccine based on the Gamma (P.1) variant 7 months after two immunizations with licensed NVX-CoV2373 resulted in significant enhancement of anti-spike antibody titers and antibody breadth including neutralization of forward drift Omicron variants. The third immunization expanded the Spike-specific memory B cell pool, induced significant somatic hypermutation, and increased serum antibody avidity, indicating considerable affinity maturation. Seven months after immunization, vaccinated animals controlled infection by either WA-1 or P.1 strain, mediated by rapid anamnestic antibody and T cell responses in the lungs. In conclusion, a third immunization with an adjuvanted, low-dose recombinant protein vaccine significantly improved the quality of B cell responses, enhanced antibody breadth, and provided durable protection against SARS-CoV-2 challenge.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS Pathogens on 1 October 2023 by Mopuri, R., Welbourn, S., et al.
A protective HIV-1 vaccine has been hampered by a limited understanding of how B cells acquire neutralizing activity. Our previous vaccines expressing two different HIV-1 envelopes elicited robust antigen specific serum IgG titers in 20 rhesus macaques; yet serum from only two animals neutralized the autologous virus. Here, we used high throughput immunoglobulin receptor and single cell RNA sequencing to characterize the overall expansion, recall, and maturation of antigen specific B cells longitudinally over 90 weeks. Diversification and expansion of many B cell clonotypes occurred broadly in the absence of serum neutralization. However, in one animal that developed neutralization, two neutralizing B cell clonotypes arose from the same immunoglobulin germline and were tracked longitudinally. Early antibody variants with high identity to germline neutralized the autologous virus while later variants acquired somatic hypermutation and increased neutralization potency. The early engagement of precursors capable of neutralization with little to no SHM followed by prolonged affinity maturation allowed the two neutralizing lineages to successfully persist despite many other antigen specific B cells. The findings provide new insight into B cells responding to HIV-1 envelope during heterologous prime and boost immunization in rhesus macaques and the development of selected autologous neutralizing antibody lineages.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nuclear Medicine and Biology on 7 June 2022 by Meijer, L., Böszörményi, K. P., et al.
The aim of this study was to investigate the application of [18F]DPA714 to visualize the inflammation process in the lungs of SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus monkeys, focusing on the presence of pulmonary lesions, activation of mediastinal lymph nodes and surrounded lung tissue.
Four experimentally SARS-CoV-2 infected rhesus monkeys were followed for seven weeks post infection (pi) with a weekly PET-CT using [18F]DPA714. Two PET images, 10 min each, of a single field-of-view covering the chest area, were obtained 10 and 30 min after injection. To determine the infection process swabs, blood and bronchoalveolar lavages (BALs) were obtained.
All animals were positive for SARS-CoV-2 in both the swabs and BALs on multiple timepoints pi. The initial development of pulmonary lesions was already detected at the first scan, performed 2-days pi. PET revealed an increased tracer uptake in the pulmonary lesions and mediastinal lymph nodes of all animals from the first scan obtained after infection and onwards. However, also an increased uptake was detected in the lung tissue surrounding the lesions, which persisted until day 30 and then subsided by day 37-44 pi. In parallel, a similar pattern of increased expression of activation markers was observed on dendritic cells in blood.
This study illustrates that [18F]DPA714 is a valuable radiotracer to visualize SARS-CoV-2-associated pulmonary inflammation, which coincided with activation of dendritic cells in blood. [18F]DPA714 thus has the potential to be of added value as diagnostic tracer for other viral respiratory infections.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
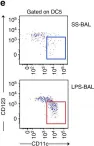
In Nat Commun on 30 April 2019 by Jardine, L., Wiscombe, S., et al.
Fig.4.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
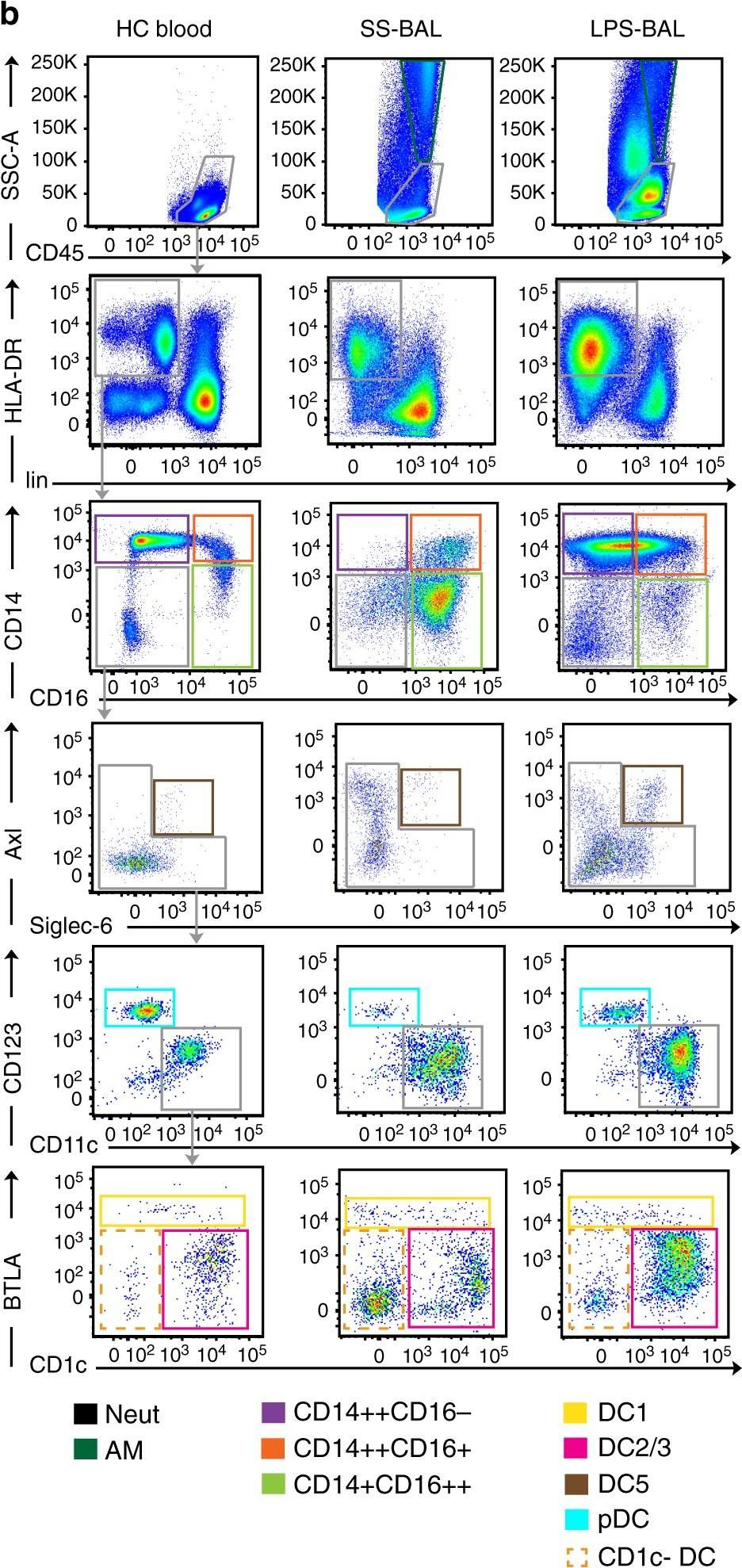
In Nat Commun on 30 April 2019 by Jardine, L., Wiscombe, S., et al.
Fig.1.B
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2