Metastatic melanoma patients benefit from the approved targeted BRAF inhibitor (BRAFi) therapy. Despite the great progress in the therapeutic approach to combat metastatic melanoma, fast emerging drug resistance in patients limits its long-term efficacy. In this study, we aimed to unravel the role of the p53 target gene CDKN1A/p21 in the response of melanoma cells towards BRAFi. We show that p53 activation increases BRAFi sensitivity in a synergistic manner exclusively in cells with a high expression of CDKN1A/p21. In a similar way, high expression of p21 was associated with a better response towards the mouse double minute 2 inhibitor (MDM2i) compared to those with low p21 expression. Indeed, p21 knockdown decreased the sensitivity towards both targeted therapies. The results indicate that the sensitivity of melanoma cells towards targeted therapies (BRAFi and MDM2i) is dependent on the p21 protein level in the cells. In addition to that, we found that p53 negatively regulates p73 expression; however, p73 seems not to have an influence on p53 expression. These findings offer new potential strategies for the treatment improvement of melanoma patients with high basal p21 levels with BRAFi by increasing treatment efficacy using combination therapies with p53 activating substances, which are able to further increase p21 expression levels. Furthermore, the data suggest that the expression and induction level of p21 could be used as a predictive biomarker in melanoma patients to forecast the outcome of a treatment with p53 activating substances and BRAFi. All in all, this manuscript shows the distinct role of p53 family members and its impact on melanoma therapy. In future, individualized treatment regimens based on p21 basal and induction levels could help melanoma patients with limited treatment options.
© 2022 The Authors. Experimental Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Product Citations: 5
Enhanced expression of p21 promotes sensitivity of melanoma cells towards targeted therapies.
In Experimental Dermatology on 1 August 2022 by Fröhlich, L. M., Makino, E., et al.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Clinical Cancer Research on 15 March 2019 by Sharif, T., Dai, C., et al.
Stem-like cancer cells, with characteristic self-renewal abilities, remain highly refractory to various clinical interventions. As such, stemness-inhibiting entities, such as tumor suppressor p53, are therapeutically pursued for their anticancer activities. Interestingly, similar implications for tumor suppressor TAp73 in regulating stemness features within stem-like cancer cells remain unknown.Experimental Design: This study utilizes various in vitro molecular biology techniques, including immunoblotting, qRT-PCR, and mass spectrometry-based proteomics, and metabolomics approaches to study the role of TAp73 in human and murine embryonal carcinoma stem-like cells (ECSLC) as well as human breast cancer stem-like cells (BCSLC). These findings were confirmed using patient-derived brain tumor-initiating cells (BTIC) and in vivo xenograft models.
TAp73 inhibition decreases the expression of stem cell transcription factors Oct4, Nanog, and Sox-2, as well as tumorsphere formation capacity in ECSLCs. In vivo, TAp73-deficient ECSLCs and BCSLCs demonstrate decreased tumorigenic potential when xenografted in mice. Mechanistically, TAp73 modifies the proline regulatory axis through regulation of enzymes GLS, OAT, and PYCR1 involved in the interconversion of proline-glutamine-ornithine. Further, TAp73 deficiency exacerbates glutamine dependency, enhances accumulation of reactive oxygen species through reduced superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) expression, and promotes differentiation by arresting cell cycle and elevating autophagy. Most importantly, the knockdown of TAp73 in CD133HI BTICs, separated from three different glioblastoma patients, strongly decreases the expression of prosurvival factors Sox-2, BMI-1, and SOD1, and profoundly decreases their self-renewal capacity as evidenced through their reduced tumorsphere formation ability.
Collectively, we reveal a clinically relevant aspect of cancer cell growth and stemness regulation through TAp73-mediated redox-sensitive metabolic reprogramming.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
In Cell Death & Disease on 11 September 2018 by Makino, E., Gutmann, V., et al.
The efficacy of targeted MAPK signalling pathway inhibitors (MAPKi) in metastatic melanoma therapy is limited by the development of resistance mechanisms that results in disease relapse. This situation still requires treatment alternatives for melanoma patients with acquired resistance to targeted therapy. We found that melanoma cells, which developed resistance towards MAPKi show an enhanced susceptibility to platinum-based drugs, such as cisplatin and carboplatin. We found that this enhanced susceptibility inversely correlates with the expression level of the p53 family member TAp73. We show that the lower expression of the TAp73 isoform in MAPKi-resistant melanoma cells enhances accumulation of DNA double-strand breaks upon cisplatin and carboplatin treatment by reducing the efficiency of nucleotide excision repair. These data suggest that a subgroup of melanoma patients with acquired resistance to MAPKi treatment and low TAp73 expression can benefit from chemotherapy with platinum-based drugs as a second-line therapy.
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
In Scientific Reports on 10 February 2015 by Jin, H., Suh, D. S., et al.
Infection with high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPVs) causes cervical cancer. E6 oncoprotein, an HPV gene product, inactivates the major gatekeeper p53. In contrast, its isoform, TAp73β, has become increasingly important, as it is resistant to E6. However, the intracellular signaling mechanisms that account for TAp73β tumor suppressor activity in cervix are poorly understood. Here, we identified that IER3 is a novel target gene of TAp73β. In particular, TAp73β exclusively transactivated IER3 in cervical cancer cells, whereas p53 and TAp63 failed to do. IER3 efficiently induced apoptosis, and its knockdown promoted survival of HeLa cells. In addition, TAp73β-induced cell death, but not p53-induced cell death, was inhibited upon IER3 silencing. Moreover, etoposide, a DNA-damaging chemotherapeutics, upregulated TAp73β and IER3 in a c-Abl tyrosine kinase-dependent manner, and the etoposide chemosensitivity of HeLa cells was largely determined by TAp73β-induced IER3. Of interest, cervical carcinomas from patients express no observable levels of two proteins. Thus, our findings suggest that IER3 is a putative tumor suppressor in the cervix, and the c-Ab1/p73β/IER3 axis is a novel and crucial signaling pathway that confers etoposide chemosensitivity. Therefore, TAp73β and IER3 induction would be a valuable checkpoint for successful therapeutic intervention of cervical carcinoma patients.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
Overexpressed TP73 induces apoptosis in medulloblastoma.
In BMC Cancer on 12 July 2007 by Castellino, R. C., De Bortoli, M., et al.
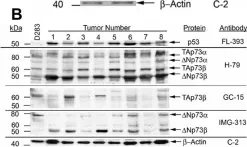
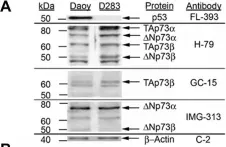
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor of childhood. Children who relapse usually die of their disease, which reflects resistance to radiation and/or chemotherapy. Improvements in outcome require a better understanding of the molecular basis of medulloblastoma growth and treatment response. TP73 is a member of the TP53 tumor suppressor gene family that has been found to be overexpressed in a variety of tumors and mediates apoptotic responses to genotoxic stress. In this study, we assessed expression of TP73 RNA species in patient tumor specimens and in medulloblastoma cell lines, and manipulated expression of full-length TAp73 and amino-terminal truncated DeltaNp73 to assess their effects on growth.
We analyzed medulloblastoma samples from thirty-four pediatric patients and the established medulloblastoma cell lines, Daoy and D283MED, for expression of TP73 RNA including the full-length transcript and the 5'-terminal variants that encode the DeltaNp73 isoform, as well as TP53 RNA using quantitative real time-RTPCR. Protein expression of TAp73 and DeltaNp73 was quantitated with immunoblotting methods. Clinical outcome was analyzed based on TP73 RNA and p53 protein expression. To determine effects of overexpression or knock-down of TAp73 and DeltaNp73 on cell cycle and apoptosis, we analyzed transiently transfected medulloblastoma cell lines with flow cytometric and TUNEL methods.
Patient medulloblastoma samples and cell lines expressed full-length and 5'-terminal variant TP73 RNA species in 100-fold excess compared to non-neoplastic brain controls. Western immunoblot analysis confirmed their elevated levels of TAp73 and amino-terminal truncated DeltaNp73 proteins. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed trends toward favorable overall and progression-free survival of patients whose tumors display TAp73 RNA overexpression. Overexpression of TAp73 or DeltaNp73 induced apoptosis under basal growth conditions in vitro and sensitized them to cell death in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
These results indicate that primary medulloblastomas express significant levels of TP73 isoforms, and suggest that they can modulate the survival and genotoxic responsiveness of medulloblastomas cells.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
In BMC Cancer on 12 July 2007 by Castellino, R. C., De Bortoli, M., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from BMC Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In BMC Cancer on 12 July 2007 by Castellino, R. C., De Bortoli, M., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from BMC Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2