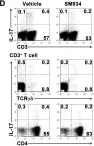
Chronic prostatitis is a common urological disorder in young and middle-aged men, characterized by frequent relapses and an unknown etiology. We investigated the potential function of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) -related ligands in chronic prostatitis in the current study.
In this study, we established the chronic experimental autoimmune prostatitis mouse model H&E staining was used to assess immune cell infiltration in prostate tissue, while RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses were performed to validate gene and protein expression differences across groups, respectively. Immunofluorescence staining was utilized to determine the spatial distribution of key proteins. Flow cytometry was conducted to analyze the proportions of immune cell populations in different experimental groups. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) was employed to knock down Igflr, and ELISA was used to measure cytokine levels in the peripheral blood of mice. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05, and all tests were conducted as two-tailed. Data analysis was performed using R software (version 4.2.2).
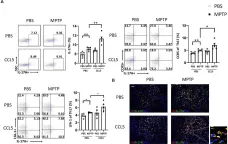
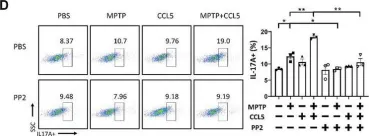
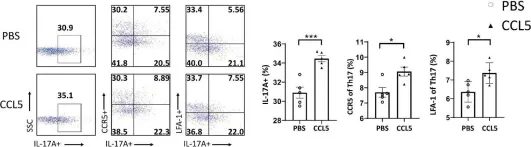
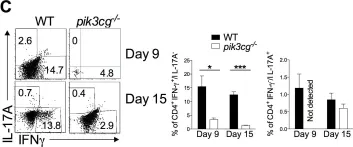
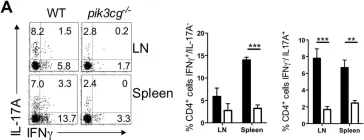
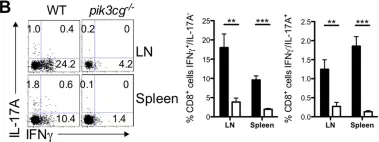
We successful established the EAP model and discovered that the expression of IGF1R, content of IGF1-related ligands, was highest in prostate tissue and CD4+ T cell subset. Furthermore, protein expression levels of IGF1R were also validated that upregulated in mouse prostate tissue. Colocalization of immunofluorescence suggested that IGF1R protein is highly expressed on CD4+ T cells. Stimulation with desIGF1, a truncated analogue of IGF1, resulted in the significantly increased prostate inflammation and pain scores observed in the EAP+desIGF1 group mouse compared to other groups In vitro study further suggested that desIGF1 could increase the proportion of Th17 cells while decreasing the proportion of Treg cells. In the EAP+AAV-shIgf1r group, the knock down function of igf1r led to the alleviative prostate inflammation and response frequency of pain behavior test. We found that calcium ion associated pathways are active in EAP by bioinformatics, and further validated that PKC-β protein with significantly increased expression noted in the EAP+desIGF1 group, and decreased in the EAP+AAV-shIgf1r group. We also found that the proportion of Th17 cells increased after activation of PKC- β by flow cytometry.
These findings support that PKC-β associated pathways mediated by IGF1/IGF1R axis may impact Th17 cell differentiation and exacerbating prostate inflammation in EAP mouse, providing new molecular targets for the clinical therapeutic strategy.
© 2025 Guan et al.
Product Citations: 197
IGF1R Promotes Th17/Treg Cell Development in Experimental Autoimmune Prostatitis.
In Journal of Inflammation Research on 5 May 2025 by Guan, Y., Yue, S., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In World Journal of Gastroenterology : WJG on 7 April 2025 by Lan, X., Zhang, H., et al.
Liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC) is a highly aggressive cancer with poor prognosis due to its complex tumor microenvironment (TME) and immune evasion. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play a critical role in tumor progression. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2), a key immune regulator, may modulate Treg activity and impact LIHC growth and metastasis.
To explore how the SOCS2 affects Treg activity in LIHC and its impact on tumor growth and metastasis.
LIHC transcriptome data from The Cancer Genome Atlas database were analyzed using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis, Estimation of Stromal and Immune Cells in Malignant Tumors Using Expression Data, and Cell-Type Identification by Estimating Relative Subsets of RNA Transcripts to evaluate immune pathways and Treg infiltration. Key prognostic genes were identified using Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis and machine learning. In vitro, co-culture experiments, migration assays, apoptosis detection, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were conducted. In vivo, tumor growth, metastasis, and apoptosis were assessed using subcutaneous and lung metastasis mouse models with hematoxylin and eosin staining, Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling, and immunohistochemistry analyses.
SOCS2 overexpression inhibited Treg cell activity, reducing LIHC cell migration and invasion while increasing apoptosis. In vivo, SOCS2 suppressed tumor growth and metastasis, confirming its therapeutic potential.
SOCS2 modulates CD4+ T function in the TME, contributing to LIHC progression. Targeting SOCS2 presents a potential therapeutic strategy for treating LIHC.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The causative effect of CXCR7 on experimental autoimmune prostatitis injury and fibrosis.
In International Immunopharmacology on 10 January 2025 by Zhang, Y., Feng, R., et al.
Chronic prostatitis and Pelvic Pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease characterized by pelvic or perineal pain and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the prostate. C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CXCR7) is an atypical chemokine receptor that has been shown to play a key role in inflammatory processes in prostate cancer. However, the role of CXCR7 in autoimmune prostate and immune regulation in CP/CPPS along with the mechanism of action for CXCR7 remains unclear. In this study, a mouse model of experimental autoimmune prostatitis (EAP) was constructed by subcutaneous injection of antigen, and CXCR7 agonist was administered to investigate the effects of CXCR7 on the proportion of immune cells and fibrosis in CP/CPPS. Western blotting, immunohistochemical staining and immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and masson's trichrome staining were used to study the regulatory mechanisms of CXCR7 in immune regulation. CXCR7 agonists can significantly reduce pain and prostatic inflammation, and in vivo flow cytometry studies showed that the antagonists restored the imbalance of the Th17/Treg cell ratio. To elucidate the potential mechanisms by which CXCR7 influences the pathogenesis of CP/CPPS, we conducted simultaneous RNA-seq and non-targeted metabolome sequencing. Our findings suggest that CXCR7 agonists alleviate fibrosis in autoimmune prostatitis by inhibiting the TGFβ/SMAD pathway. This study provides the foundation to target the immunological function of CXCR7 as a novel therapy for CP/CPPS.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Flotillin-2 dampens T cell antigen sensitivity and functionality.
In JCI Insight on 20 December 2024 by Moon, S., Zhao, F., et al.
T cell receptor (TCR) engagement triggers T cell responses, yet how TCR-mediated activation is regulated at the plasma membrane remains unclear. Here, we report that deleting the membrane scaffolding protein Flotillin-2 (Flot2) increases T cell antigen sensitivity, resulting in enhanced TCR signaling and effector function in response to weak TCR stimulation. T cell-specific Flot2-deficient mice exhibited reduced tumor growth and enhanced immunity to infection. Flot2-null CD4+ T cells exhibited increased Th1 polarization, proliferation, Nur77 induction, and phosphorylation of ZAP70 and ERK1/2 upon weak TCR stimulation, indicating a sensitized TCR-triggering threshold. Single-cell RNA-Seq suggested that Flot2-null CD4+ T cells follow a similar route of activation as WT CD4+ T cells but exhibit higher occupancy of a discrete activation state under weak TCR stimulation. Given prior reports that TCR clustering influences sensitivity of T cells to stimuli, we evaluated TCR distribution with super-resolution microscopy. Flot2 ablation increased the number of surface TCR nanoclusters on naive CD4+ T cells. Collectively, we posit that Flot2 modulates T cell functionality to weak TCR stimulation, at least in part, by regulating surface TCR clustering. Our findings have implications for improving T cell reactivity in diseases with poor antigenicity, such as cancer and chronic infections.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In International Immunopharmacology on 10 September 2024 by Zhu, S., Zou, M., et al.
Until 2021, colon cancer was a leading cancer globally. Early detection improves outcomes; however, advanced cases still having poor prognosis. Therefore, an understanding of associated molecular mechanisms is crucial for developing new preventive and therapeutic strategies for colon cancer.
The TCGA database was analyzed to assess melanocortin 1receptor (MC1R) expression in colon cancer and its link with patient prognosis. Further, models and diverse experimental techniques were employed to investigate the impact of MC1R on colon cancer progression and its underlying mechanism was elucidated.
In a follow-up study of clinical patients, the important role of MC1R was identified in the development of colon cancer. First, MC1R was expressed more highly in colon tumor tissues than in adjacent tissues. In addition, MC1R was associated with colon cancer prognosis, and higher expression of MC1R tended to predict a worse prognosis. This conclusion was verified in MC1R-/- mice, which showed a greater resistance to tumor growth than wild-type mice, as expected. Further investigation revealed a significant change in the portion of Tregs in MC1R-/- mice, while the portion of CD4 + and CD8 + T cells remained unchanged. The in vitro experiments revealed a weaker ability of the MC1R-/- T cells to differentiate into Tregs. Previous studies report that the functional integrity of Tregs is interwoven with cellular metabolism. Therefore, MC1R was deduced to regulate the differentiation of Tregs by reprogramming the metabolism. As expected, MC1R-/- T cells exhibited weaker mitochondrial function and a lower aerobic oxidation capacity. Concurrently, the MC1R-/- T cells had stronger limiting effects on colon cancer cells. According to these results, the MC1R inhibitor was hypothesized as a potential therapeutic agent to suppress colon cancer. The results showed that upon MC1R suppression, the tumors in the mice developed more slowly, and the mice survived longer, potentially providing a novel strategy to treat clinical colon cancer.
By regulating Tregs differentiation, MC1R overexpression in colon cancer correlates with poor prognosis, while MC1R inhibition shows potential as a therapeutic approach to slow tumor growth and enhance survival.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
In Front Aging Neurosci on 29 November 2023 by Zhao, J., An, K., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Aging Neurosci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Front Aging Neurosci on 29 November 2023 by Zhao, J., An, K., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Aging Neurosci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Front Aging Neurosci on 29 November 2023 by Zhao, J., An, K., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Aging Neurosci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
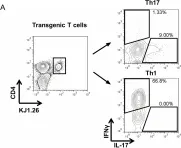
In PLoS One on 3 May 2014 by Wachowicz, K., Hermann-Kleiter, N., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS One on 21 November 2012 by Patakas, A., Benson, R. A., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS One on 3 October 2012 by Comerford, I., Litchfield, W., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS One on 3 October 2012 by Comerford, I., Litchfield, W., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS One on 3 October 2012 by Comerford, I., Litchfield, W., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS One on 6 March 2012 by Hou, L. F., He, S. J., et al.
Fig.6.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9