Enhancers possess both structural elements mediating promoter looping and functional elements mediating gene expression. Traditional models of enhancer-mediated gene regulation imply genomic overlap or immediate adjacency of these elements. We test this model by combining densely-tiled CRISPRa screening with nucleosome-resolution Region Capture Micro-C topology analysis. Using this integrated approach, we comprehensively define the cis -regulatory landscape for the tumor suppressor PTEN , identifying and validating 10 distinct enhancers and defining their 3D spatial organization. Unexpectedly, we identify several long-range functional enhancers whose promoter proximity is facilitated by chromatin loop anchors several kilobases away, and demonstrate that accounting for this spatial separation improves the computational prediction of validated enhancers. Thus, we propose a new model of enhancer organization incorporating spatial separation of essential functional and structural components.
Product Citations: 17
IntegrativePTENEnhancer Discovery Reveals a New Model of Enhancer Organization
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 22 September 2023 by Cerda-Smith, C. G., Hutchinson, H. M., et al.
In Haematologica on 1 June 2022 by Kuzilkova, D., Bugarin, C., et al.
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive cancer arising from lymphoblasts of T-cell origin. While TALL accounts for only 15% of childhood and 25% of adult ALL, 30% of patients relapse with a poor outcome. Targeted therapy of resistant and high-risk pediatric T-ALL is therefore urgently needed, together with precision medicine tools allowing the testing of efficacy in patient samples. Furthermore, leukemic cell heterogeneity requires drug response assessment at the single-cell level. Here we used single-cell mass cytometry to study signal transduction pathways such as JAK-STAT, PI3K-AKT-mTOR and MEK-ERK in 16 diagnostic and five relapsed T-ALL primary samples, and investigated the in vitro response of cells to Interleukin-7 (IL-7) and the inhibitor BEZ-235. T-ALL cells showed upregulated activity of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR and MEK-ERK pathways and increased expression of proliferation and translation markers. We found that perturbation induced by the ex vivo administration of either IL-7 or BEZ-235 reveals a high degree of exclusivity with respect to the phospho-protein responsiveness to these agents. Notably, these response signatures were maintained from diagnosis to relapse in individual patients. In conclusion, we demonstrated the power of mass cytometry single-cell profiling of signal transduction pathways in T-ALL. Taking advantage of this advanced approach, we were able to identify distinct clusters with different responsiveness to IL-7 and BEZ-235 that can persist at relapse. Collectively our observations can contribute to a better understanding of the complex signaling network governing T-ALL behavior and its correlation with influence on the response to therapy.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In IScience on 21 January 2022 by Stensland, Z. C., Coleman, B. M., et al.
Autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) is caused by aberrant activation of the immune system allowing autoreactive B and T cells to target the thyroid gland leading to disease. Although AITD is more frequently diagnosed in adults, children are also affected but rarely studied. Here, we performed phenotypic and functional characterization of peripheral blood immune cells from pediatric and adult-onset AITD patients and age-matched controls using mass cytometry. Major findings indicate that unlike adult-onset AITD patients, pediatric AITD patients exhibit a decrease in anergic B cells (BND) and DN2 B cells and an increase in immature B cells compared to age-matched controls. These results indicate alterations in peripheral blood immune cells seen in pediatric-onset AITD could lead to rapid progression of disease. Hence, this study demonstrates diversity of AITD by showing differences in immune cell phenotypes and function based on age of onset, and may inform future therapies.© 2021 The Authors.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
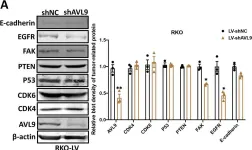
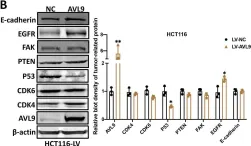
AVL9 promotes colorectal carcinoma cell migration via regulating EGFR expression.
In Biological Procedures Online on 6 January 2022 by Wu, Q., Chen, J., et al.
Despite advanced treatments could inhibit progression of colorectal carcinoma (CRC), the recurrence and metastasis remain challenging issues. Accumulating evidences implicated that AVL9 played a vital role in human cancers, but it's biological function and mechanism in CRC remain unclear.
To investigate the biological role and mechanism of AVL9 in colorectal carcinoma.
AVL9 expression was significantly upregulated in tumor tissues than that in matched normal tissues both at mRNA and protein levels. High expression of AVL9 was closely correlated with M status, stages and poor prognosis of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) patients. Functionally, AVL9 overexpression promoted cell migration rather than cell proliferation in vitro, whereas AVL9 knockdown exhibited the contrary results. Mechanistically, AVL9 regulated EGFR expression, and knockdown of EGFR restrained AVL9-induced cell migration.
These findings demonstrated that AVL9 contributed to CRC cell migration by regulating EGFR expression, suggesting a potential biomarker and treatment target for CRC.
© 2021. The Author(s).
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
RSRC1 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by regulating PTEN expression.
In Molecular Medicine Reports on 1 August 2019 by Yu, S., Gautam, N., et al.
Arginine/serine‑rich coiled coil 1 (RSRC1) is a gene which plays a significant role in the constitutive and alternative splicing of mRNA and transcriptional regulation. It has been implicated in various neurological disorders, as well as in cancer. However, its role in gastric cancer (GC) remains unknown. Thus, the present study aimed to investigate the role of RSRC1 in GC. RSRC1 expression in GC tissues was determined by RT‑qPCR and immunohistochemical staining. The effects of RSRC1 on cell proliferation and migration were detected using a Cell Counting Kit‑8 assay, 5‑ethynyl‑2'‑deoxyuridine (EdU) incorporation assay and a Transwell migration assay. Western blot analysis and RT‑qPCR were used to explore the molecular mechanisms of of action of RSRC1 in GC. The results indicated that RSRC1 expression was downregulated in GC tissues compared to paired normal tissues and the reduced expression of RSRC1 was shown to contribute to a poor prognosis of patients with GC. RSRC1 knockdown promoted the proliferation and migration of GC cells. In addition, the knockdown of RSRC1 decreased the expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN), a potent tumor suppressor gene controlling cellular growth and viability. On the whole, the findings of the present study indicate that RSRC1 functions as a tumor suppressor gene in GC and that it may exert its effects by regulating PTEN expression.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
In Biol Proced Online on 6 January 2022 by Wu, Q., Chen, J., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Biol Proced Online by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Biol Proced Online on 6 January 2022 by Wu, Q., Chen, J., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Biol Proced Online by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
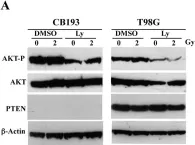
In Int J Oncol on 1 August 2013 by Millet, P., Granotier, C., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
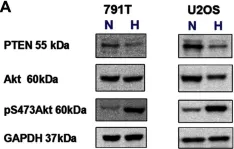
In PLoS One on 21 June 2013 by Adamski, J., Price, A., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4