Regenerative medicine aims to repair tissue defects and functional abnormalities by enhancing endogenous cellular processes. Additional to cell-based therapy, viral and nonviral gene therapies have raised substantial interest as promising approaches that allow the direct modulation of key signaling pathways for tissue regeneration in the body. E26 transformation-specific (ETS) variant transcription factor 2 (ETV2) is a well-validated transcription factor which enables vascular regeneration. The therapeutic efficacy of this factor was demonstrated using lentiviral-based in vivo transduction of ETV2 in a murine model of hindlimb ischemia (HLI). However, given the theoretical safety risks inherent to the clinical use of lentivirus, alternative approaches are considered desirable. Here, we investigated the use of a messenger RNA (mRNA)-based approach to in vivo induction of ETV2. Consistent with previous reports using ETV2 lentivirus, we show that ETV2 translated from synthetic mRNA promotes the upregulation of key endothelial genes in vitro. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the intramuscular injection of ETV2 mRNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticle (LNP) induces local expression of ETV2 protein in skeletal muscle stromal cells and accelerates blood flow recovery in a murine HLI model. These results provide the first demonstration of ETV2 mRNA with LNP as a potential therapeutic tool for targeting peripheral artery disease.
© 2025 The Authors.
Product Citations: 286
In Molecular Therapy. Nucleic Acids on 9 September 2025 by Toyonaga, H., Arai, K., et al.
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Genetics
In IScience on 20 June 2025 by Kaji, E., Nagao, J. I., et al.
Oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC) is an opportunistic infection caused by Candida albicans. IL-17-mediated immunity driven by Th17 cells plays a crucial role in defense against this infection. However, the location and mechanism by which the Th17 immune response is induced during OPC remain unclear. Here, we show that C. albicans in the gut enhances protection against OPC. Intestinal C. albicans is taken up by the mucosal immune system and triggers a systemic C. albicans-responsive Th17 cell response. Upon oral infection with C. albicans, these Th17 cells migrate from the gut to the oral region and accumulate in the tongue tissue, resulting in antifungal immune responses. The pathobiont-reactive Th17 cells developed in the gut strongly provide IL-17A not only locally in the mouth but also systemically in the serum upon OPC. Our findings highlight that fungal pathogen-responsive Th17 cells in the gut-mouth axis enhance protection against OPC.
© 2025 The Author(s).
In STAR Protocols on 20 June 2025 by Zaun, G., Liu, S., et al.
Murine orthotopic tumor models can accurately resemble cancer biology characteristics including metastasis, drug sensitivity, and remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. Here, we present a protocol for establishing murine orthotopic lung tumors and assessing contralateral pulmonary metastasis by flow cytometry. We describe steps for marking tumor cells with label retention dyes, preparing cell mixtures in Matrigel, and performing intrapulmonary injection. We then detail procedures for ex vivo processing of lungs followed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) data analysis and quantification of metastatic capacity. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Kalkavan et al.1.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer Research
In vivo haemopoietic stem cell gene therapy enabled by postnatal trafficking.
In Nature on 28 May 2025 by Milani, M., Fabiano, A., et al.
Lentiviral vector (LV)-mediated ex vivo gene therapy for haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) has delivered on the promise of a 'one-and-done' treatment for several genetic diseases1. However, ex vivo manipulation and patient conditioning before transplantation are major hurdles that could be overcome by an in vivo approach. Here we demonstrate that in vivo gene delivery to HSPCs after systemic LV administration is enabled by the substantial trafficking of these cells from the liver to the bone marrow in newborn mice. We improved gene-transfer efficiency using a phagocytosis-shielded LV, successfully reaching bona fide HSPCs capable of long-term multilineage output and engraftment after serial transplantation, as confirmed by clonal tracking. HSPC mobilization further increased gene transfer, extending the window of intervention, although permissiveness to LV transduction declined with age. We successfully tested this in vivo strategy in mouse models of adenosine deaminase deficiency, autosomal recessive osteopetrosis and Fanconi anaemia. Interestingly, in vivo gene transfer provided a selective advantage to corrected HSPCs in Fanconi anaemia, leading to near-complete haematopoietic reconstitution and prevention of bone marrow failure. Given that circulating HSPCs in humans are also most abundant shortly after birth, in vivo HSPC gene transfer holds strong translational potential across multiple diseases.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Enhancing the potency of in vivo lentiviral vector mediated gene therapy to hepatocytes.
In Nature Communications on 23 May 2025 by Canepari, C., Milani, M., et al.
In vivo gene therapy to the liver using lentiviral vectors (LV) may represent a one-and-done therapeutic approach for monogenic diseases. Increasing LV gene therapy potency is crucial for reducing the effective doses, thus alleviating dose-dependent toxicities and facilitating manufacturing. LV-mediated liver transduction may be enhanced by positively selecting LV-transduced hepatocytes after treatment (a posteriori) or by augmenting the initial fraction of LV-targeted hepatocytes (a priori). We show here that the a posteriori enhancement increased transgene output without expansion of hepatocytes bearing LV genomic integrations near cancer genes, in mouse models of hemophilia, an inherited coagulation disorder. Furthermore, we enhanced hepatocyte transduction a priori in mice by transiently inhibiting antiviral pathways and/or through a fasting regimen. The most promising transduction-enhancer combination synergized with phagocytosis-shielded LV, resulting in a remarkable 40-fold increase in transgene output. Overall, our work highlights the potential of minimally invasive, cost-effective treatments capable of improving the potency of in vivo LV gene therapy to hepatocytes, in order to expand its applicability and ease clinical translation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
In Nat Commun on 29 November 2021 by Heil, J., Olsavszky, V., et al.
Fig.1.F

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
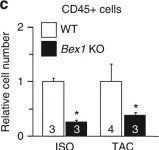
In Nat Commun on 30 November 2017 by Accornero, F., Schips, T. G., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2