Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most lethal primary brain tumor with intra-tumoral hierarchy of glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs). The heterogeneity of GSCs within GBM inevitably leads to treatment resistance and tumor recurrence. Molecular mechanisms of different cellular state GSCs remain unclear. Here, we find that classical (CL) and mesenchymal (MES) GSCs are enriched in reactive immune region and high CL-MES signature informs poor prognosis in GBM. Through integrated analyses of GSCs RNA sequencing and single-cell RNA sequencing datasets, we identify specific GSCs targets, including MEOX2 for the CL GSCs and SRGN for the MES GSCs. MEOX2-NOTCH and SRGN-NFκB axes play important roles in promoting proliferation and maintaining stemness and subtype signatures of CL and MES GSCs, respectively. In the tumor microenvironment, MEOX2 and SRGN mediate the resistance of CL and MES GSCs to macrophage phagocytosis. Using genetic and pharmacologic approaches, we identify FDA-approved drugs targeting MEOX2 and SRGN. Combined CL and MES GSCs targeting demonstrates enhanced efficacy, both in vitro and in vivo. Our results highlighted a therapeutic strategy for the elimination of heterogeneous GSCs populations through combinatorial targeting of MEOX2 and SRGN in GSCs.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 243
In Nature Communications on 26 March 2025 by Lu, C., Kang, T., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 20 March 2025 by Romano, M., Musicò, A., et al.
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive breast cancer subtype characterized by the absence of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, estrogen and progesterone receptors, limiting targeted therapy options. Cisplatin, a chemotherapeutic agent, induces DNA damage and exhibits some efficacy against triple-negative breast cancer, but its effectiveness is often reduced by chemoresistance and systemic toxicity. A very promising strategy to augment cisplatin treatment can be based on combining it with the biologic Cetuximab, an epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, which boosts cisplatin efficacy by inducing ferroptosis. To optimize this synergy in a biocompatible and precise manner, we developed a nanoplatform based on red blood cell-derived extracellular vesicles for the synergistic delivery of Cetuximab and cisplatin. This formulation increases cisplatin uptake, as demonstrated in vitro and in patient-derived organoids, effectively reduces chemoresistance by downregulating hypoxia-related genes and upregulating ferroptosis-associated genes, and enhances cisplatin cytotoxicity while mitigating hemotoxicity compared to free cisplatin administration.
-
Cancer Research
-
Cardiovascular biology
The microRNA-6510 as a potential tumor suppressor in head and neck cancer.
In Scientific Reports on 18 February 2025 by Sobecka-Giel, A., Ostrowska, K., et al.
Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most common cancer worldwide, with approximately 830,000 new cases and 430,000 deaths reported annually. Due to their heterogeneity, these neoplasms differ in their clinical course and response to the therapy. Therefore, it has become imperative to identify specific biological molecules that can potentially establish novel prognostic markers or targets for molecular therapy of HNSCC. MicroRNAs are a class of short, non-coding RNAs that function as post-transcriptional regulators of genes expression. They have been shown to be directly involved in oncogenesis, acting as tumor suppressors or oncogenes. Our previous study demonstrated that miRNA hsa-miR-6510-3p is significantly downregulated in tumor tissue compared to histologically normal tissue from HNSCC patients. Its significant downregulation in tumor tissue is associated with lower chances for recovery and patient's survival. This study aimed to determine the biological role of miR-6510-3p in HNSCC pathogenesis and its impact on biological processes occurring in cancer cells such as cell cycle, cell proliferation, migration or induction of cell death. We have also examined the impact of the miR-6510-3p on expression of cancer stem cell phenotype markers as well as on sensitivity of HNSCC cells to ionizing radiation. We observed that transfection of HNSCC cells with hsa-miR-6510-3p causes the cell cycle arrest in G2/M phase and is associated with a decrease of cell proliferation, migration and colony-forming ability of cancer cells. We have also demonstrated that hsa-miR-6510-3p induces cell death, increases the sensitivity of HNSCC cells to ionizing radiation and causes a loss of the stemness properties responsible for the occurrence of metastases and relapses of the disease. These results indicated the importance of miR-6510-3p as a marker and a driver of HNSCC disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
In Nature Communications on 9 January 2025 by Yang, L. X., Qi, C., et al.
Liver fibrosis is a critical liver disease that can progress to more severe manifestations, such as cirrhosis, yet no effective targeted therapies are available. Here, we identify that ATF4, a master transcription factor in ER stress response, promotes liver fibrosis by facilitating a stress response-independent epigenetic program in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Unlike its canonical role in regulating UPR genes during ER stress, ATF4 activates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) gene transcription under fibrogenic conditions. HSC-specific depletion of ATF4 suppresses liver fibrosis in vivo. Mechanistically, TGFβ resets ATF4 to orchestrate a unique enhancer program for the transcriptional activation of pro-fibrotic EMT genes. Analysis of human data confirms a strong correlation between HSC ATF4 expression and liver fibrosis progression. Importantly, a small molecule inhibitor targeting ATF4 translation effectively mitigates liver fibrosis. Together, our findings identify a mechanism promoting liver fibrosis and reveal new opportunities for treating this otherwise non-targetable disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
In Discov Oncol on 24 November 2024 by Chen, D. & Yin, R.
Engrailed 2 (EN2) is a homeodomain-containing protein whose aberrant expression is observed in various cancer types, yet its role in breast cancer remains unclear. This study investigates the roles and mechanisms of EN2 in breast cancer progression. Using online dataset analysis, we assessed the correlation between EN2 expression and breast cancer progression and chemotherapeutic sensitivity. Functional assays, including RT-qPCR, Western blot, cell viability, transwell migration and invasion, spheroid formation, and flow cytometry, were conducted to explore EN2's role. Mechanistic insights were obtained through luciferase reporter assays, ChIP, and Caspase 3 activity detection. Our results showed that EN2 is highly expressed in breast cancer patients, negatively correlating with survival rates and positively with disease progression and reduced chemotherapy sensitivity. Functional experiments confirmed EN2's oncogenic role, and it was found to promote the expression of the oncogenic Tenascin-C (TNC) gene. Notably, EN2 directly interacts with the super-enhancer region within the TNC locus. Elevated TNC expression mitigated the effects of EN2 knockdown on breast cancer cell progression. Our study unveils a novel mechanism by which EN2 regulates the TNC locus super-enhancer, thereby activating oncogenic pathways in breast cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
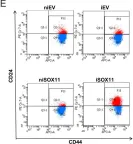
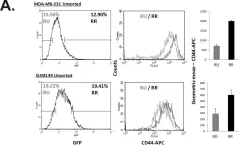
In Elife on 10 September 2020 by Oliemuller, E., Newman, R., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
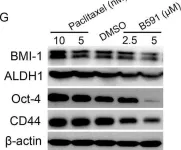
In Oncogene on 1 May 2019 by Zhou, H., Yu, C., et al.
Fig.3.G

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncogene by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
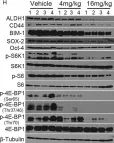
In Oncogene on 1 May 2019 by Zhou, H., Yu, C., et al.
Fig.5.H

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncogene by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
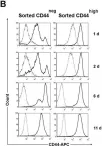
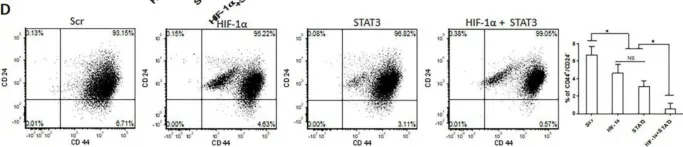
In Oncotarget on 20 July 2018 by Di Stefano, C., Grazioli, P., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
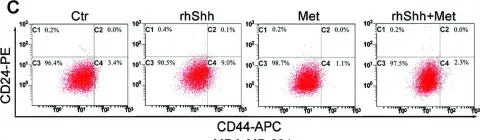
In Cancers (Basel) on 14 October 2017 by Soleymani Abyaneh, H., Gupta, N., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
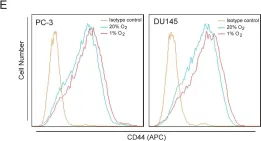
In Int J Mol Med on 1 July 2015 by Fan, C., Wang, Y., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Oncotarget on 30 April 2015 by Jung, K., Gupta, N., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS One on 5 January 2012 by Ma, Y., Liang, D., et al.
Fig.5.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In PLoS One on 5 January 2012 by Ma, Y., Liang, D., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9