In patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intratumoural and intertumoural heterogeneity increases chemoresistance and mortality rates. However, such morphological and phenotypic diversities are not typically captured by organoid models of PDAC. Here we show that branched organoids embedded in collagen gels can recapitulate the phenotypic landscape seen in murine and human PDAC, that the pronounced molecular and morphological intratumoural and intertumoural heterogeneity of organoids is governed by defined transcriptional programmes (notably, epithelial-to-mesenchymal plasticity), and that different organoid phenotypes represent distinct tumour-cell states with unique biological features in vivo. We also show that phenotype-specific therapeutic vulnerabilities and modes of treatment-induced phenotype reprogramming can be captured in phenotypic heterogeneity maps. Our methodology and analyses of tumour-cell heterogeneity in PDAC may guide the development of phenotype-targeted treatment strategies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 21
In Nature Biomedical Engineering on 1 June 2025 by Papargyriou, A., Najajreh, M., et al.
-
Cancer Research
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 18 April 2025 by Prakash, P. G., Kumar, N., et al.
The uterine cervix is a critical mucosal interface that balances immune defense and reproductive function, yet how its distinct epithelial compartments coordinate responses to infection remains unclear. Here, we integrate patient-derived 3D cervical organoids, single-cell transcriptomics and native tissue analysis to construct a high-resolution atlas of epithelial cell diversity and immune dynamics during Chlamydia trachomatis infection. We demonstrate that cervical organoids precisely mirror native tissue at both transcriptional and cellular levels, identifying epithelial subtypes with region-specific immune specializations. Upon infection, ectocervical epithelia reinforce barrier integrity, whereas endocervical epithelia, particularly uninfected bystander cells, exhibit extensive transcriptional reprogramming characterized by robust interferon activation, antigen presentation, and antimicrobial defense. Infection profoundly reshapes epithelial intercellular communication, positioning bystander cells as central signaling hubs that coordinate immune responses and tissue regeneration. Our findings highlight a sophisticated epithelial-intrinsic immune network critical for cervical mucosal defense and establish a physiologically relevant platform for studying human host-pathogen interactions and guiding targeted mucosal therapies against reproductive tract infections and pathologies.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Experimental & Molecular Medicine on 1 April 2025 by Lee, H. J., Lim, S. H., et al.
Phospholipase D6 (PLD6) is a critical enzyme involved in mitochondrial fusion with a key role in spermatogenesis. However, the role of PLD6 in cancer remains unknown. Notably, Wnt signaling, energy metabolism and mitochondrial function show complex interactions in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. Here we found that PLD6 is highly expressed in CRC and positively correlated with poor prognosis. We present a novel function of PLD6 in activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling by enhancing mitochondrial metabolism. PLD6 depletion suppresses the oncogenic properties of CRC cells and impairs mitochondrial respiration, leading to reduced mitochondrial length, membrane potential, calcium levels and reactive oxygen species. PLD6 depletion also disrupts mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming by inhibiting the tricarboxylic acid cycle and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, resulting in altered intracellular levels of citrate and acetyl-CoA-both key modulators of Wnt/β-catenin activation. PLD6-mediated acetyl-CoA production enhances β-catenin stability by promoting its acetylation via the acetyltransferases CREB-binding protein and P300/CREB-binding-protein-associated factor. Consequently, PLD6 ablation reduces cancer stem cell-associated gene expression downstream of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, suppressing stem-like traits and chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil. Furthermore, PLD6 depletion attenuates CRC tumorigenesis in both subcutaneous and orthotopic tumor models. Overall, PLD6 acts as an oncogenic switch by promoting mitochondria-mediated retrograde signaling, thereby regulating Wnt signaling in CRC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
GM-CSF-dependent CD301b+ lung dendritic cells confer tolerance to inhaled allergens
Preprint on Research Square on 4 June 2024 by Nakano, H., Wilkinson, C., et al.
Abstract The severity of allergic asthma is driven by the balance between allergen-specific T regulatory (Treg) and T helper (Th)2 cells. However, it is unclear whether specific subsets of conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) promote the differentiation of these two T cell lineaeges. We have identified a subset of lung resident type 2 cDCs (cDC2s) that display high levels of CD301b and have potent Treg-inducing activity ex vivo. Single cell RNA sequencing and adoptive transfer experiments show that during allergic sensitization, many CD301b+ cDC2s transition in a stepwise manner to CD200+ cDC2s that selectively promote Th2 differentiation. GM-CSF augments the development and maintenance of CD301b+ cDC2s in vivo, and also selectively expands Treg-inducing CD301b+ cDC2s derived from bone marrow. Upon their adoptive transfer to recipient mice, lung-derived CD301b+ cDC2s confer immunological tolerance to inhaled allergens. Thus, GM-CSF maintains lung homeostasis by increasing numbers of Treg-inducing CD301b+ cDC2s.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Bioscience on 4 June 2024 by Peng, Z., Bao, L., et al.
The adult intestinal epithelium is a complex, self-renewing tissue composed of specialized cell types with diverse functions. Intestinal stem cells (ISCs) located at the bottom of crypts, where they divide to either self-renew, or move to the transit amplifying zone to divide and differentiate into absorptive and secretory cells as they move along the crypt-villus axis. Enteroendocrine cells (EECs), one type of secretory cells, are the most abundant hormone-producing cells in mammals and involved in the control of energy homeostasis. However, regulation of EEC development and homeostasis is still unclear or controversial. We have previously shown that protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) 1, a histone methyltransferase and transcription co-activator, is important for adult intestinal epithelial homeostasis.
To investigate how PRMT1 affects adult intestinal epithelial homeostasis, we performed RNA-Seq on small intestinal crypts of tamoxifen-induced intestinal epithelium-specific PRMT1 knockout and PRMT1fl/fl adult mice. We found that PRMT1fl/fl and PRMT1-deficient small intestinal crypts exhibited markedly different mRNA profiles. Surprisingly, GO terms and KEGG pathway analyses showed that the topmost significantly enriched pathways among the genes upregulated in PRMT1 knockout crypts were associated with EECs. In particular, genes encoding enteroendocrine-specific hormones and transcription factors were upregulated in PRMT1-deficient small intestine. Moreover, a marked increase in the number of EECs was found in the PRMT1 knockout small intestine. Concomitantly, Neurogenin 3-positive enteroendocrine progenitor cells was also increased in the small intestinal crypts of the knockout mice, accompanied by the upregulation of the expression levels of downstream targets of Neurogenin 3, including Neuod1, Pax4, Insm1, in PRMT1-deficient crypts.
Our finding for the first time revealed that the epigenetic enzyme PRMT1 controls mouse enteroendocrine cell development, most likely via inhibition of Neurogenin 3-mediated commitment to EEC lineage. It further suggests a potential role of PRMT1 as a critical transcriptional cofactor in EECs specification and homeostasis to affect metabolism and metabolic diseases.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
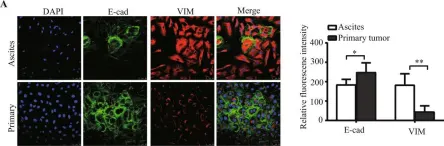
In Oncogene on 1 August 2021 by Li, Y., Fei, H., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
IHC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Oncogene by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
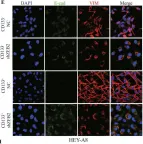
In Oncogene on 1 August 2021 by Li, Y., Fei, H., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Oncogene by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
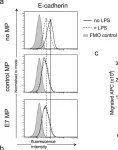
In Sci Rep on 5 February 2018 by Zhang, J., Burn, C., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3