The only FDA-approved oral immunotherapy for a food allergy provides protection against accidental exposure to peanuts. However, this therapy often causes discomfort or side effects and requires long-term commitment. Better preventive and therapeutic solutions are urgently needed. We develop a tolerance-inducing vaccine technology that utilizes glycosylation-modified antigens to induce antigen-specific non-responsiveness. The glycosylation-modified antigens are administered intravenously (i.v.) or subcutaneously (s.c.) and traffic to the liver or lymph nodes, respectively, leading to preferential internalization by antigen-presenting cells, educating the immune system to respond in an innocuous way. In a mouse model of cow's milk allergy, treatment with glycosylation-modified β-lactoglobulin (BLG) is effective in preventing the onset of allergy. In addition, s.c. administration of glycosylation-modified BLG shows superior safety and potential in treating existing allergies in combination with anti-CD20 co-therapy. This platform provides an antigen-specific immunomodulatory strategy to prevent and treat food allergies.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 22
In Cell Reports Medicine on 16 January 2024 by Cao, S., Maulloo, C. D., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports on 28 March 2023 by Jakob, M. O., Spari, D., et al.
It is generally believed that environmental or cutaneous bacteria are the main origin of surgical infections. Therefore, measures to prevent postoperative infections focus on optimizing hygiene and improving asepsis and antisepsis. In a large cohort of patients with infections following major surgery, we identified that the causative bacteria are mainly of intestinal origin. Postoperative infections of intestinal origin were also found in mice undergoing partial hepatectomy. CCR6+ group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) limited systemic bacterial spread. Such bulwark function against host invasion required the production of interleukin-22 (IL-22), which controlled the expression of antimicrobial peptides in hepatocytes, thereby limiting bacterial spread. Using genetic loss-of-function experiments and punctual depletion of ILCs, we demonstrate that the failure to restrict intestinal commensals by ILC3s results in impaired liver regeneration. Our data emphasize the importance of endogenous intestinal bacteria as a source for postoperative infection and indicate ILC3s as potential new targets.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 3 January 2023 by Wang, J., Cheng, M., et al.
Pigs are the most suitable model to study various therapeutic strategies and drugs for human beings, while knowledge about tissue- and cell type-specific transcriptomes and heterogeneity is poorly available. Here, we focused on the intestinal immunity of pigs. Through single-cell sequencing (scRNA-seq) and flow cytometry analysis of the types of immune cells in the jejunum of pigs, we found that innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) existed in the lamina propria lymphocytes (LPLs) of the jejunum. Then, through flow sorting of Live/Dead (L/D) - Lineage(LIN) - CD45 + cells and scRNA-seq, we found that ILCs in the porcine jejunum were mainly ILC3s, with a small number of ILC1s, ILC2s and NK cells. Through a gene expression map, we found that ILCs coexpressed IL-7Rα, ID2 and other genes and differentially expressed RORC, GATA3 and other genes but did not express the CD3 gene. According to their gene expression profiles, ILC3s can be divided into four subgroups, and genes such as CXCL8, CXCL2, IL-22, IL-17 and NCR2 are differentially expressed. To further detect and identify ILC3s, we prepared RORC monoclonal antibodies and verified the classification of ILCs in the porcine jejunum subgroup and the expression of related hallmark genes at the protein level by flow cytometry. For systematically characterizing of ILCs in the porcin intestines, we combined our pigs ILCs dataset with publicly available humans and mice ILCs data and identified that the humans and pigs ILCs shared more common features than that of mice in gene signatures and cell states. Our results for the first time showed in detail the gene expression of porcine jejunal ILCs, the subtype classification of ILCs and the markers of various ILCs, which provides a basis for in-depth exploration of porcine intestinal mucosal immunity. Graphical abstract
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Veterinary Research
In Cell Reports on 19 April 2022 by Corral, D., Charton, A., et al.
Tissue-resident innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) regulate tissue homeostasis, protect against pathogens at mucosal surfaces, and are key players at the interface of innate and adaptive immunity. How ILCs adapt their phenotype and function to environmental cues within tissues remains to be fully understood. Here, we show that Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection alters the phenotype and function of lung IL-18Rα+ ILC toward a protective interferon-γ-producing ILC1-like population. This differentiation is controlled by type 1 cytokines and is associated with a glycolytic program. Moreover, a BCG-driven type I milieu enhances the early generation of ILC1-like cells during secondary challenge with Mtb. Collectively, our data reveal how tissue-resident ILCs adapt to type 1 inflammation toward a pathogen-tailored immune response.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Flow cytometry analysis of the subpopulations of mouse keratinocytes and skin immune cells.
In STAR Protocols on 18 March 2022 by Sakamoto, K., Goel, S., et al.
Skin is our body's outermost physical barrier and an immunological interface enriched with various immune and non-immune cells. However, efficient generation of single-cell suspensions for flow cytometry analysis can be challenging. Here, we provide protocols to obtain epidermal and whole skin cell suspensions as well as gating strategies to identify mouse keratinocytes and skin immune cell subsets via flow cytometry. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Sakamoto et al. (2021).
© 2021.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
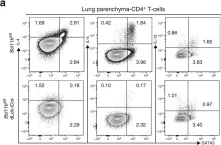
In Nat Commun on 26 April 2018 by Lorentsen, K. J., Cho, J. J., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
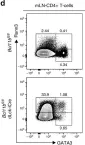
In Nat Commun on 26 April 2018 by Lorentsen, K. J., Cho, J. J., et al.
Fig.7.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2