Arenaviral vaccine vectors encoding simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) immunogens are capable of inducing efficacious humoral and cellular immune responses in nonhuman primates. Several studies have evaluated the use of immune modulators to further enhance vaccine-induced T-cell responses. The hematopoietic growth factor Flt3L drives the expansion of various bone marrow progenitor populations, and administration of Flt3L was shown to promote expansion of dendritic cell populations in spleen and blood, which are targets of arenaviral vectors. Therefore, we evaluated the potential of Flt3 signaling to enhance the immunogenicity of arenaviral vaccines encoding SIV immunogens (SIVSME543 Gag, Env, and Pol) in rhesus macaques, with a rhesus-specific engineered Flt3L-Fc fusion protein. In healthy animals, administration of Flt3L-Fc led to a 10- to 100-fold increase in type 1 dendritic cells 7 days after dosing, with no antidrug antibody (ADA) generation after repeated dosing. We observed that administration of Flt3L-Fc fusion protein 7 days before arenaviral vaccine increased the frequency and activation of innate immune cells and enhanced T-cell activation with no treatment-related adverse events. Flt3L-Fc administration induced early innate immune activation, leading to a significant enhancement in magnitude, breadth, and polyfunctionality of vaccine-induced T-cell responses. The Flt3L-Fc enhancement in vaccine immunogenicity was comparable to a combination with αCTLA-4 and supports the use of safe and effective variants of Flt3L to augment therapeutic vaccine-induced T-cell responses.IMPORTANCEInduction of a robust human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell response through therapeutic vaccination is considered essential for HIV cure. Arenaviral vaccine vectors encoding simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) immunogens have demonstrated strong immunogenicity and efficacy in nonhuman primates. Here, we demonstrate that the immunogenicity of arenaviral vectors encoding SIV immunogens can be enhanced by administration of Flt3L-Fc fusion protein 7 days before vaccination. Flt3L-Fc-mediated increase in dendritic cells led to robust improvements in vaccine-induced T- and B-cell responses compared with vaccine alone, and Flt3L-Fc dosing was not associated with any treatment-related adverse events. Importantly, immune modulation by either Flt3L-Fc or αCTLA-4 led to comparable enhancement in vaccine response. These results indicate that the addition of Flt3L-Fc fusion protein before vaccine administration can significantly enhance vaccine immunogenicity. Thus, safe and effective Flt3L variants could be utilized as part of a combination therapy for HIV cure.
Product Citations: 22
In Journal of Virology on 23 July 2024 by Boopathy, A. V., Nekkalapudi, A., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
EP300-ZNF384 transactivates IL3RA to promote the progression of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
In Cell Communication and Signaling : CCS on 2 April 2024 by Hou, Z., Ren, Y., et al.
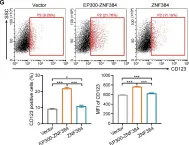
The EP300-ZNF384 fusion gene is an oncogenic driver in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). In the present study, we demonstrated that EP300-ZNF384 substantially induces the transcription of IL3RA and the expression of IL3Rα (CD123) on B-ALL cell membranes. Interleukin 3 (IL-3) supplementation promotes the proliferation of EP300-ZNF348-positive B-ALL cells by activating STAT5. Conditional knockdown of IL3RA in EP300-ZF384-positive cells inhibited the proliferation in vitro, and induced a significant increase in overall survival of mice, which is attributed to impaired propagation ability of leukemia cells. Mechanistically, the EP300-ZNF384 fusion protein transactivates the promoter activity of IL3RA by binding to an A-rich sequence localized at -222/-234 of IL3RA. Furthermore, forced EP300-ZNF384 expression induces the expression of IL3Rα on cell membranes and the secretion of IL-3 in CD19-positive B precursor cells derived from healthy individuals. Doxorubicin displayed a selective killing of EP300-ZNF384-positive B-ALL cells in vitro and in vivo. Collectively, we identify IL3RA as a direct downstream target of EP300-ZNF384, suggesting CD123 is a potent biomarker for EP300-ZNF384-driven B-ALL. Targeting CD123 may be a novel therapeutic approach to EP300-ZNF384-positive patients, alternative or, more likely, complementary to standard chemotherapy regimen in clinical setting.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Peptide-scFv antigen recognition domains effectively confer CAR T cell multiantigen specificity.
In Cell Reports Medicine on 20 February 2024 by Zoine, J. T., Immadisetty, K., et al.
The emergence of immune escape is a significant roadblock to developing effective chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies against hematological malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Here, we demonstrate feasibility of targeting two antigens simultaneously by combining a GRP78-specific peptide antigen recognition domain with a CD123-specific scFv to generate a peptide-scFv bispecific antigen recognition domain (78.123). To achieve this, we test linkers with varying length and flexibility and perform immunophenotypic and functional characterization. We demonstrate that bispecific CAR T cells successfully recognize and kill tumor cells that express GRP78, CD123, or both antigens and have improved antitumor activity compared to their monospecific counterparts when both antigens are expressed. Protein structure prediction suggests that linker length and compactness influence the functionality of the generated bispecific CARs. Thus, we present a bispecific CAR design strategy to prevent immune escape in AML that can be extended to other peptide-scFv combinations.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Bio-protocol on 20 October 2023 by Flórez-Grau, G., Escalona, J. C., et al.
Dendritic cells have been investigated for cell-based immunotherapy for various applications. The low abundance of dendritic cells in blood hampers their clinical application, resulting in the use of monocyte-derived dendritic cells as an alternative cell type. Limited knowledge is available regarding blood-circulating human dendritic cells, which can be divided into three subsets: type 2 conventional dendritic cells, type 1 conventional dendritic cells, and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. These subsets exhibit unique and desirable features for dendritic cell-based therapies. To enable efficient and reliable human research on dendritic cell subsets, we developed an efficient isolation protocol for the three human dendritic cell subsets, resulting in pure populations. The sequential steps include peripheral blood mononuclear cell isolation, magnetic-microbead lineage depletion (CD14, CD56, CD3, and CD19), and individual magnetic-microbead isolation of the three human dendritic cell subsets.
©Copyright : © 2023 The Authors; This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Chemokines form nanoparticles with DNA and can superinduce TLR-driven immune inflammation.
In The Journal of Experimental Medicine on 4 July 2022 by Du, Y., Ah Kioon, M. D., et al.
Chemokines control the migratory patterns and positioning of immune cells to organize immune responses to pathogens. However, many chemokines have been associated with systemic autoimmune diseases that have chronic IFN signatures. We report that a series of chemokines, including CXCL4, CXCL10, CXCL12, and CCL5, can superinduce type I IFN (IFN-I) by TLR9-activated plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), independently of their respective known chemokine receptors. Mechanistically, we show that chemokines such as CXCL4 mediate transcriptional and epigenetic changes in pDCs, mostly targeted to the IFN-I pathways. We describe that chemokines physically interact with DNA to form nanoparticles that promote clathrin-mediated cellular uptake and delivery of DNA in the early endosomes of pDCs. Using two separate mouse models of skin inflammation, we observed the presence of CXCL4 associated with DNA in vivo. These data reveal a noncanonical role for chemokines to serve as nucleic acid delivery vectors to modulate TLR signaling, with implications for the chronic presence of IFN-I by pDCs in autoimmune diseases.
© 2022 Du et al.
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Commun Signal on 2 April 2024 by Hou, Z., Ren, Y., et al.
Fig.1.G

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Commun Signal by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
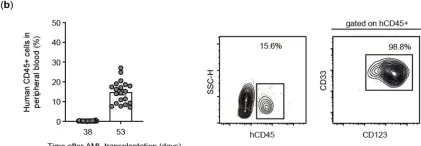
In Viruses on 14 July 2021 by Morgan, M. A., Kloos, A., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Viruses by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
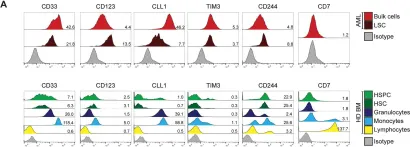
In Leukemia on 1 January 2019 by Haubner, S., Perna, F., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Leukemia by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3