Axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel), anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy demonstrated remarkable efficacy with manageable toxicity in relapsed/refractory indolent B-cell lymphomas in the ZUMA-5 trial.
Here, we report associations of product attributes, serum biomarkers, clinical features, and tumor characteristics with outcome in 124 follicular lymphoma (FL) patients.
In univariate and multivariate analyses, pre-treatment inflammatory markers, including TNFα and IL12p40, as well as total metabolic tumor volume (TMTV) associated with disease progression. Conversely, T-naïve-like product phenotype associated with improved outcome, particularly in high TMTV patients. These covariates improved risk stratification when combined with the FL International Prognostic Index. Post-infusion, CAR T-cell expansion associated with improved outcome, while serum inflammatory and immuno-modulatory markers, including TNFα associated with disease progression and occurrence of high-grade cytokine release syndrome or neurologic events, presenting targets to improve the therapeutic index of axi-cel in FL. Tumor gene expression profiling revealed that both type I and II IFN signaling associated with disease progression and higher expression of T cell exhaustion markers, including TIM3 and LAG3. Pre- or post-treatment CD19 expression on tumor was not associated with outcome.
These findings offer insights into mechanisms of resistance and toxicity, risk stratification, and strategies for development of next generation CAR-T approaches.
gov NCT03105336.
Kite, a Gilead Company. .
Product Citations: 138
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 19 June 2025 by Poddar, S., Yan, J., et al.
-
Cancer Research
In Pharmaceutics on 24 May 2025 by Patel, A., Tong, S., et al.
Background and Objectives: Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) overexpressed in melanoma plays a critical role in disease progression. Our previous studies demonstrated that nNOS inhibitors exhibited potent anti-melanoma activity and regulated PD-L1 expressions in the presence of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). However, the role of nNOS in the melanoma immune response has not been well defined. Methods: Changes in gene expression profiles after nNOS inhibitor treatment were determined by transcriptomic analysis. A melanoma mouse model was used to determine the effects of nNOS inhibition on peripheral T cells and the in vivo anti-tumor activity of combining nNOS inhibitors with immune checkpoint blockade. Changes in human T cell activation through interleukin-2 (IL-2) production were investigated using an ex vivo co-culture system with human melanoma cells. Results: Cellular RNA analysis revealed significant changes in the genes involved in key signaling pathways after nNOS inhibitor HH044 treatment. Immunophenotyping of mouse peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) after prolonged HH044 treatment showed marked increases in CD4+ and CD8+PD-1+ T cells. Ex vivo studies demonstrated that co-culturing human PBMCs with melanoma cells inhibited T cell activation, decreasing IL-2-secreting T cells both in the presence and absence of IFN-γ. PBMCs from a significant portion of donors (7/11, 64%), however, were reactivated by nNOS inhibitor pretreatment, displaying a significant increase in IL-2+ T cells. Distinctive T cell characteristics were noted at baseline among the responders with increased CD4+RORγt+ and reduced CD4 naïve T cells. In vivo mouse studies demonstrated that nNOS inhibitors, when combined with PD-1 blockade, significantly reduced tumor growth more effectively than monotherapy. Additionally, the median survival was extended from 43 days in the control mice to 176.5 days in mice co-treated with HH044 and anti-PD-1. Conclusions: Targeting nNOS is a promising approach to enhancing the anti-melanoma activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors, not only interfering with melanoma biological activities but also regulating the tumor microenvironment, which subsequently affects T cell activation and tumor immune response.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In IScience on 16 May 2025 by Lebrec, H., Bui, J., et al.
In autoimmunity, an imbalance of effector (Teff) and regulatory (Treg)T cells contributes to inflammation and tissue destruction. CD2, highly expressed on Teff and at lower levels on Treg and naive T cells (Tn), is an attractive target for depleting Teff at sites of inflammation. SBT115301 is a second generation CD2-targeting fusion protein containing the cognate receptor of CD2, lymphocyte function associated antigen-3 (LFA-3; CD58). In in vitro and in vivo studies, SBT115301 preferentially decreased CD2hi-expressing Teff cells compared to Treg and Tn. In a phase 1 clinical trial, SBT115301 selectively reduced memory T cells. SBT115301 was well tolerated aside from decreases of CD4+ T cells in some participants in the highest dose IM and IV cohorts. Anti-drug antibodies decreased exposure of SBT115301 in some participants without affecting the pharmacodynamics. These data support further study of SBT115301 as a monotherapy or in combination with other drugs in autoimmune indications.
© 2025 Sonoma Biotherapeutics.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In IScience on 16 May 2025 by Lin, S., Ma, Y., et al.
This phase 1b/2 clinical trial (NCT04775680) evaluated the safety, efficacy, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ADG106, a ligand-blocking agonistic antibody targeting CD137 (4-1BB), combined with toripalimab in patients with advanced malignancies. ADG106 0.75-3 mg/kg plus toripalimab 240 mg were administered every 3 weeks. One dose-limiting toxicity occurred in 1 subject at 1.5 mg/kg and 2 in another subject at 3 mg/kg. Grade ≥ 3 treatment related adverse events occurred in 4/25 patients (16%). The overall disease control rate was 29.2% (7/24), including 1 partial response (PR) patient with a duration of response and a progression-free survival of 17.6 and 24.5 months. Circulating biomarkers suggested increased soluble CD137, CD3-CD16+CD56+ natural killer (NK) cells, interferon γ (IFN-γ), TNFα, and IL-6 after therapy. Elevated baseline memory T cells and PD-L1, activation of immune-related pathways, along with enhanced T cell proliferation and increased IFN-γ following treatment were observed in the PR patient. ADG106 in combination with toripalimab demonstrated a manageable safety profile but no efficacy conclusions could be drawn.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Inc.
-
Cancer Research
CD8+ and CD8- NK Cells and Immune Checkpoint Networks in Peripheral Blood During Healthy Pregnancy.
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 6 January 2025 by Meggyes, M., Nagy, D. U., et al.
Pregnancy involves significant immunological changes to support fetal development while protecting the mother from infections. A growing body of evidence supports the importance of immune checkpoint pathways, especially at the maternal-fetal interface, although limited information is available about the peripheral expression of these molecules by CD8+ and CD8- NK cell subsets during the trimesters of pregnancy. Understanding the dynamics of these immune cells and their checkpoint pathways is crucial for elucidating their roles in pregnancy maintenance and potential complications. This study aims to investigate the peripheral expression and functional characteristics of CD8+ and CD8- NK cell subsets throughout pregnancy, providing insights into their contributions to maternal and fetal health. A total of 34 healthy women were enrolled from the first, 30 from the second and 40 from the third trimester of pregnancy. At the same time, 35 healthy age-matched non-pregnant women formed the control group. From peripheral blood, mononuclear cells were separated and stored at -80 °C. CD8+ and CD8- NK cell subsets were analyzed from freshly thawed samples, and surface and intracellular staining was performed using flow cytometric analyses. The proportions of CD56+ NK cells in peripheral blood were similar across groups. While CD8- NKdim cells increased significantly in all trimesters compared to non-pregnant controls, CD8+ NKdim cells showed no significant changes. CD8- NKbright cells had higher frequencies throughout pregnancy, whereas CD8+ NKbright cells significantly increased only in the first and second trimesters. The expression levels of immune checkpoint molecules, such as PD-1 and PD-L1, and cytotoxic-activity-related molecules were stable, with notable perforin and granzyme B increases in CD8- NKbright cells throughout pregnancy. Our study shows that peripheral NK cell populations, especially CD8- subsets, are predominant during pregnancy. This shift suggests a crucial role for CD8- NK cells in balancing maternal immune tolerance and surveillance. The stable expression of immune checkpoint molecules indicates that other regulatory mechanisms may be at work. These findings enhance our understanding of peripheral immune dynamics in pregnancy and suggest that targeting CD8- NKbright cell functions could help manage pregnancy-related immune complications. This research elucidates the stable distribution and functional characteristics of peripheral NK cells during pregnancy, with CD8- subsets being more prevalent. The increased activity of CD8- NKbright cells suggests their critical role in maintaining immune surveillance. Our findings provide a basis for future studies to uncover the mechanisms regulating NK cell function in pregnancy, potentially leading to new treatments for immune-related pregnancy complications.
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Front Oncol on 12 November 2019 by Li, X., Wang, R., et al.
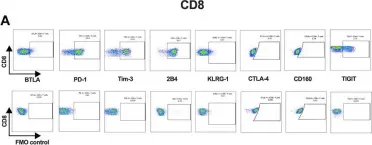
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Front Immunol on 25 February 2015 by Ziegler, H., Welker, C., et al.
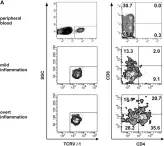
Fig.9.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Front Immunol on 25 February 2015 by Ziegler, H., Welker, C., et al.
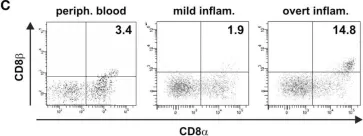
Fig.9.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Front Immunol on 25 February 2015 by Ziegler, H., Welker, C., et al.
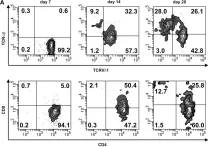
Fig.5.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Front Immunol on 25 February 2015 by Ziegler, H., Welker, C., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5