The mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) is an important source of inherited extranuclear variation. Clonal increases in mtDNA mutation heteroplasmy have been implicated in aging and disease, although the impact of this shift on cell function is challenging to assess. Reprogramming to pluripotency affects mtDNA mutation heteroplasmy. We reprogrammed three human fibroblast lines with known heteroplasmy for deleterious mtDNA point or deletion mutations. Quantification of mutation heteroplasmy in the resulting 76 induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) clones yielded a bimodal distribution, creating three sets of clones with high levels or absent mutation heteroplasmy with matched nuclear genomes. iPSC clones with elevated deletion mutation heteroplasmy show altered growth dynamics, which persist in iPSC-derived progenitor cells. We identify transcriptomic and metabolic shifts consistent with increased investment in neutral lipid synthesis as well as increased epigenetic age in high mtDNA deletion mutation iPSC, consistent with changes occurring in cellular aging. Together, these data demonstrate that high mtDNA mutation heteroplasmy induces changes occurring in cellular aging.
© 2024 The Author(s). Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Product Citations: 18
In Aging Cell on 1 March 2025 by Vandiver, A. R., Torres, A., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cell Biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Cell Rep Methods on 18 November 2024 by Sun, P., Yuan, Y., et al.
Progress has been made in generating spinal cord and trunk derivatives from neuromesodermal progenitors (NMPs). However, maintaining the self-renewal of NMPs in vitro remains a challenge. In this study, we developed a cocktail of small molecules and growth factors that induces human embryonic stem cells to produce self-renewing NMPs (srNMPs) under chemically defined conditions. These srNMPs maintain the state of neuromesodermal progenitors in prolonged culture and have the potential to generate mesodermal cells and neurons, even at the single-cell level. Additionally, suspended srNMP aggregates can spontaneously differentiate into all tissue types of early embryonic trunks. Furthermore, transplanted srNMP-derived muscle satellite cells or progenitors of motor neurons were integrated into skeletal muscle or the spinal cord, respectively, and contributed to regeneration in mouse models. In summary, srNMPs hold great promise for applications in developmental biology and as renewable cell sources for cell therapy for trunk and spinal cord injuries.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 28 September 2024 by Wesely, J., Rusielewicz, T., et al.
Amino-terminal (Nt-) acetylation (NTA) is a common protein modification, affecting 80% of cytosolic proteins in humans. The human essential gene, NAA10, encodes the enzyme NAA10, as the catalytic subunit for the N-terminal acetyltransferase A (NatA) complex, including the accessory protein, NAA15. The first human disease directly involving NAA10 was discovered in 2011, and it was named Ogden syndrome (OS), after the location of the first affected family residing in Ogden, Utah, USA. Since that time, other variants have been found in NAA10 and NAA15. Here we describe the generation of 31 iPSC lines, with 16 from females and 15 from males. This cohort includes CRISPR-mediated correction to the wild-type genotype in 4 male lines, along with editing one female line to generate homozygous wild-type or mutant clones. Following the monoclonalizaiton and screening for X-chromosome activation status in female lines, 3 additional pairs of female lines, in which either the wild type allele is on the active X chromosome (Xa) or the pathogenic variant allele is on Xa, have been generated. Subsets of this cohort have been successfully used to make cardiomyocytes and neural progenitor cells (NPCs). These cell lines are made available to the community via the NYSCF Repository.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Genetics
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In eLife on 5 January 2024 by Jarc, L., Bandral, M., et al.
The unlimited expansion of human progenitor cells in vitro could unlock many prospects for regenerative medicine. However, it remains an important challenge as it requires the decoupling of the mechanisms supporting progenitor self-renewal and expansion from those mechanisms promoting their differentiation. This study focuses on the expansion of human pluripotent stem (hPS) cell-derived pancreatic progenitors (PP) to advance novel therapies for diabetes. We obtained mechanistic insights into PP expansion requirements and identified conditions for the robust and unlimited expansion of hPS cell-derived PP cells under GMP-compliant conditions through a hypothesis-driven iterative approach. We show that the combined stimulation of specific mitogenic pathways, suppression of retinoic acid signaling, and inhibition of selected branches of the TGFβ and Wnt signaling pathways are necessary for the effective decoupling of PP proliferation from differentiation. This enabled the reproducible, 2000-fold, over 10 passages and 40-45 d, expansion of PDX1+/SOX9+/NKX6-1+ PP cells. Transcriptome analyses confirmed the stabilization of PP identity and the effective suppression of differentiation. Using these conditions, PDX1+/SOX9+/NKX6-1+ PP cells, derived from different, both XY and XX, hPS cell lines, were enriched to nearly 90% homogeneity and expanded with very similar kinetics and efficiency. Furthermore, non-expanded and expanded PP cells, from different hPS cell lines, were differentiated in microwells into homogeneous islet-like clusters (SC-islets) with very similar efficiency. These clusters contained abundant β-cells of comparable functionality as assessed by glucose-stimulated insulin secretion assays. These findings established the signaling requirements to decouple PP proliferation from differentiation and allowed the consistent expansion of hPS cell-derived PP cells. They will enable the establishment of large banks of GMP-produced PP cells derived from diverse hPS cell lines. This approach will streamline SC-islet production for further development of the differentiation process, diabetes research, personalized medicine, and cell therapies.
© 2023, Jarc, Bandral et al.
In Nature Cell Biology on 1 December 2023 by Noack, F., Vangelisti, S., et al.
Gene expression is regulated by multiple epigenetic mechanisms, which are coordinated in development and disease. However, current multiomics methods are frequently limited to one or two modalities at a time, making it challenging to obtain a comprehensive gene regulatory signature. Here, we describe a method-3D genome, RNA, accessibility and methylation sequencing (3DRAM-seq)-that simultaneously interrogates spatial genome organization, chromatin accessibility and DNA methylation genome-wide and at high resolution. We combine 3DRAM-seq with immunoFACS and RNA sequencing in cortical organoids to map the cell-type-specific regulatory landscape of human neural development across multiple epigenetic layers. Finally, we apply a massively parallel reporter assay to profile cell-type-specific enhancer activity in organoids and to functionally assess the role of key transcription factors for human enhancer activation and function. More broadly, 3DRAM-seq can be used to profile the multimodal epigenetic landscape in rare cell types and different tissues.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
Cell Biology
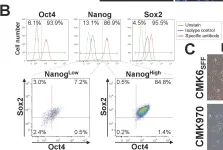
In PLoS One on 8 February 2014 by Ono, T., Suzuki, Y., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Chlorocebus sabaeus (Green monkey)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1